|
London Defence Positions
The London Defence Positions were a late 19th century scheme of earthwork fortifications in the south-east of England, designed to protect London from foreign invasion landing on the south coast. The positions were a carefully surveyed contingency plan for a line of entrenchments, which could be quickly excavated in a time of emergency. The line to be followed by these entrenchments was supported by thirteen permanent small polygonal forts or redoubts called London Mobilisation Centres, which were equipped with all the stores and ammunition that would be needed by the troops tasked with digging and manning the positions. Origins The 1859 Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kingdom report on Britain's defences believed that London was practically undefendable; they proposed a fort at Shooters Hill to defend the Royal Arsenal at Woolwich, but it was never acted upon. Following a number of proposals by senior military figures, an 1888 memorandum written by Colonel John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reigate Fort - Geograph
Reigate ( ) is a town in Surrey, England, around south of central London. The settlement is recorded in Domesday Book in 1086 as ''Cherchefelle'' and first appears with its modern name in the 1190s. The earliest archaeological evidence for human activity is from the Paleolithic and Neolithic, and during the Roman period, tile making took place to the north east of the modern centre. A motte-and-bailey castle was erected in Reigate in the late 11th or early 12th century. It was originally constructed of timber, but the curtain walls were rebuilt in stone about a century later. In the first half of the 13th century, an Augustinian priory was founded to the south of the modern town centre. The priory was closed during the Reformation and was rebuilt as a private residence for William Howard, the 1st Baron Howard of Effingham. The castle was abandoned around the same time and fell into disrepair. During the medieval and early modern periods, Reigate was primarily an agricultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volunteer Force (Great Britain)
The Volunteer Force was a citizen army of part-time rifle, artillery and engineer corps, created as a popular movement throughout the British Empire in 1859. Originally highly autonomous, the units of volunteers became increasingly integrated with the British Army after the Childers Reforms in 1881, before forming part of the Territorial Force in 1908. Most of the regiments of the present Territorial Army Infantry, Artillery, Engineers and Signals units are directly descended from Volunteer Force units. The British Army following the Crimea Prior to the Crimean War, the British military (i.e., ''land forces'') was made up of multiple separate forces, with a basic division into the ''Regular Forces'' (including the British Army, composed primarily of cavalry and infantry, and the ''Ordnance Military Corps'' of the Board of Ordnance, made up of the Royal Artillery, Royal Engineers, and the Royal Sappers and Miners though not including the originally civilian Commissariat D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merstham
Merstham is a town in the borough of Reigate and Banstead in Surrey, England. It lies 25 miles south of Charing Cross and 2 miles south of the Greater London border. Part of the North Downs Way runs along the northern boundary of the town. Merstham has community associations, an early medieval church and a football club. Neighbourhoods Old Merstham Old Merstham forms the north and north-west of modern Merstham and is the original village centre. There is a small day school by the railway station, a pub, a few barbershops and a small number of other shops. The Merstham Estate/New Merstham After World War II the London County Council built the Merstham Estate, originally entirely public housing, was built to a geometric layout in the eastern fields. This area has its own parade of shops, the Brook recreation ground, three schools, and a youth/community centre along Radstock Way. Oakley, a small country house, is listed and has Victorian gothic architecture features. South Mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reigate
Reigate ( ) is a town in Surrey, England, around south of central London. The settlement is recorded in Domesday Book in 1086 as ''Cherchefelle'' and first appears with its modern name in the 1190s. The earliest archaeological evidence for human activity is from the Paleolithic and Neolithic, and during the Roman period, tile making took place to the north east of the modern centre. A motte-and-bailey castle was erected in Reigate in the late 11th or early 12th century. It was originally constructed of timber, but the curtain walls were rebuilt in stone about a century later. In the first half of the 13th century, an Augustinian priory was founded to the south of the modern town centre. The priory was closed during the Reformation and was rebuilt as a private residence for William Howard, the 1st Baron Howard of Effingham. The castle was abandoned around the same time and fell into disrepair. During the medieval and early modern periods, Reigate was primarily an agricultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betchworth
Betchworth is a village and civil parish in the Mole Valley district of Surrey, England. The village centre is on the north bank of the River Mole and south of the A25 road, almost east of Dorking and west of Reigate. London is north of the village. Service sector occupations dominate Betchworth's economy – its station and road links make it a part of the London commuter belt – combined with crop agriculture and services for a relatively large retired proportion of the population. A former lime quarry, rebuilt manor house and Grade I-listed church are within its boundaries. History Toponymy State records show the name as ''Becesworde'' (11th century), ''Beceswrde'' (12th century) and ''Bechesworth'' (13th century). The name is generally agreed to mean a "farm or enclosure belonging to a person or family called Becci". Pre-Roman settlement Bronze Age artefacts have been found at Betchworth only since 1944. No Roman villas, farms or camps have been found. Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Hill, Surrey
Box Hill is a summit of the North Downs in Surrey, approximately south-west of London. The hill gets its name from the ancient box woodland found on the steepest west-facing chalk slopes overlooking the River Mole. The western part of the hill is owned and managed by the National Trust, whilst the village of Box Hill lies on higher ground to the east. The highest point is Betchworth Clump at above OD, although the Salomons Memorial (at 172 metres) overlooking the town of Dorking is the most popular viewpoint. Box Hill lies within the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and forms part of the Mole Gap to Reigate Escarpment Site of Special Scientific Interest. The north- and south-facing slopes support an area of chalk downland, noted for its orchids and other rare plant species. The hill provides a habitat for 38 species of butterfly, and has given its name to a species of squash bug, now found throughout south-east England. An estimated 850,000 people visit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pewley Hill
Pewley Hill is a hill, and a street so named, near Guildford in England. It links to the open space at Pewley Down and was used as the site of a semaphore station and a defensive fort in the nineteenth century. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries much of the land was built upon. Pewley Hill was part of lands granted by William the Conqueror to the Testard family. It takes its name from the de-la-Puille family who acquired it from Richard Testard in 1255. The Puille family name was also reflected in the manor of Poyle and the Poyle Charity. An Admiralty semaphore station was built at Pewley Hill in 1822 forming part of the London-Portsmouth semaphore line. The building remains, with a cupola on top which was added after the semaphore went out of use. In 1866 Guildford Corporation built a new reservoir at the top of Pewley Hill. Pewley Hill Fort (or Mobilization Centre) was built in around 1890 as part of the London Defence Positions scheme, running from Guildford along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essex
Essex () is a county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the River Thames to the south, and Greater London to the south and south-west. There are three cities in Essex: Southend, Colchester and Chelmsford, in order of population. For the purposes of government statistics, Essex is placed in the East of England region. There are four definitions of the extent of Essex, the widest being the ancient county. Next, the largest is the former postal county, followed by the ceremonial county, with the smallest being the administrative county—the area administered by the County Council, which excludes the two unitary authorities of Thurrock and Southend-on-Sea. The ceremonial county occupies the eastern part of what was, during the Early Middle Ages, the Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of Essex. As well as rural areas and urban areas, it forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn. The river rises at Thames Head in Gloucestershire, and flows into the North Sea near Tilbury, Essex and Gravesend, Kent, via the Thames Estuary. From the west it flows through Oxford (where it is sometimes called the Isis), Reading, Henley-on-Thames and Windsor. The Thames also drains the whole of Greater London. In August 2022, the source of the river moved five miles to beyond Somerford Keynes due to the heatwave in July 2022. The lower reaches of the river are called the Tideway, derived from its long tidal reach up to Teddington Lock. Its tidal section includes most of its London stretch and has a rise and fall of . From Oxford to the Estuary the Thames drops by 55 metres. Running through some of the drier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guildford
Guildford () is a town in west Surrey, around southwest of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The name "Guildford" is thought to derive from a crossing of the River Wey, a tributary of the River Thames that flows through the town centre. The earliest evidence of human activity in the area is from the Mesolithic and Guildford is mentioned in the will of Alfred the Great from . The exact location of the main Anglo-Saxon settlement is unclear and the current site of the modern town centre may not have been occupied until the early 11th century. Following the Norman Conquest, a motte-and-bailey castle was constructed, which was developed into a royal residence by Henry III. During the late Middle Ages, Guildford prospered as a result of the wool trade and the town was granted a charter of incorporation by Henry VII in 1488. The River Wey N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
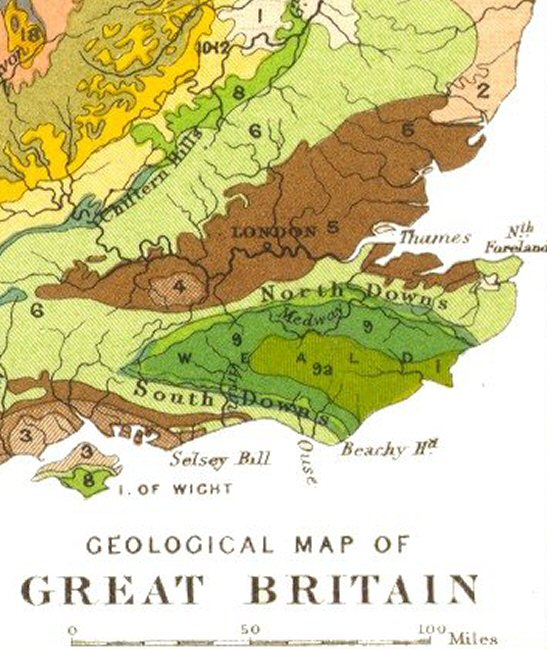
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but some to the south. Geography The narrow spine of the Hog's Bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



.jpg)