|
Lübeck Nordic Film Days
The Lübeck Nordic Film Days (german: Nordische Filmtage Lübeck) is a film festival for movies from the Nordic countries">Nordic and Baltic countries">film festival">/ref> (german: Nordische Filmtage Lübeck) is a film festival for movies from the Nordic countries">Nordic and Baltic countries held annually in Lübeck, Germany, since 1956 on the first weekend in November. It is the only festival in Germany, and the only one in Europe apart from the Rouen Nordic Film Festival founded in Rouen, France, which is entirely devoted to the presentation of films from the North and Northeast of Europe. Thus is the most important festival for films from Scandinavia and the Baltic countries outside Scandinavia. The festival also presents films made in the state of Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany. Feature films, documentaries and short films from Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway and Sweden are presented at this five-day event every year at the beginning o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Festival
A film festival is an organized, extended presentation of films in one or more cinemas or screening venues, usually in a single city or region. Increasingly, film festivals show some films outdoors. Films may be of recent date and, depending upon the festival's focus, can include international and domestic releases. Some film festivals focus on a specific filmmaker, genre of film (e.g. horror films), or on a subject matter. Several film festivals focus solely on presenting short films of a defined maximum length. Film festivals are typically annual events. Some film historians, including Jerry Beck, do not consider film festivals as official releases of the film. The most prestigious film festivals in the world, known as the "Big Five", are (listed chronologically according to the date of foundation): Venice, Cannes, Berlin (the original ''Big Three''), Toronto, and Sundance. History The Venice Film Festival in Italy began in 1932 and is the oldest film festival still runn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordic Countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden; the autonomous territories of the Faroe Islands and Greenland; and the autonomous region of Åland. The Nordic countries have much in common in their way of life, History of Scandinavia, history, religion and Nordic model, social structure. They have a long history of political unions and other close relations but do not form a singular entity today. The Scandinavism, Scandinavist movement sought to unite Denmark, Norway and Sweden into one country in the 19th century. With the dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden (Norwegian independence), the independence of Finland in the early 20th century and the 1944 Icelandic constitutional referendum, this movement expanded into the modern organised Nordic cooperation. Since 196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
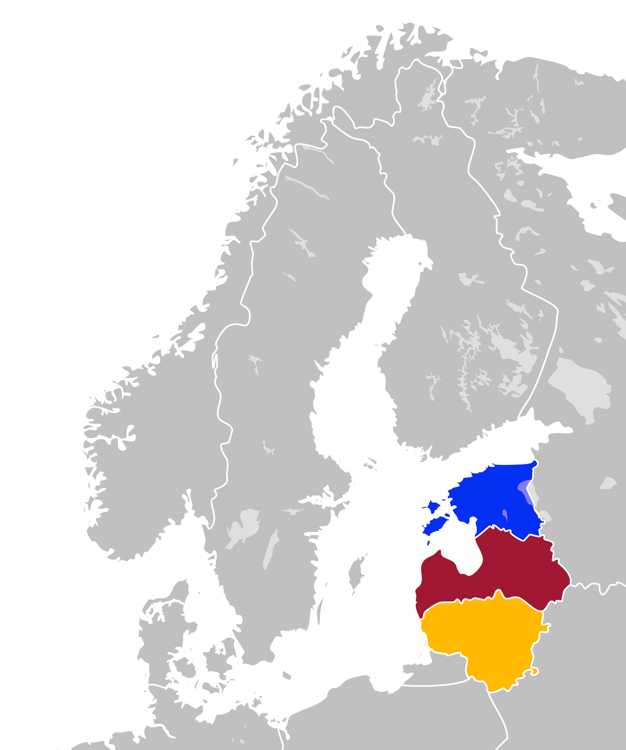
Baltic Countries
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state of Schleswig-Holstein, after its capital of Kiel, and is the 35th-largest city in Germany. The city lies in Holstein, northeast of Hamburg, on the mouth of the River Trave, which flows into the Bay of Lübeck in the borough of Travemünde, and on the Trave's tributary Wakenitz. The city is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, and is the southwesternmost city on the Baltic, as well as the closest point of access to the Baltic from Hamburg. The port of Lübeck is the second-largest German Baltic port after the port of Rostock. The city lies in the Northern Low Saxon dialect area of Low German. Lübeck is famous for having been the cradle and the ''de facto'' capital of the Hanseatic League. Its city centre is Germany's most e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rouen Nordic Film Festival
The Rouen Nordic Film Festival (french: Festival du Cinéma Nordique) was a film festival hold in Rouen, France for screening and competition films made in Nordic and Baltic countries, the Netherlands and Belgium. In December 2010, the organisers, in conflict with the City Council, announce their intention to put an end to the festival. The Grand Jury Prize * 2010 - : Upperdog (2009), Director: Sara Johnsen * 2009 - : Cold Lunch (2008), Director: Eva Sørhaug * 2008 - : Temporary release (2007), Director: Erik Clausen * 2007 - : Reprise (2006), Director: Joachim Trier * 2005 - : Uno (2004), Director: Aksel Hennie * 2004 - : Falling Sky (2002) ( no, Himmelfall), Director: Gunnar Vikene * 2003 - : Noi the Albino (2003) is, Nói albínói), Director: Dagur Kári * 2002 - : Drift (2001), Director: Michiel van Jaarsveld * 2001 - : 101 Reykjavík (2000), Director: Baltasar Kormákur * 2000 - : Magnetist's Fifth Winter (1999) ( no, Magnetisörens femte vinter), Director: Morten Henriksen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes part of Finland), or more broadly to include all of Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population in the region live in the more temperate southern regions, with the northern parts having long, cold, winters. The region became notable during the Viking Age, when Scandinavian peoples participated in large scale raiding, conquest, colonization and trading mostly throughout Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig. Its capital city is Kiel; other notable cities are Lübeck and Flensburg. The region is called ''Slesvig-Holsten'' in Danish and pronounced . The Low German name is ''Sleswig-Holsteen'', and the North Frisian name is ''Slaswik-Holstiinj''. In more dated English, it is also known as ''Sleswick-Holsatia''. Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. It covers an area of , making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states). Schleswig was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it escaped full co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Germany
Northern Germany (german: link=no, Norddeutschland) is a linguistic, geographic, socio-cultural and historic region in the northern part of Germany which includes the coastal states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Lower Saxony and the three city-states Berlin, Hamburg and Bremen. It contrasts with Southern Germany, Western Germany and Eastern Germany. Language Northern Germany generally refers to the ''Sprachraum'' area north of the Uerdingen and Benrath line isoglosses, where Low German dialects are spoken. These comprise the Low Saxon dialects in the west (including the Westphalian language area up to the Rhineland), the East Low German region along the Baltic coast with Western Pomerania, the Altmark and northern Brandenburg, as well as the North Low German dialects. Although from the 19th century onwards, the use of Standard German was strongly promoted especially by the Prussian administration, Low German dialects are still present in rural areas, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bille August
Bille August (born 9 November 1948) is a Danish director, screenwriter, and cinematographer of film and television. In a career spanning over four decades, he has been the recipient of numerous accolades, making him one of the most acclaimed contemporary Danish filmmakers. August's 1987 film '' Pelle the Conqueror'' won the Palme d'Or, Academy Award and Golden Globe Award. He is one of only nine directors to win the Palme d'Or twice, winning the award again in 1992 for '' The Best Intentions'', based on the autobiographical script by Ingmar Bergman. His filmography includes '' The House of the Spirits'', based on the novel by Isabel Allende; ''Smilla's Sense of Snow''; '' Les Misérables''; ''Night Train to Lisbon'', '' Silent Heart'', '' The Chinese Widow'' and ''A Fortunate Man''. He has received five Robert Awards (including Best Film and Best Director) and three Bodil Awards for Best Danish Film. He is also a Knight of the Order of the Dannebrog. Life and career A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasse Hallström
Lars Sven "Lasse" Hallström (; born 2 June 1946) is a Swedish film director. He first became known for directing almost all the music videos by the pop group ABBA, and subsequently became a feature film director. He was nominated for an Academy Award for Best Director for '' My Life as a Dog (Mitt liv som hund)'' (1985) and later for '' The Cider House Rules'' (1999). His other celebrated directorial works include '' What's Eating Gilbert Grape'' (1993) and '' Chocolat'' (2000). Early life Hallström was born in Stockholm, Sweden. His father Nils Hallström was a dentist and his mother was the writer Karin Lyberg (1907–2000). His maternal grandfather, Ernst Lyberg, was the Minister of Finance in the first cabinet of Carl Gustaf Ekman (1926–1928) and leader of the Liberal Party of Sweden (1930–1933). His father was also enthusiastic about film and made a film called ''Sommarstad'' in 1939. Career Hallström attended Adolf Fredrik's Music School in Stockholm. He made his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aki Kaurismäki
Aki Olavi Kaurismäki (; born 4 April 1957) is a Finnish film director and screenwriter. He is best known for the award-winning '' Drifting Clouds'' (1996), ''The Man Without a Past'' (2002), '' Le Havre'' (2011) and '' The Other Side of Hope'' (2017), as well as for the mockumentary '' Leningrad Cowboys Go America'' (1989). He is described as Finland's best-known film director. Career After graduating in media studies from the University of Tampere, Kaurismäki worked as a bricklayer, postman, and dish-washer, long before pursuing his interest in cinema, first as a critic, and later as a screenwriter & director. He started his career as a co-screenwriter and actor in films made by his older brother, Mika Kaurismäki. He played the main role in Mika's film '' The Liar'' (1981). Together they founded the production company Villealfa Filmproductions and later the Midnight Sun Film Festival. His debut as an independent director was ''Crime and Punishment'' (1983), an adaptation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Palais_du_Cinema.jpg)