North Downs on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The North Downs are a ridge of
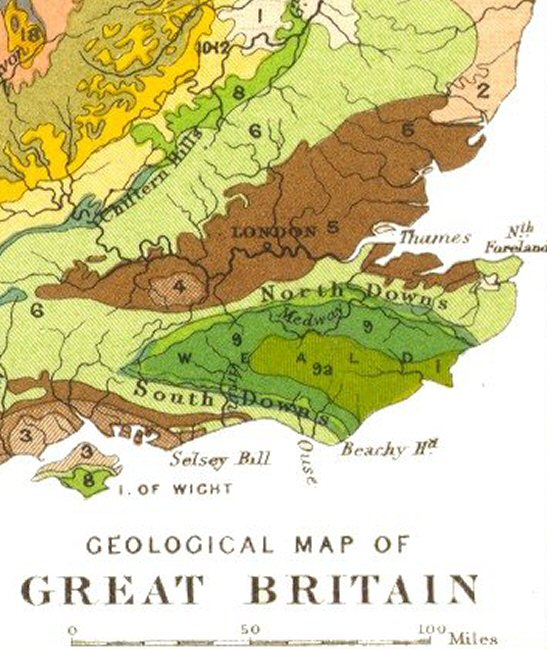
 The narrow spine of the
The narrow spine of the
 * The ''
* The ''
 Following the Cretaceous, the sea covering the south of England began to retreat and the land was pushed higher. The Weald (the area covering modern day south Surrey, south Kent and north Sussex) was lifted by the same geological processes that created the Alps, resulting in an
Following the Cretaceous, the sea covering the south of England began to retreat and the land was pushed higher. The Weald (the area covering modern day south Surrey, south Kent and north Sussex) was lifted by the same geological processes that created the Alps, resulting in an
 Calcaerous woodland occurs on thin soils where chalk is close to the surface. These conditions are most often found on the escarpment of the North Downs and on valley slopes, but may also occur on the plateau of the
Calcaerous woodland occurs on thin soils where chalk is close to the surface. These conditions are most often found on the escarpment of the North Downs and on valley slopes, but may also occur on the plateau of the
 In about 3000 BC the emergence of
In about 3000 BC the emergence of
 The landscape of the Downs has been greatly shaped by man. There has been
The landscape of the Downs has been greatly shaped by man. There has been
Image:Wye Downs 1.jpg, The North Downs at the
KentDowns AONB siteSurrey Hills AONB siteDownlands Trust site
{{coord, 51, 16, N, 0, 30, W, display=title, region:GB_type:mountain_source:GNS-enwiki Geology of England Hills of Kent Hills of Surrey Hills of Hampshire Borough of Ashford Natural regions of England Chalk landforms
chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk ...
hills in south east England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
that stretch from Farnham
Farnham ( /ˈfɑːnəm/) is a market town and civil parish in Surrey, England, around southwest of London. It is in the Borough of Waverley, close to the county border with Hampshire. The town is on the north branch of the River Wey, a trib ...
in Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. ...
to the White Cliffs of Dover
The White Cliffs of Dover is the region of English coastline facing the Strait of Dover and France. The cliff face, which reaches a height of , owes its striking appearance to its composition of chalk accented by streaks of black flint, deposi ...
in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB; , AHNE) is an area of countryside in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland, that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Areas are designated in recognition of thei ...
(AONBs): the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs
The Kent Downs is an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) in Kent, England. They are the eastern half of the North Downs and stretch from the London/Surrey borders to the White Cliffs of Dover, including a small section of the London Borough ...
. The North Downs Way
The North Downs Way National Trail is a long-distance path in southern England, opened in 1978. It runs from Farnham to Dover, past Guildford, Dorking, Merstham, Otford and Rochester, along the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty ...
National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham
Farnham ( /ˈfɑːnəm/) is a market town and civil parish in Surrey, England, around southwest of London. It is in the Borough of Waverley, close to the county border with Hampshire. The town is on the north branch of the River Wey, a trib ...
to Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
.
The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill
Botley Hill is a hill in Surrey and is the highest point of the North Downs with a height of . The Prime Meridian crosses the hill.
