|
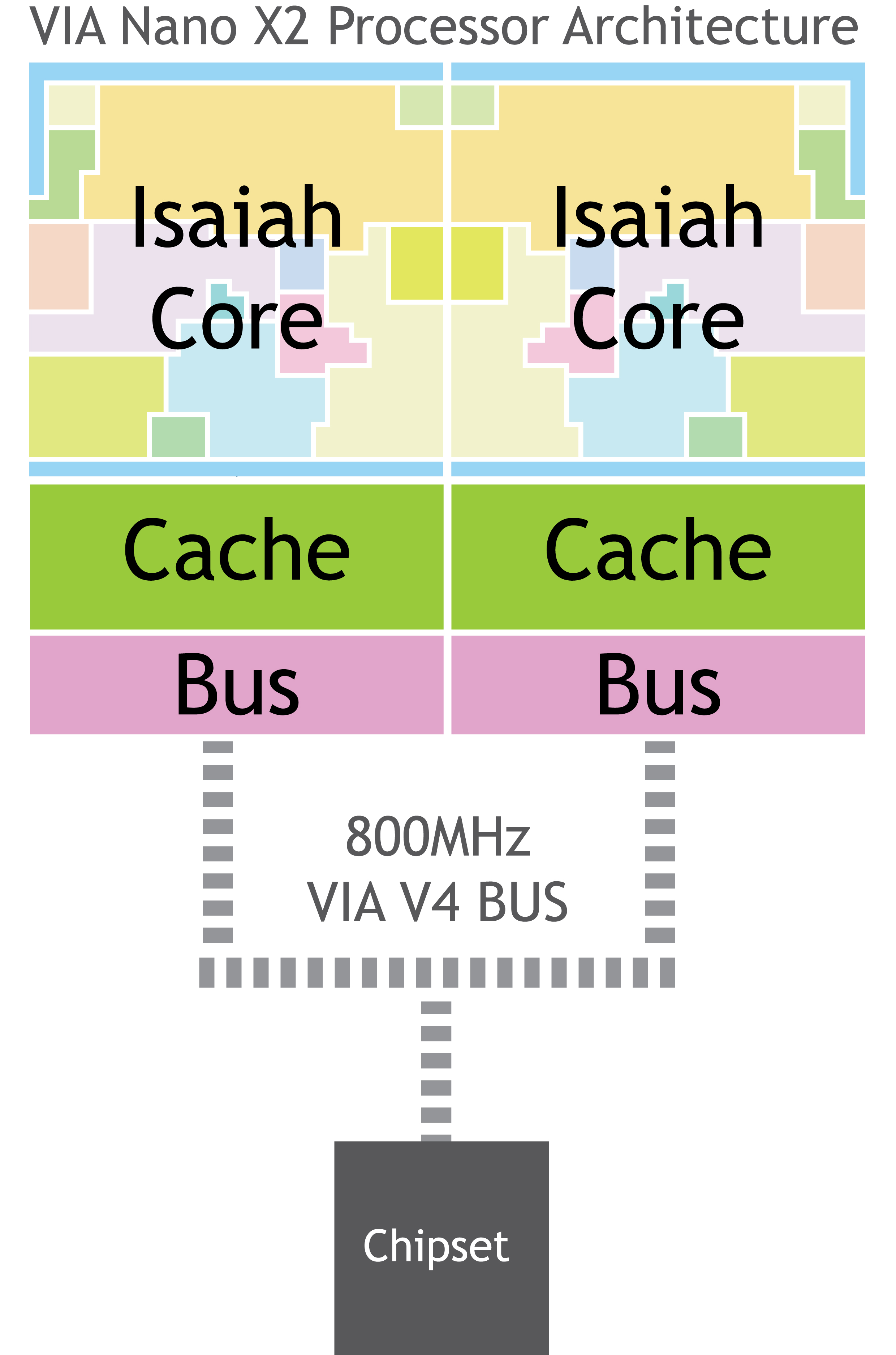
VIA Nano
The VIA Nano (formerly Code name#Commercial code names in the computer industry, code-named VIA Isaiah) is a 64-bit CPU for personal computers. The VIA Nano was released by VIA Technologies in 2008 after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology. This new Isaiah 64-bit architecture was designed from scratch, unveiled on 24 January 2008, and launched on 29 May, including low-voltage variants and the Nano brand name. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances. History Unlike Intel and AMD, VIA uses two distinct development code names for each of its CPU cores. In this case, the codename 'CN' was used in the United States by Centaur Technology. Biblical names are used as codes by VIA in Taiwan, and Isaiah was the choice for this particular processor and architecture. It is expected that the VIA Isaiah will be twice as fast in integer performance and four times as fast in floating-po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIA Rail
Via Rail Canada Inc. (), operating as Via Rail or Via, is a Canadian Crown corporation that is mandated to operate intercity passenger rail service in Canada. It receives an annual subsidy from Transport Canada to offset the cost of operating services connecting remote communities. Via Rail operates over 500 trains per week across eight Canadian provinces and of track, 97 per cent of which is owned and maintained by other railway companies, mostly by Canadian National Railway (CN). Via Rail carried approximately 4.39 million passengers in 2017, the majority along the ''Corridor'' routes connecting the major cities of the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor, and had an on-time performance of 73 per cent. History Background Yearly passenger levels on Canada's passenger trains peaked at 60 million during World War II. Following the war the growth of air travel and the personal automobile caused significant loss of mode share for Canada's passenger train operators. By the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core 2
Intel Core 2 is the processor family encompassing a range of Intel's consumer 64-bit x86-64 single-, dual-, and quad-core microprocessors based on the Core microarchitecture. The single- and dual-core models are single- die, whereas the quad-core models comprise two dies, each containing two cores, packaged in a multi-chip module. The Core 2 range was the last flagship range of Intel desktop processors to use a front-side bus. The introduction of Core 2 relegated the Pentium brand to the mid-range market, and reunified laptop and desktop CPU lines for marketing purposes under the same product name, which were formerly divided into the Pentium 4, Pentium D, and Pentium M brands. The ''Core 2'' processor line was introduced on July 27, 2006, comprising the ''Duo'' (dual-core) and ''Extreme'' (dual- or quad-core CPUs for enthusiasts), and in 2007, the ''Quad'' (quad-core) and ''Solo'' (single-core) sub-brands. Intel Core 2 processors with vPro technology (designed for businesses) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIMD
Single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA), but it should not be confused with an ISA. SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously. Such machines exploit data level parallelism, but not concurrency: there are simultaneous (parallel) computations, but each unit performs the exact same instruction at any given moment (just with different data). SIMD is particularly applicable to common tasks such as adjusting the contrast in a digital image or adjusting the volume of digital audio. Most modern CPU designs include SIMD instructions to improve the performance of multimedia use. SIMD has three different subcategories in Flynn's 1972 Taxonomy, one of which is SIMT. SIMT should not be confused with software thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSE4
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more precise details of 47 instructions became available at the Spring 2007 Intel Developer Forum in Beijing, in the presentation. SSE4 is fully compatible with software written for previous generations of Intel 64 and IA-32 architecture microprocessors. All existing software continues to run correctly without modification on microprocessors that incorporate SSE4, as well as in the presence of existing and new applications that incorporate SSE4. SSE4 subsets Intel SSE4 consists of 54 instructions. A subset consisting of 47 instructions, referred to as ''SSE4.1'' in some Intel documentation, is available in Penryn. Additionally, ''SSE4.2'', a second subset consisting of the 7 remaining instructions, is first available in Nehalem-based Core i7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, science, technology policy, and video games. ''Ars Technica'' was privately owned until May 2008, when it was sold to Condé Nast Digital, the online division of Condé Nast Publications. Condé Nast purchased the site, along with two others, for $25 million and added it to the company's ''Wired'' Digital group, which also includes ''Wired'' and, formerly, Reddit. The staff mostly works from home and has offices in Boston, Chicago, London, New York City, and San Francisco. The operations of ''Ars Technica'' are funded primarily by advertising, and it has offered a paid subscription service since 2001. History Ken Fisher, who serves as the website's current editor-in-chief, and Jon Stokes created ''Ars Technica'' in 1998. Its purpose was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PC Perspective
PC Perspective (often shortened to PCPer) is a web site dedicated to news and reviews of personal computing and gaming hardware. PCPer's "About Us" page. March 22, 2018. PC Perspective specializes in hardware that is most relevant to home users and enthusiasts. The site also has an active online community, a weekly podcast, and founder Ryan Shrout was the co-host of 's This Week in Computer Hardware. History PCPer was founded by Ryan Shrout in 2004. Shrout previously ran the |
HotHardware
''HotHardware'' is an online publication about computer hardware, consumer electronics and related technologies, mobile computing and PC gaming. It regularly features coverage of new products and technologies from vendors including Intel, Dell, AMD and NVIDIA. "Daily Hardware Round-ups" also offer reviews and news submitted by other technology-related sites. Content is organized by category and is searchable through a content management system (CMS), with a blog A blog (a truncation of "weblog") is a discussion or informational website published on the World Wide Web consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries (posts). Posts are typically displayed in reverse chronological order ...-style comments section for registered users, and a web forum with integrated comments section, topic tagging/filing and a content rating system. Forum members can also take part in contests to win hardware that has been featured on the site. References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel Atom
Intel Atom is the brand name for a line of IA-32 and x86-64 instruction set ultra-low-voltage processors by Intel Corporation designed to reduce electric consumption and power dissipation in comparison with ordinary processors of the Intel Core series. Atom is mainly used in netbooks, nettops, embedded applications ranging from health care to advanced robotics, mobile Internet devices (MIDs) and phones. The line was originally designed in 45 nm complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) technology and subsequent models, codenamed ''Cedar'', used a 32 nm process. The first generation of Atom processors are based on the Bonnell microarchitecture. On December 21, 2009, Intel announced the ''Pine Trail'' platform, including new Atom processor code-named ''Pineview'' (Atom N450), with total kit power consumption down 20%. On December 28, 2011, Intel updated the Atom line with the ''Cedar'' processors. In December 2012, Intel launched the 64-bit ''Centerton'' family of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X86 Virtualization
x86 virtualization is the use of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities on an x86/x86-64 CPU. In the late 1990s x86 virtualization was achieved by complex software techniques, necessary to compensate for the processor's lack of hardware-assisted virtualization capabilities while attaining reasonable performance. In 2005 and 2006, both Intel (VT-x) and AMD (AMD-V) introduced limited hardware virtualization support that allowed simpler virtualization software but offered very few speed benefits. Greater hardware support, which allowed substantial speed improvements, came with later processor models. Software-based virtualization The following discussion focuses only on virtualization of the x86 architecture protected mode. In protected mode the operating system kernel runs at a higher privilege such as ring 0, and applications at a lower privilege such as ring 3. In software-based virtualization, a host OS has direct access to hardware while the guest OSs have limited acce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Design Power
The thermal design power (TDP), sometimes called thermal design point, is the maximum amount of heat generated by a computer chip or component (often a CPU, GPU or system on a chip) that the cooling system in a computer is designed to dissipate under any workload. Some sources state that the peak power rating for a microprocessor is usually 1.5 times the TDP rating. Intel has introduced a new metric called ''scenario design power'' (SDP) for some Ivy Bridge Y-series processors. Calculation The ''average CPU power'' (ACP) is the power consumption of central processing units, especially server processors, under "average" daily usage as defined by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) for use in its line of processors based on the K10 microarchitecture ( Opteron 8300 and 2300 series processors). Intel's thermal design power (TDP), used for Pentium and Core 2 processors, measures the energy consumption under high workload; it is numerically somewhat higher than the "average" ACP rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Speed
In computing, the clock rate or clock speed typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses, which are used to synchronize the operations of its components, and is used as an indicator of the processor's speed. It is measured in the SI unit of frequency hertz (Hz). The clock rate of the first generation of computers was measured in hertz or kilohertz (kHz), the first personal computers (PCs) to arrive throughout the 1970s and 1980s had clock rates measured in megahertz (MHz), and in the 21st century the speed of modern CPUs is commonly advertised in gigahertz (GHz). This metric is most useful when comparing processors within the same family, holding constant other features that may affect performance. Determining factors Binning Manufacturers of modern processors typically charge premium prices for processors that operate at higher clock rates, a practice called binning. For a given CPU, the clock rates are determined at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |