|
Léva
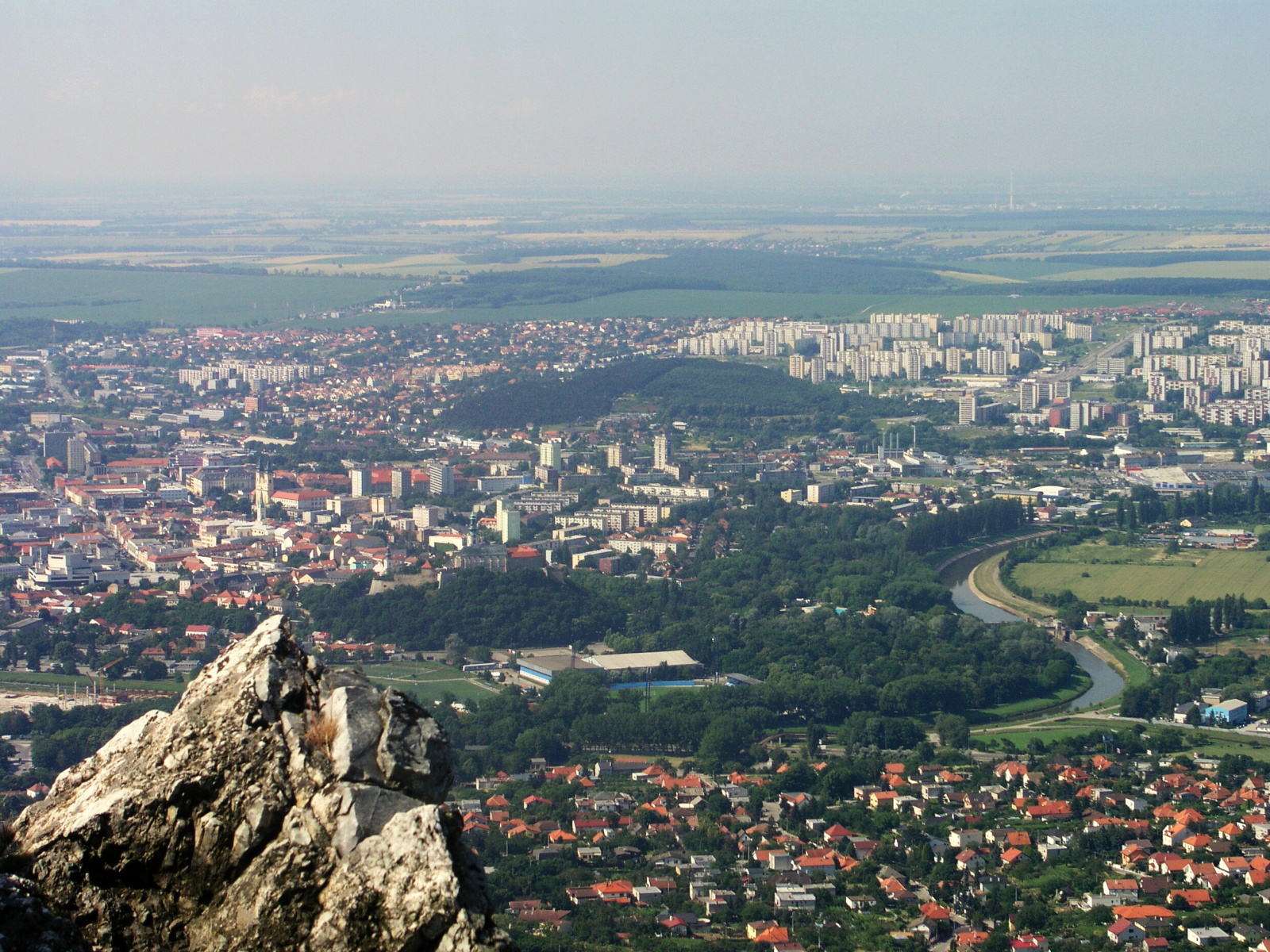
Levice (; hu, Léva, Hungarian pronunciation: ; german: Lewenz, literally lionesses) is a town in western Slovakia. The town lies on the left bank of the lower Hron river. The Old Church Slavonic, Old Slavic name of the town was ''Leva'', which means "the Left One". The town is located in the north-eastern corner of the Danubian Lowland (''Podunajská nížina''), east of Bratislava, south-east of Nitra, south-west of Banská Štiavnica, south-west of Zvolen and from the border with Hungary. It is the capital of the Levice District, which is the largest district in Slovakia at . The town's heraldic animal is lion (in Slovak ''lev''), and the town's colours are green and yellow. History Levice is first mentioned as Leua, one of the villages belonging to the parish of Martin of Tours, St. Martin's Church in Bratka ( hu, Baratka) in 1156. It was part of the Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus Tekov (''Bars''). First attacked by the Ottoman Empire, Turks in 1544, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levice District
Levice District ( sk, okres Levice; hu, Lévai járás) is a district in the Nitra Region of western Slovakia. It is the largest of Slovakia's 79 districts. The west of the district was in the Hungarian county of Bars until 1918, while the east of the district was in Hont County Hont County was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Most of its territory is now part of Slovakia, while a smaller southern portion is part of Hungary. Today, in Slovakia Hont is the informal designation of the corres ...: Farná in the south was in the county of Esztergom (Ostrihom). Municipalities ''Source'': References Districts of Slovakia {{Nitra-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of about 78,353, it is the fifth largest city in Slovakia. Nitra is also one of the oldest cities in Slovakia; it was the political center of the Principality of Nitra. Today, it is a seat of a ''kraj'' (Nitra Region), and an '' okres'' (Nitra District). Etymology The first mention of Nitra dates back to the 9th century. The name of the city is derived from the Nitra river. The name is Indo-European, but the question of its pre-Slavic or Slavic origin has not been satisfactorily answered. Nitra might be derived from the old Indo-European root ''neit-'', ''nit-'' meaning "to cut" or "to burn" using a derivation element ''-r-'' (see also slash-and-burn agricultural technique). The same root is still present in the Slovak verb ''nietiť'' (to make a fire), but also in othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
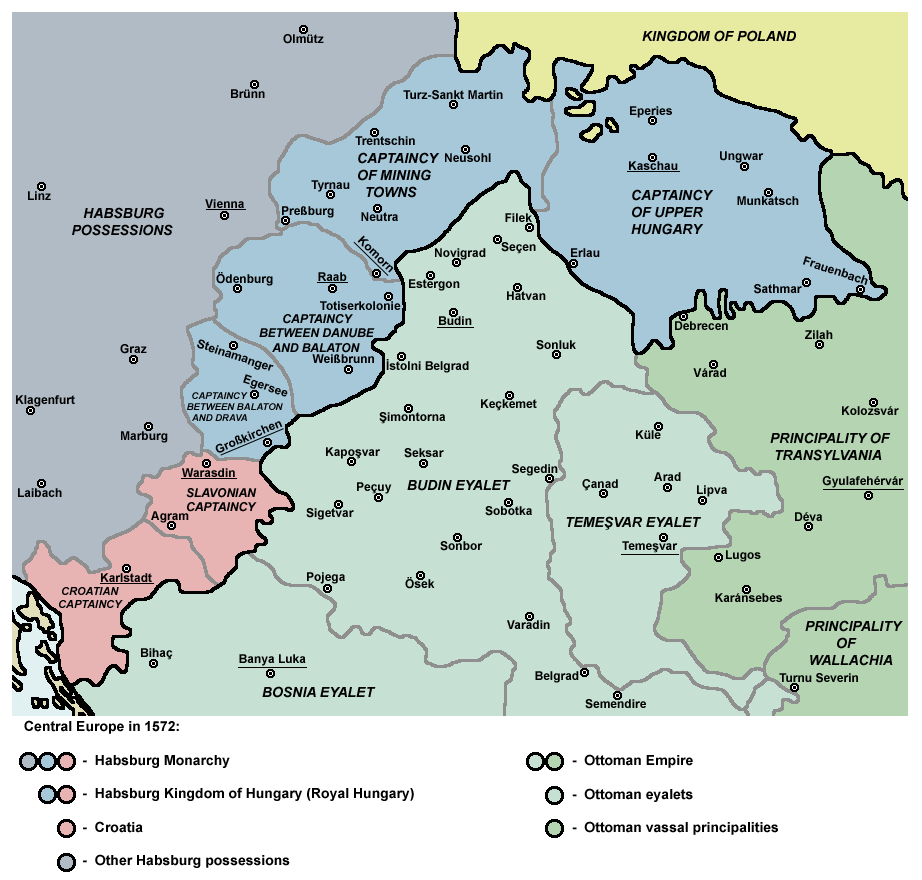
Captaincies Of The Kingdom Of Hungary
The Captaincies of the Kingdom of Hungary ( hu, Magyar királyi főkapitányságok) were administrative divisions, military districts in the 16th and 17th centuries. The Ottoman Empire meant a constant threat to the kingdom, therefore the Habsburg Hungarian kings needed to establish a well-working military administration. The captaincy (''főkapitányság'') was administered by the Royal Captain-general of the Captaincy. In 1542, the Hungarian kingdom, primarily for military and administrative purposes, was divided into two captaincies, Captaincy of Cisdanubia (mostly Upper Hungary) and Captaincy of Transdanubia (the remaining territories). Captaincy of Győr was founded in 1556. In 1563 Captaincy of Lower Hungary was established (today approx. the present-day regions of western and central Slovakia). By 1566, Kanizsa at southwestern Transdanubia also evolved into a new captaincy.Pálffy 1999, p. 92. Irrespective of the military districts, there were coexistent superior (''nemesi' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitra Region
The Nitra Region ( sk, Nitriansky kraj, ; hu, Nyitrai kerület) is one of the administrative regions of Slovakia. It was first established in 1923 and from 1996 exists in its present borders. It consists of seven districts ( sk, okres) and 354 municipalities, from which 16 have a town status. The economy of the region focuses more on agriculture, than in other Slovak regions. Nitra is its seat, largest city, and cultural and economic center. Geography This region with a long history is situated in the southwest of Slovakia, mostly in the eastern part of the Danubian Lowland. It is divided into two sub-units: the Danubian Flat in the south-west, with eastern part of the Žitný ostrov island, and the Danubian Hills in the north, centre and east. Mountain ranges reaching into the region are: Považský Inovec in the north-west, where the region's highest point, Veľký Inovec, is located, Tribeč in the north from Nitra, Pohronský Inovec in the north-east and Štiavnické v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerződés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It formally ended World War I between most of the Allies of World War I and the Kingdom of Hungary. French diplomats played the major role in designing the treaty, with a view to establishing a French-led coalition of the newly formed states. It regulated the status of the Kingdom of Hungary and defined its borders generally within the #Borders of Hungary, ceasefire lines established in November–December 1918 and left Hungary as a Landlocked country, landlocked state that included , 28% of the that had constituted the pre-war Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen, Kingdom of Hungary (the Hungarian half of the Austria-Hungary, Austro-Hungarian monarchy). The truncated kingdom had a population of 7.6 million, 36% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי, , common_name = Czechoslovakia , life_span = 1918–19391945–1992 , p1 = Austria-Hungary , image_p1 = , s1 = Czech Republic , flag_s1 = Flag of the Czech Republic.svg , s2 = Slovakia , flag_s2 = Flag of Slovakia.svg , image_flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia.svg , flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia , flag_type = Flag(1920–1992) , flag_border = Flag of Czechoslovakia , image_coat = Middle coat of arms of Czechoslovakia.svg , symbol_type = Middle coat of arms(1918–1938 and 1945–1961) , image_map = Czechoslovakia location map.svg , image_map_caption = Czechoslovakia during the interwar period and the Cold War , national_motto = , anthems = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuruc
Kuruc (, plural ''kurucok''), also spelled kurutz, refers to a group of armed anti-Habsburg insurgents in the Kingdom of Hungary between 1671 and 1711. Over time, the term kuruc has come to designate Hungarians who advocate strict national independence and the term labanc to designate Hungarians who advocate cooperating with outside powers. The term kuruc is used in both a positive sense to mean “patriotic” and in a negative sense to mean “chauvinistic.” The term labanc is almost always used in a negative sense to mean “disloyal” or “traitorous.” The kuruc army was composed mostly of impoverished lower Hungarian nobility and serfs, including Hungarian Protestant peasants and Slavs. They managed to conquer large parts of Hungary in several uprisings from Transylvania before they were defeated by Habsburg imperial troops. Name The word ''kuruc'' was first used in 1514 for the armed peasants led by György Dózsa. 18th-century scholar Matthias Bel supposed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Habsburg, french: Maison des Habsbourg and also known as the House of Austriagerman: link=no, Haus Österreich, ; es, link=no, Casa de Austria; nl, Huis van Oostenrijk, pl, dom Austrii, la, Domus Austriæ, french: Maison d'Autriche; hu, Ausztria Háza; it, Casa d'Austria; pt, Casa da Áustria is one of the most prominent and important dynasties in European history. The house takes its name from Habsburg Castle, a fortress built in the 1020s in present-day Switzerland by Radbot of Klettgau, who named his fortress Habsburg. His grandson Otto II, Count of Habsburg, Otto II was the first to take the fortress name as his own, adding "Count of Habsburg" to his title. In 1273, Count Radbot's seventh-generation descendant Rudolph I of German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
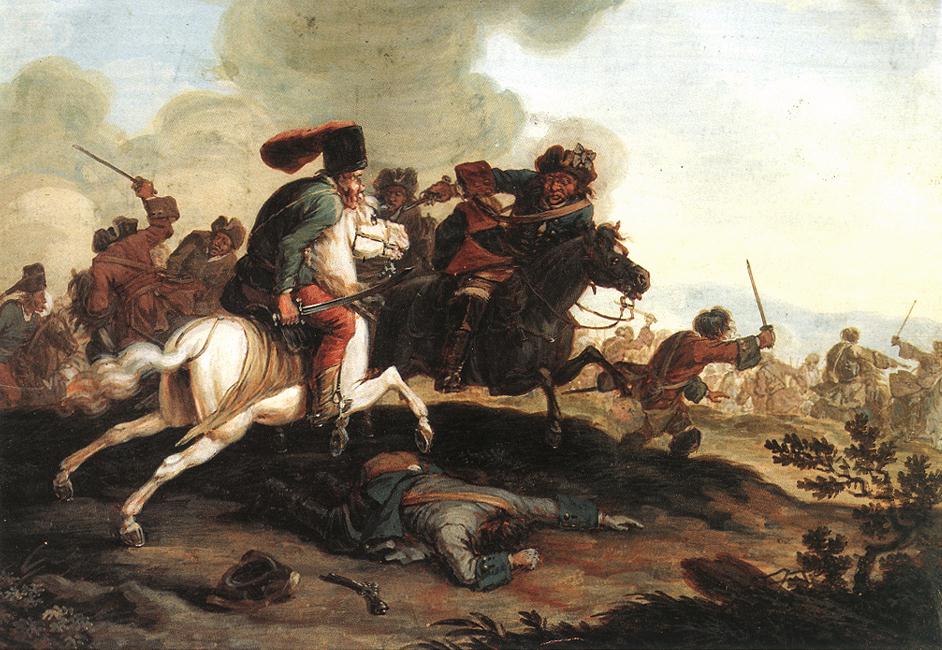
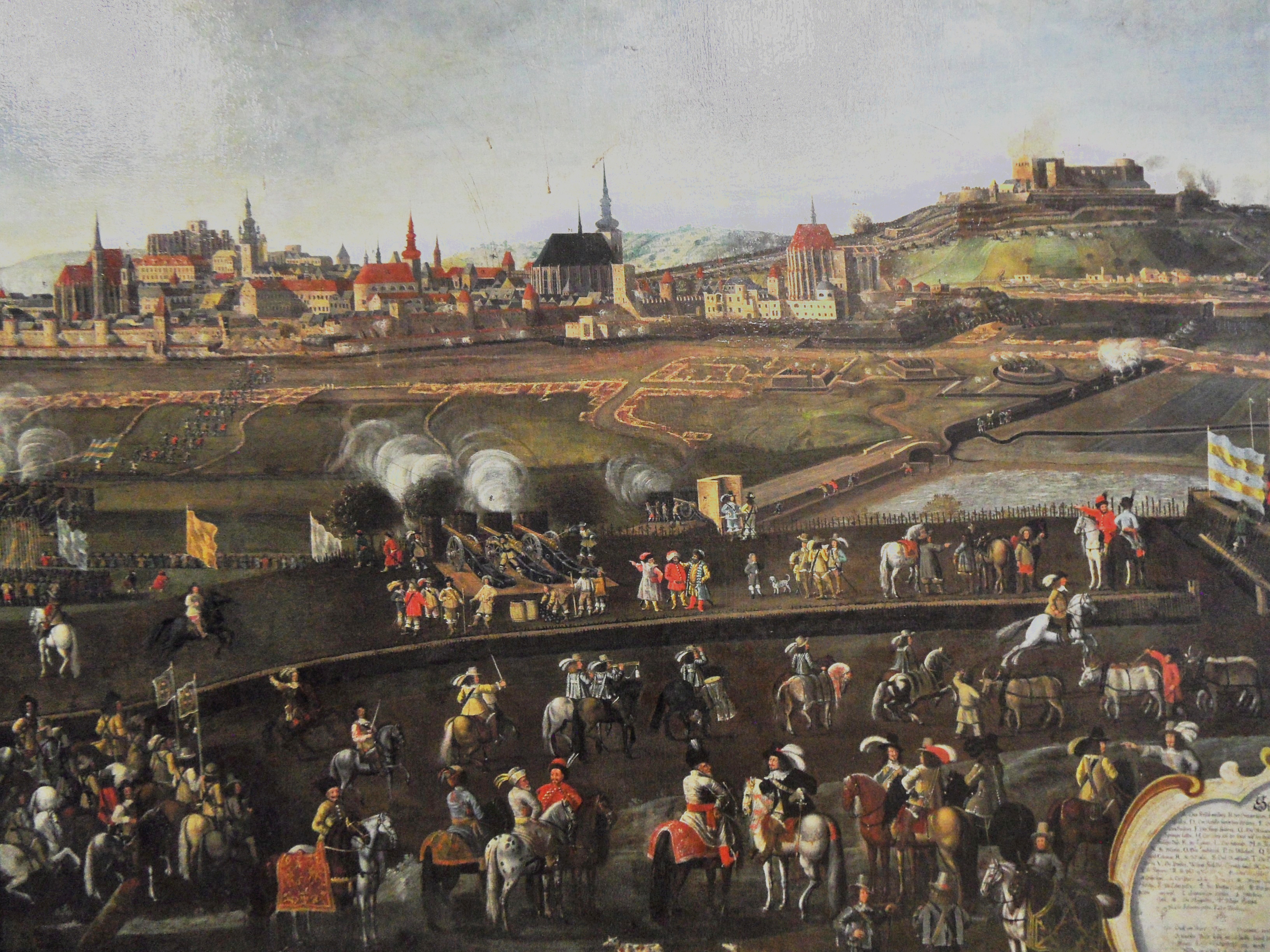
Battle Of Levice
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Louis Raduit De Souches
Jean-Louis Raduit de Souches (16 August 1608 to 12 August 1682), also known as Ludwig de Souches, was a French-born professional soldier who spent a number of years in the Swedish Army before switching to Imperial service in 1642. Although he was a capable officer who reached the rank of Field Marshal, his career was marred by a tendency to quarrel with his colleagues and superiors. Born into a family of minor French Protestant nobility, de Souches went into exile after the Siege of La Rochelle in 1629. He served in the Swedish army when it entered the Thirty Years' War against Emperor Ferdinand III and by 1642 was colonel of an infantry regiment. However, he fell out with his superior officer and switched sides, joining the Imperial army. He established his reputation in the defence of Brno against the Swedes in 1645 and was promoted Field Marshal in 1664. When Emperor Leopold joined the Franco-Dutch War in 1673, de Souches was appointed commander of Imperial forces in the Low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)