|
Madras System
The Monitorial System, also known as Madras System or Lancasterian System, was an education method that took hold during the early 19th century, because of Spanish, French, and English colonial education that was imposed into the areas of expansion. This method was also known as "mutual instruction" or the "Bell–Lancaster method" after the British educators Andrew Bell and Joseph Lancaster who both independently developed it. The method was based on the abler pupils being used as 'helpers' to the teacher, passing on the information they had learned to other students. Monitorial Systems The Monitorial System was found very useful by 19th-century educators, as it proved to be a cheap way of making primary education more inclusive, thus making it possible to increase the average class size. Joseph Lancaster's motto for his method was ''Qui docet, discit'' – "He who teaches, learns." The methodology was adopted by the Roman Catholic Church in England and Wales, and later by the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick John Gladman
Frederick John Gladman (1 February 1839 – 12 November 1884) was an Australian educationist and author whose work had an influence on the formation of Australia's educational system. His textbooks were used as late as the 1930s to train teachers. Biography Gladman was born on 1 February 1839 in London. He attended a monitorial school until he was fourteen. Gladman then served an apprenticeship as a pupil-teacher at the British and Foreign School in Bushey, Hertfordshire. Later he received a year of teacher training from Borough Road Training College in London. He had a successful career teaching at a small school in Surrey from 1859 until 1862. In 1863, at the young age of 24, he was given the position of headmaster of a larger school in Great Yarmouth. In 1869 he entered the University of London, ultimately receiving two Bachelor's degrees. Gladman then returned to Borough Road Training College to serve as a headmaster. Gladman was employed by the British and Foreign Schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudbury Model
A Sudbury school is a type of school, usually for the K-12 age range, where students have complete responsibility for their own education, and the school is run by a direct democracy in which students and staff are equal citizens. Students use their time however they wish, and learn as a by-product of ordinary experience rather than through coursework. There is no predetermined educational syllabus, prescriptive curriculum or standardized instruction. This is a form of democratic education. Daniel Greenberg, one of the founders of the original Sudbury Model school, writes that the two things that distinguish a Sudbury Model school are that everyone is treated equally (adults and children together) and that there is no authority other than that granted by the consent of the governed. While each Sudbury Model school operates independently and determines their own policies and procedures, they share a common culture. The intended culture within a Sudbury school has been described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horace Mann
Horace Mann (May 4, 1796August 2, 1859) was an American educational reformer, slavery abolitionist and Whig politician known for his commitment to promoting public education. In 1848, after public service as Secretary of the Massachusetts State Board of Education, Mann was elected to the United States House of Representatives (1848–1853). From September 1852 to his death, he served as President of Antioch College. About Mann's intellectual progressivism, the historian Ellwood P. Cubberley said: Arguing that universal public education was the best way to turn unruly American children into disciplined, judicious republican citizens, Mann won widespread approval from modernizers, especially in the Whig Party, for building public schools. Most U.S. states adopted a version of the system Mann established in Massachusetts, especially the program for normal schools to train professional teachers. Educational historians credit Horace Mann, along with Henry Barnard and Catharine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Schools Museum (Hitchin)
The British Schools Museum is an educational museum based in original Edwardian and Victorian school buildings in Hitchin in Hertfordshire, England. The museum complex is made up of Grade II listed school buildings housing infants, girls and boys schools with houses for Master and Mistress. It includes a monitorial schoolroom based on the educational theories of Joseph Lancaster for 300 boys, which opened in 1837, and a rare galleried classroom, dating from 1853. History of the school The first school on the site was a schoolroom for 200 boys and 100 girls. It was founded in 1810 by local lawyer William Wilshere in a disused malthouse. This schoolroom was the first monitorial school for the sons of the poor in Hertfordshire. Teaching was based on Joseph Lancaster's methods of monitorial teaching. He developed a system in which large numbers of younger scholars could be taught by older scholars under the supervision of the master (for boys) or mistress (for girls). This method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
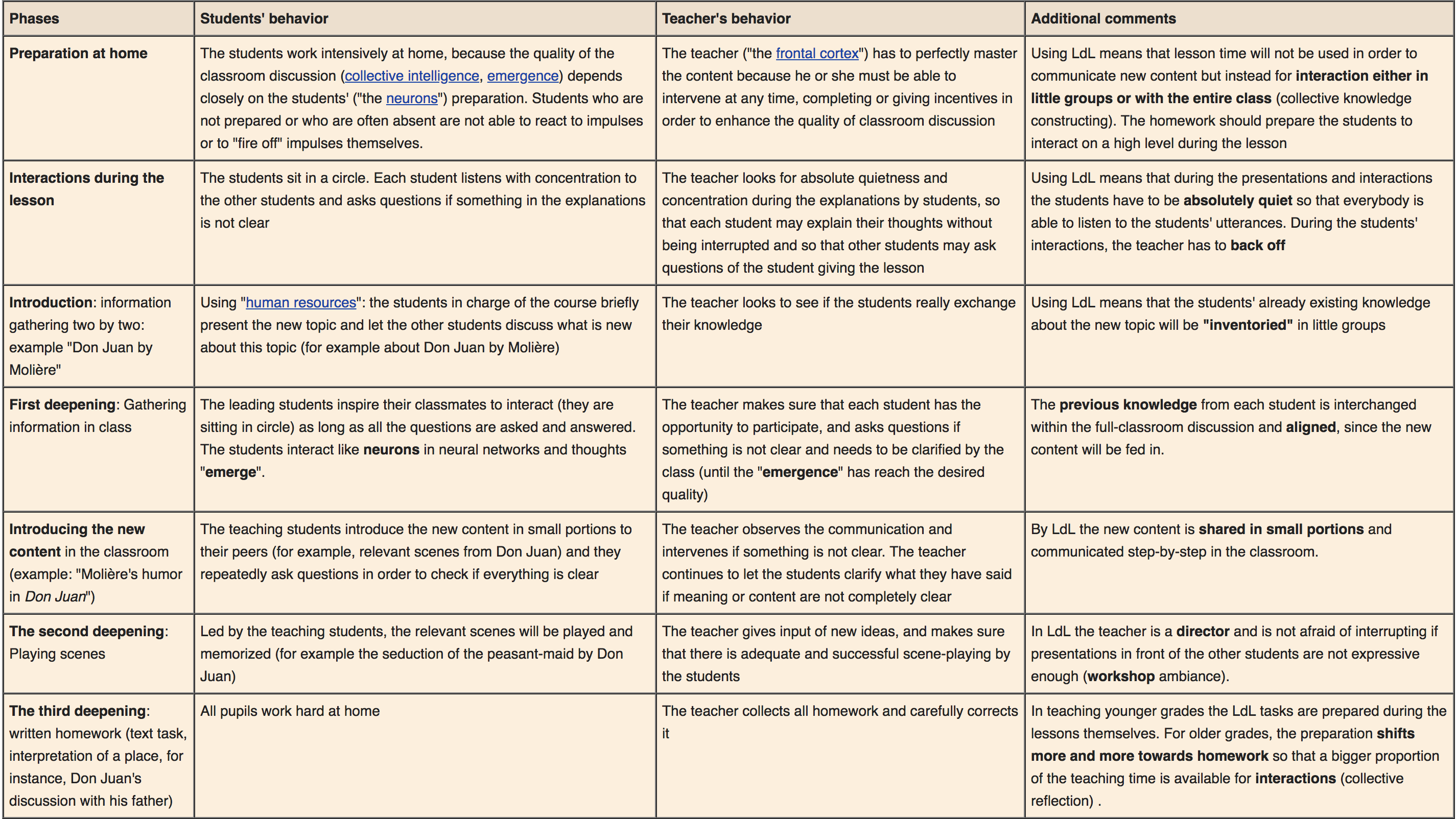
Learning By Teaching
In the field of pedagogy, learning by teaching (German: ''Lernen durch Lehren'', short LdL) is a method of teaching in which students are made to learn material and prepare lessons to teach it to the other students. There is a strong emphasis on acquisition of life skills along with the subject matter. This method was originally defined by Jean-Pol Martin in the 1980s. Background The method of having students teach other students has been present since antiquity. Most often this was due to lack of resources. For example, the Monitorial System was an education method that became popular on a global scale during the early 19th century. It was developed in parallel by Scotsman Andrew Bell who had worked in Madras and Joseph Lancaster who worked in London; each attempted to educate masses of poor children with scant resources by having older children teach younger children what they had already learned. Systematic research into intentionally improving education, by having stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For government statistical purposes, it forms part of the East of England region. Hertfordshire covers . It derives its name – via the name of the county town of Hertford – from a hart (stag) and a ford, as represented on the county's coat of arms and on the flag. Hertfordshire County Council is based in Hertford, once the main market town and the current county town. The largest settlement is Watford. Since 1903 Letchworth has served as the prototype garden city; Stevenage became the first town to expand under post-war Britain's New Towns Act of 1946. In 2013 Hertfordshire had a population of about 1,140,700, with Hemel Hempstead, Stevenage, Watford and St Albans (the county's only ''city'') each having between 50,000 and 100,000 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitchin
Hitchin () is a market town and unparished area in the North Hertfordshire Districts of England, district in Hertfordshire, England, with an estimated population of 35,842. History Hitchin is first noted as the central place of the Hicce people, a tribe holding 300 Hide (unit), hides of land as mentioned in a 7th-century document,Gover, J E B, Mawer, A and Stenton, F M 1938 ''The Place-Names of Hertfordshire'' English Place-Names Society volume XV, 8 the Tribal Hidage. Hicce, or Hicca, may mean ''the people of the horse.'' The tribal name is Old English and derives from the Middle Angles, Middle Anglian people. It has been suggested that Hitchin was the location of 'Councils of Clovesho, Clofeshoh', the place chosen in 673 by Theodore of Tarsus the Archbishop of Canterbury during the Synod of Hertford, the first meeting of representatives of the fledgling Christianity, Christian churches of Anglo-Saxon England, to hold annual synods of the churches as Theodore attempted to conso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Schools Museum
The British Schools Museum is an educational museum based in original Edwardian and Victorian school buildings in Hitchin in Hertfordshire, England. The museum complex is made up of Grade II listed school buildings housing infants, girls and boys schools with houses for Master and Mistress. It includes a monitorial schoolroom based on the educational theories of Joseph Lancaster for 300 boys, which opened in 1837, and a rare galleried classroom, dating from 1853. History of the school The first school on the site was a schoolroom for 200 boys and 100 girls. It was founded in 1810 by local lawyer William Wilshere in a disused malthouse. This schoolroom was the first monitorial school for the sons of the poor in Hertfordshire. Teaching was based on Joseph Lancaster's methods of monitorial teaching. He developed a system in which large numbers of younger scholars could be taught by older scholars under the supervision of the master (for boys) or mistress (for girls). This met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British And Foreign School Society
The British and Foreign School Society (BFSS) offers charitable aid to educational projects in the UK and around the world by funding schools, other charities and educational bodies. It was significant in the history of education in England, supporting free British Schools and teacher training in the 19th century; it continued in the latter role until the 1970s. In the 19th century it fiercely competed with the National Society for Promoting Religious Education, which had the support of the established Church of England, the local parishes, and Oxford and Cambridge universities. Both institutions promoted the monitorial system, whereby few paid teachers supervise the senior students who in turn taught the younger students. Current status As its teacher training colleges have closed and the Society has gathered more capital, it has used its funds to provide grants for educational projects around the world. Details of its activities can be found in its Annual Reports and the rest of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarah Trimmer
Sarah Trimmer (''née'' Kirby; 6 January 1741 – 15 December 1810) was a writer and critic of 18th-century British children's literature, as well as an educational reformer. Her periodical, ''The Guardian of Education'', helped to define the emerging genre by seriously reviewing children's literature for the first time; it also provided the first history of children's literature, establishing a canon of the early landmarks of the genre that scholars still use today. Trimmer's most popular children's book, ''Fabulous Histories'', inspired numerous children's animal stories and remained in print for over a century. Trimmer was also an active philanthropist. She founded several Sunday schools and charity schools in her parish. To further these educational projects, she wrote textbooks and manuals for women interested in starting their own schools. Trimmer's efforts inspired other women, such as Hannah More, to establish Sunday school programs and to write for children and the poor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal. According to the 2011 Indian census, Chennai is the sixth-most populous city in the country and forms the fourth-most populous urban agglomeration. The Greater Chennai Corporation is the civic body responsible for the city; it is the oldest city corporation of India, established in 1688—the second oldest in the world after London. The city of Chennai is coterminous with Chennai district, which together with the adjoining suburbs constitutes the Chennai Metropolitan Area, the 36th-largest urban area in the world by population and one of the largest metropolitan economies of India. The traditional and de facto gateway of South India, Chennai is among the most-visited Indian cities by foreign tourists. It was ranked the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |