|
List Of VIA Microprocessor Cores
This article lists x86-compliant microprocessors sold by VIA Technologies, grouped by technical merits: cores within same group have much in common. Cyrix design (Cyrix III) * All models support: '' MMX, 3DNow!'' Centaur Technology design Cyrix III, C3 * All models support: '' MMX, 3DNow!'' C3, C7 * All models support: '' MMX, SSE'' * SSE2, SSE3, NX bit supported by Esther (C5J) Nano * See List of Nano microprocessors CHA * Currently in development. Details listed below are subject to change, * 8 cores + "NCORE" neural processor for AI acceleration. * supports: MMX SSE SSE2 SSE3 SSSE3 SSE4.1 SSE4.2 AES AVX AVX2 FMA3 SHA AVX512 AVX512F AVX512CD AVX512BW AVX512DQ AVX512VL AVX512IFMA AVX512VBMI. See also * List of VIA C3 microprocessors * List of VIA C7 microprocessors * List of VIA Eden microprocessors * List of VIA Nano microprocessors References External links Via C3 product pageVia C7 product page Via Nano product page {{VIA VIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86 Architecture
x86 (also known as 80x86 or the 8086 family) is a family of complex instruction set computer (CISC) instruction set architectures initially developed by Intel based on the Intel 8086 microprocessor and its 8088 variant. The 8086 was introduced in 1978 as a fully 16-bit extension of Intel's 8-bit 8080 microprocessor, with memory segmentation as a solution for addressing more memory than can be covered by a plain 16-bit address. The term "x86" came into being because the names of several successors to Intel's 8086 processor end in "86", including the 80186, 80286, 80386 and 80486 processors. The term is not synonymous with IBM PC compatibility, as this implies a multitude of other computer hardware. Embedded systems and general-purpose computers used x86 chips before the PC-compatible market started, some of them before the IBM PC (1981) debut. , most desktop and laptop computers sold are based on the x86 architecture family, while mobile categories such as smartphones o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) is a single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series of Central processing units (CPUs) shortly after the appearance of Advanced Micro Devices (AMD's) 3DNow!. SSE contains 70 new instructions (65 unique mnemonics using 70 encodings), most of which work on single precision floating-point data. SIMD instructions can greatly increase performance when exactly the same operations are to be performed on multiple data objects. Typical applications are digital signal processing and graphics processing. Intel's first IA-32 SIMD effort was the MMX instruction set. MMX had two main problems: it re-used existing x87 floating-point registers making the CPUs unable to work on both floating-point and SIMD data at the same time, and it only worked on integers. SSE floating-point instructions operate on a new independent register set, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of VIA Eden Microprocessors
The Eden microprocessors from VIA Technologies are fifth- and sixth-generation CPUs targeted at the embedded market. Embedded processors Eden ESP "Samuel 2" (150 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, 3DNow!'' "Nehemiah" (130 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, VIA PadLock (AES, RNG)'' Eden-N "Nehemiah" (130 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, VIA PadLock (AES, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported Eden "Esther" (standard-voltage, 90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, NX bit, VIA PadLock (SHA, AES, Montgomery Multiplier, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported with up to 8 ACPI P-states * Idle power 500 mW "Esther" (ultra-low-voltage, 90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, NX bit, VIA PadLock (SHA, AES, Montgomery Multiplier, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported with up to 8 ACPI P-states Eden X2 "Eden X2" (40 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, x86-64, NX bit, x86 virtualization, VIA PadLock (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of VIA C7 Microprocessors
The C7 microprocessor from VIA Technologies is a seventh-generation CPU targeted at the consumer and embedded market. Desktop processors C7 "Esther" (90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, NX bit, VIA PadLock (SHA, AES, Montgomery Multiplier, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported with 2 ACPI P-states C7-D "Esther" (90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, NX bit, VIA PadLock (SHA, AES, Montgomery Multiplier, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported on Model D 1.8 and 2.0 with 2 ACPI P-states Mobile processors C7-M "Esther" (standard-voltage, 90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, NX bit, VIA PadLock (SHA, AES, Montgomery Multiplier, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported with up to 8 ACPI P-states "Esther" (ultra-low-voltage, 90 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, SSE2, SSE3, NX bit, VIA PadLock (SHA, AES, Montgomery Multiplier, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported with up to 8 ACPI P-states External links VIA C7 produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of VIA C3 Microprocessors
The C3 microprocessor from VIA Technologies is a fifth-generation CPU targeted at the desktop and mobile markets. Desktop processors C3 "Samuel 2" (150 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, 3DNow!, LongHaul'' * FPU runs at 50% of core speed "Ezra"/"Ezra-T" (130 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, 3DNow!, LongHaul'' * FPU runs at 50% of core speed "Nehemiah" (130 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, VIA PadLock (AES, RNG), LongHaul'' Mobile processors C3-M "Ezra"/"Ezra-T" (130 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, 3DNow!, LongHaul'' * FPU runs at 50% of core speed "Nehemiah" (130 nm) * All models support: '' MMX, SSE, VIA PadLock (AES, RNG)'' * VIA PowerSaver supported External links VIA C3 product pageVIA C3-M product pageVIA Processor specification comparison See also * List of VIA microprocessors {{VIA *C3 VIA Via or VIA may refer to the following: Science and technology * MOS Technology 6522, Versatile Interface Adapter * ''Via'' (moth), a gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of VIA Nano Microprocessors
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
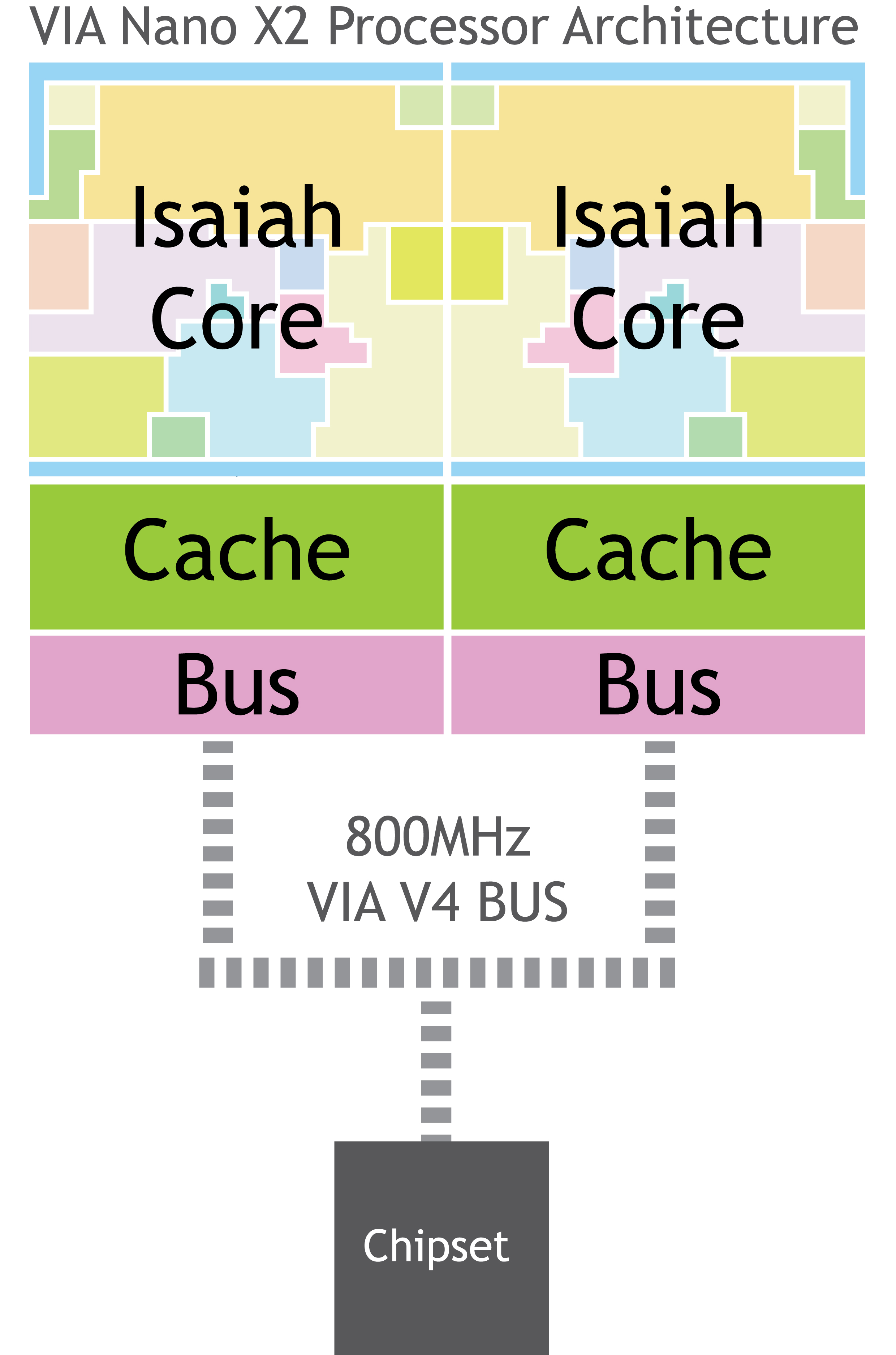
VIA QuadCore
The VIA Nano (formerly code-named VIA Isaiah) is a 64-bit CPU for personal computers. The VIA Nano was released by VIA Technologies in 2008 after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology. This new Isaiah 64-bit architecture was designed from scratch, unveiled on 24 January 2008, and launched on 29 May, including low-voltage variants and the Nano brand name. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances. History Unlike Intel and AMD, VIA uses two distinct development code names for each of its CPU cores. In this case, the codename 'CN' was used in the United States by Centaur Technology. Biblical names are used as codes by VIA in Taiwan, and Isaiah was the choice for this particular processor and architecture. It is expected that the VIA Isaiah will be twice as fast in integer performance and four times as fast in floating-point performance as the previous-generation VIA Esther a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIA Nano
The VIA Nano (formerly Code name#Commercial code names in the computer industry, code-named VIA Isaiah) is a 64-bit CPU for personal computers. The VIA Nano was released by VIA Technologies in 2008 after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology. This new Isaiah 64-bit architecture was designed from scratch, unveiled on 24 January 2008, and launched on 29 May, including low-voltage variants and the Nano brand name. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances. History Unlike Intel and AMD, VIA uses two distinct development code names for each of its CPU cores. In this case, the codename 'CN' was used in the United States by Centaur Technology. Biblical names are used as codes by VIA in Taiwan, and Isaiah was the choice for this particular processor and architecture. It is expected that the VIA Isaiah will be twice as fast in integer performance and four times as fast in floating-po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIA Eden
VIA Eden is a name of a variant of VIA's C3/ C7 x86 processors, designed to be used in embedded devices. They have smaller package sizes, lower power consumption, and somewhat lower computing performance than their C equivalents, due to reduced clock rates. They are often used in EPIA mini-ITX, nano-ITX, and Pico-ITX motherboards. In addition to x86 instruction decoding, the processors have a second undocumented Alternate Instruction Set. The Eden is available in four main versions: * Eden ESP: Samuel 2 and Nehemiah cores (300 MHz-1.0 GHz) - EBGA 35mm×35mm package, 66/100/133 MHz FSB * Eden-N: Nehemiah core (533 MHz-1.0 GHz) - NanoBGA 15mm×15mm package, 133 MHz FSB * Eden: Esther core (400 MHz-1.2 GHz) - NanoBGA2 21mm×21mm package, 400 MT/s FSB * Eden ULV: Esther core (500 MHz-1.5 GHz) - NanoBGA2 21mm×21mm package, 400 MT/s FSB The Eden ULV 500 MHz was the first variant to achieve a TDP of 1W .http://www.viatech.com/en/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NX Bit
The NX bit (no-execute) is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors. However, the NX bit is being increasingly used in conventional von Neumann architecture processors for security reasons. An operating system with support for the NX bit may mark certain areas of memory as non-executable. The processor will then refuse to execute any code residing in these areas of memory. The general technique, known as executable space protection, also called Write XOR Execute, is used to prevent certain types of malicious software from taking over computers by inserting their code into another program's data storage area and running their own code from within this section; one class of such attacks is known as the buffer overflow attack. The term NX bit originated with Advanced Micro Devices (AMD), as a marketing term. Intel markets the feat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSE3
SSE3, Streaming SIMD Extensions 3, also known by its Intel code name Prescott New Instructions (PNI), is the third iteration of the SSE instruction set for the IA-32 (x86) architecture. Intel introduced SSE3 in early 2004 with the Prescott revision of their Pentium 4 CPU. In April 2005, AMD introduced a subset of SSE3 in revision E (Venice and San Diego) of their Athlon 64 CPUs. The earlier SIMD instruction sets on the x86 platform, from oldest to newest, are MMX, 3DNow! (developed by AMD, but not supported by Intel processors), SSE, and SSE2. SSE3 contains 13 new instructions over SSE2. Changes The most notable change is the capability to work horizontally in a register, as opposed to the more or less strictly vertical operation of all previous SSE instructions. More specifically, instructions to add and subtract the multiple values stored within a single register have been added. These instructions can be used to speed up the implementation of a number of DSP and 3D operati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streaming SIMD Extensions, SSE instruction set, and is intended to fully replace MMX (instruction set), MMX. Intel extended SSE2 to create SSE3 in 2004. SSE2 added 144 new instructions to SSE, which has 70 instructions. Competing chip-maker AMD added support for SSE2 with the introduction of their Opteron and Athlon 64 ranges of x86-64, AMD64 64-bit CPUs in 2003. Features Most of the SSE2 instructions implement the integer vector operations also found in MMX. Instead of the MMX registers they use the XMM registers, which are wider and allow for significant performance improvements in specialized applications. Another advantage of replacing MMX with SSE2 is avoiding the mode switching penalty for issuing x87 instructions present in MMX because it i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |