|
MacDonald White Paper
The White Paper of 1939Occasionally also known as the MacDonald White Paper (e.g. Caplan, 2015, p.117) after Malcolm MacDonald, the British Colonial Secretary, who presided over its creation. was a policy paper issued by the British government, led by Neville Chamberlain, in response to the 1936–1939 Arab revolt in Palestine. After its formal approval in the House of Commons on 23 May 1939,by 268 votes to 179. it acted as the governing policy for Mandatory Palestine from 1939 to the 1948 British departure. After the war, the Mandate was referred to the United Nations. The policy, first drafted in March 1939, was prepared by the British government unilaterally as a result of the failure of the Arab-Zionist London Conference. The paper called for the establishment of a Jewish national home in an independent Palestinian state within 10 years, rejecting the Peel Commission's idea of partitioning Palestine. It also limited Jewish immigration to 75,000 for five years and ruled th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command Paper
A command paper is a document issued by the UK Government and presented to Parliament. White papers, green papers, treaties, government responses, draft bills, reports from Royal Commissions, reports from independent inquiries and various government organisations can be released as command papers, so called because they are presented to Parliament formally "By His Majesty's Command". Dissemination Command papers are: * produced by government departments * printed on behalf of His Majesty's Stationery Office * presented to Parliament "by Command of His Majesty" by the appropriate government minister * recorded by the House of Commons and the House of Lords * published by government departments on gov.uk * subject to statutory legal deposit Numbering Command papers are numbered. Since 1870 they have been prefixed with an abbreviation of "command" which has changed over time to allow for new sequences. See also *Office of Public Sector Information The Office of Public Sector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amin Al-Husseini
Mohammed Amin al-Husseini ( ar, محمد أمين الحسيني 1897 – 4 July 1974) was a Palestinian Arab nationalist and Muslim leader in Mandatory Palestine. Al-Husseini was the scion of the al-Husayni family of Jerusalemite Arab notables, who trace their origins to the eponymous grandson of Muhammad. Husseini received education in Islamic, Ottoman, and Catholic schools. In 1912, he went to pursue further studies in Cairo's ''Dar al-Da'wa wa al-Irshad'', an Islamic seminary under the tutelage of Salafist theologian Muhammad Rashid Rida. After studying there for two years, he went on to serve in the Ottoman army in World War I. At war's end he stationed himself in Damascus as a supporter of the Arab Kingdom of Syria. Following the Franco-Syrian War and the collapse of Arab Hashemite rule in Damascus, his early position on pan-Arabism shifted to a form of local nationalism for Palestinian Arabs and he moved back to Jerusalem. From as early as 1920 he actively opposed Zio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sykes–Picot Agreement
The Sykes–Picot Agreement () was a 1916 secret treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from the Russian Empire and the Kingdom of Italy, to define their mutually agreed Sphere of influence, spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition of the Ottoman Empire. The agreement was based on the premise that the Triple Entente would achieve success in defeating the Ottoman Empire during World War I and formed part of a series of secret agreements contemplating its partition. The primary negotiations leading to the agreement took place between 23 November 1915 and 3 January 1916, on which date the British and French diplomats, Mark Sykes and François Georges-Picot, initialled an agreed memorandum. The agreement was ratified by their respective governments on 9 and 16 May 1916. The agreement effectively divided the Ottoman provinces outside the Arabian Peninsula into areas of British and French control and influence. The British- and French-controlled count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jihad
Jihad (; ar, جهاد, jihād ) is an Arabic word which literally means "striving" or "struggling", especially with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it can refer to almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God's guidance, such as struggle against one's evil inclinations, proselytizing, or efforts toward the moral betterment of the Muslim community (''Ummah''), though it is most frequently associated with war. In classical Islamic law (''sharia''), the term refers to armed struggle against unbelievers, while modernist Islamic scholars generally equate military ''jihad'' with defensive warfare. In Sufi circles, spiritual and moral jihad has been traditionally emphasized under the name of ''greater jihad''. The term has gained additional attention in recent decades through its use by various insurgent Islamic extremist, militant Islamist, and terrorist individuals and organizations whose ideology is based on the Islamic notion of ''jihad''. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria (region)
Syria (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other synonyms are Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. In modern times, the term "Syria" alone is used to refer to the Arab Republic of Syria. The term is originally derived from Assyria, an ancient civilization centered in northern Mesopotamia, modern-day Iraq. During the Hellenistic period, the term Syria was applied to the entire Levant as Coele-Syria. Under Roman rule, the term was used to refer to the province of Syria, later divided into Syria Phoenicia and Coele Syria, and to the province of Syria Palaestina. Under the Byzantines, the provinces of Syria Prima and Syria Secunda emerged out of Coele Syria. After the Muslim conquest of the Levant, the term was superseded by the Ara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
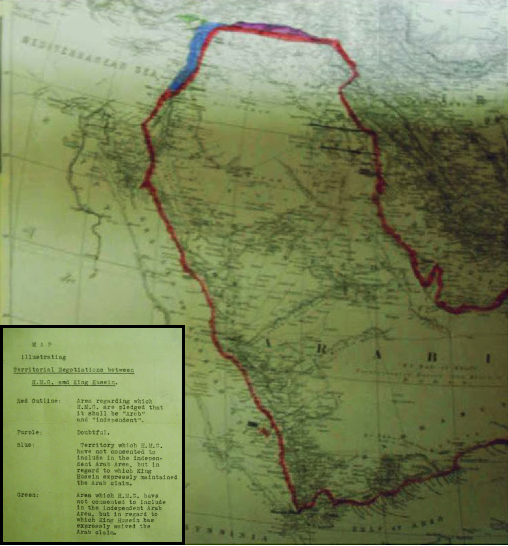
McMahon–Hussein Correspondence
The McMahon–Hussein Correspondence is a series of letters that were exchanged during World War I in which the Government of the United Kingdom agreed to recognize Arab independence in a large region after the war Quid pro quo, in exchange for the Sharif of Mecca launching the Arab Revolt against the Ottoman Empire. The correspondence had a significant influence on Middle Eastern history during and after the war; a dispute over Palestine (region), Palestine continued thereafter. The correspondence is composed of ten letters that were exchanged from July 1915 to March 1916 between Hussein bin Ali, Sharif of Mecca and Lieutenant Colonel (British Army), Lieutenant Colonel Henry McMahon (diplomat), Sir Henry McMahon, List of ambassadors of the United Kingdom to Egypt, British High Commissioner to Egypt. Whilst there was some military value in the Arab manpower and local knowledge alongside the British Army, the primary reason for the arrangement was to counteract the Ottoman entry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Of Arabia
Thomas Edward Lawrence (16 August 1888 – 19 May 1935) was a British archaeologist, army officer, diplomat, and writer who became renowned for his role in the Arab Revolt (1916–1918) and the Sinai and Palestine Campaign (1915–1918) against the Ottoman Empire during the First World War. The breadth and variety of his activities and associations, and his ability to describe them vividly in writing, earned him international fame as Lawrence of Arabia, a title used for the 1962 film based on his wartime activities. He was born out of wedlock in August 1888 to Sarah Junner (1861–1959), a governess, and Sir Thomas Chapman, 7th Baronet (1846–1919), an Anglo-Irish nobleman. Chapman left his wife and family in Ireland to cohabit with Junner. Chapman and Junner called themselves Mr and Mrs Lawrence, using the surname of Sarah's likely father; her mother had been employed as a servant for a Lawrence family when she became pregnant with Sarah. In 1896, the Lawrences moved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. At , the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula includes Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Yemen, as well as the southern portions of Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the classical era, the southern portions of modern-day Syria, Jordan, and the Sinai Peninsula were also considered parts of Arabia (see Arabia Petraea). The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and southwest, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the northeast, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashemite
The Hashemites ( ar, الهاشميون, al-Hāshimīyūn), also House of Hashim, are the royal family of Jordan, which they have ruled since 1921, and were the royal family of the kingdoms of Hejaz (1916–1925), Syria (1920), and Iraq (1921–1958). The family had ruled the city of Mecca continuously from the 10th century, frequently as vassals of outside powers, and were given the thrones of the Hejaz, Syria, Iraq, and Jordan following their World War I alliance with the British Empire; this arrangement became known as the "Sharifian solution". The family belongs to the Dhawu Awn, one of the branches of the Ḥasanid Sharifs of Mecca, also referred to as Hashemites. Their eponymous ancestor is traditionally considered to be Hashim ibn Abd Manaf, great-grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Ḥasanid Sharifs of Mecca (from whom the Hashemite royal family is directly descended), including the Hashemites' ancestor Qatadah ibn Idris, were Zaydī Shīʿas until the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (European part of Turkey), Egypt, Iran, the Levant (including Syria (region), Ash-Shām and Cyprus), Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), and the Socotra Governorate, Socotra Archipelago (a part of Yemen). The term came into widespread usage as a replacement of the term Near East (as opposed to the Far East) beginning in the early 20th century. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions, and has been viewed by some to be discriminatory or too Eurocentrism, Eurocentric. The region includes the vast majority of the territories included in the closely associated definition of Western Asia (including Iran), but without the South Caucasus, and additionally includes all of Egypt (not just the Sina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)