Geography
Botley Hill is a Marilyn (a hill with topographic prominence of at least 150m), and the third highes ...
, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley
Bromley is a large town in Greater London, England, within the London Borough of Bromley. It is south-east of Charing Cross, and had an estimated population of 87,889 as of 2011.
Originally part of Kent, Bromley became a market town, char ...
, the highest point in Greater London
Greater may refer to:
*Greatness, the state of being great
*Greater than, in inequality (mathematics), inequality
*Greater (film), ''Greater'' (film), a 2016 American film
*Greater (flamingo), the oldest flamingo on record
*Greater (song), "Greate ...
at an elevation of .
Etymology
'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – theSouth Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. ...
– which runs roughly parallel to them but some to the south.
Geography

 The narrow spine of the
The narrow spine of the Hog's Back
The Hog's Back is a hilly ridge, part of the North Downs in Surrey, England. It runs between Farnham in the west and Guildford in the east.
Name
Compared with the main part of the Downs to the east of it, it is a narrow elongated ridge, hence ...
between Farnham and Guildford
Guildford ()
is a town in west Surrey, around southwest of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The name "Guildf ...
forms the western extremity of the North Downs, whilst the cliffs between Folkestone
Folkestone ( ) is a port town on the English Channel, in Kent, south-east England. The town lies on the southern edge of the North Downs at a valley between two cliffs. It was an important harbour and shipping port for most of the 19th and 20t ...
and Deal
A deal, or deals may refer to:
Places United States
* Deal, New Jersey, a borough
* Deal, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* Deal Lake, New Jersey
Elsewhere
* Deal Island (Tasmania), Australia
* Deal, Kent, a town in England
* Deal, ...
terminate the ridge in the east. The North Downs cuesta
A cuesta (from Spanish ''cuesta'' "slope") is a hill or ridge with a gentle slope on one side, and a steep slope on the other. In geology the term is more specifically applied to a ridge where a harder sedimentary rock overlies a softer layer ...
has a steep south-facing scarp slope and a more gentle north-facing dip slope
A dip slope is a topographic (geomorphic) surface which slopes in the same direction, and often by the same amount, as the true dip or apparent dip of the underlying strata.Jackson, JA, J Mehl and K Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology.'' Amer ...
. Its southern boundary is defined by the low-lying Vale of Holmesdale
Holmesdale, also known as the Vale of Holmesdale, is a valley in South-East England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of ...
at the foot of the escarpment, in which the underlying stratum is primarily gault clay
The Gault Formation is a geological formation of stiff blue clay deposited in a calm, fairly deep-water marine environment during the Lower Cretaceous Period (Upper and Middle Albian). It is well exposed in the coastal cliffs at Copt Point in ...
. The northern boundary is less apparent but occurs where the chalk submerges below the more recent Paleocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 mya (unit), million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), E ...
deposits.
The Downs are highest near the Kent–Surrey border, often reaching heights in excess of above sea level at the crest of the escarpment. The highest point is Botley Hill
Botley Hill is a hill in Surrey and is the highest point of the North Downs with a height of . The Prime Meridian crosses the hill.
Geography
Botley Hill is a Marilyn (a hill with topographic prominence of at least 150m), and the third highes ...
in Surrey at . The County top
The mountains and hills of the British Isles are categorised into various lists based on different combinations of elevation, prominence, and other criteria such as isolation. These lists are used for peak bagging, whereby hillwalkers attempt ...
of Kent at Betsom's Hill, with a height of , is nearby, and the highest point in Greater London, Westerham Heights, at , is on the northern side of the same hill. East of the Medway Valley the Downs become broader and flatter, extending as far as the Isle of Thanet
The Isle of Thanet () is a peninsula forming the easternmost part of Kent, England. While in the past it was separated from the mainland by the Wantsum Channel, it is no longer an island.
Archaeological remains testify to its settlement in anc ...
.
The ridge of the North Downs is intersected by the valleys of a series of rivers: the Wey, Mole
Mole (or Molé) may refer to:
Animals
* Mole (animal) or "true mole", mammals in the family Talpidae, found in Eurasia and North America
* Golden moles, southern African mammals in the family Chrysochloridae, similar to but unrelated to Talpida ...
, Darent, Medway
Medway is a unitary authority district and conurbation in Kent, South East England. It had a population of 278,016 in 2019. The unitary authority was formed in 1998 when Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with the Borough of Gillingham to for ...
and Stour. These drain much of the Weald
The Weald () is an area of South East England between the parallel chalk escarpments of the North and the South Downs. It crosses the counties of Hampshire, Surrey, Sussex and Kent. It has three separate parts: the sandstone "High Weald" in the ...
to the south. The western rivers are tributaries of the Thames
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the R ...
; they have carved steep valleys through the chalk and provide natural corridor routes. In addition to existing rivers, the Downs are crossed by a number of wind gap
A wind gap (or air gap) is a gap through which a waterway once flowed that is now dry as a result of stream capture. A water gap is a similar feature, but one in which a waterway still flows. Water gaps and wind gaps often provide routes which ...
s – prehistoric river valleys no longer occupied by rivers – including those at Farnham
Farnham ( /ˈfɑːnəm/) is a market town and civil parish in Surrey, England, around southwest of London. It is in the Borough of Waverley, close to the county border with Hampshire. The town is on the north branch of the River Wey, a trib ...
, Betchworth
Betchworth is a village and civil parish in the Mole Valley district of Surrey, England. The village centre is on the north bank of the River Mole and south of the A25 road, almost east of Dorking and west of Reigate. London is north of the ...
, Caterham
Caterham () is a town in the Tandridge District of Surrey, England. The town is administratively divided into two: Caterham on the Hill, and Caterham Valley, which includes the main town centre in the middle of a dry valley but rises to equal ...
, Lyminge
Lyminge is a village in southeast Kent, England. It lies about five miles (8 km) from Folkestone and the Channel Tunnel, on the road passing through the Elham Valley. At the 2011 Census the population of Etchinghill was included. The N ...
and Hawkinge
Hawkinge ( ) is a town and civil parish in the Folkestone and Hythe district of Kent, England. The original village of Hawkinge is actually just less than a mile (c. 1.3 km) due east of the present village centre; the village of Hawkinge ...
. Except for the river valleys and wind gaps, the crest of the escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escar ...
is almost continuous along its length. The dip slope
A dip slope is a topographic (geomorphic) surface which slopes in the same direction, and often by the same amount, as the true dip or apparent dip of the underlying strata.Jackson, JA, J Mehl and K Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology.'' Amer ...
is dissected by many small dry valley
A dry valley may develop on many kinds of permeable rock, such as limestone and chalk, or sandy terrains that do not regularly sustain surface water flow. Such valleys do not hold surface water because it sinks into the permeable bedrock.
There ...
s, and in the broad eastern part in Kent, by further river valleys such as that of the Little Stour
The Little Stour is one of the tributaries of the River Stour in the English county of Kent. The upper reaches of the river is known as the Nailbourne, whilst the lower reaches were once known as the Seaton Navigation.
The intermittent source ...
.
Leith Hill
Leith Hill in southern England is the highest summit of the Greensand Ridge, approximately southwest of Dorking, Surrey and southwest of Charing Cross, central London. It reaches above mean sea level, above sea level, and is the second highe ...
(the highest point in Surrey) is sometimes incorrectly referred to as part of the North Downs, but it is located on the parallel Greensand Ridge
The Greensand Ridge, also known as the Wealden Greensand is an extensive, prominent, often wooded, mixed greensand/sandstone escarpment in south-east England. Forming part of the Weald, a former dense forest in Sussex, Surrey and Kent, it runs ...
and does not consist of chalk.
Geology
Rock types
TheDownland
Downland, chalkland, chalk downs or just downs are areas of open chalk hills, such as the North Downs. This term is used to describe the characteristic landscape in southern England where chalk is exposed at the surface. The name "downs" is deriv ...
of the North Downs consists of distinct lithostratigraphic
Lithostratigraphy is a sub-discipline of stratigraphy, the geology, geological science associated with the study of stratum, strata or rock layers. Major focuses include geochronology, comparative geology, and petrology.
In general, strata are ...
units (the types of strata, the names of which are always capitalised):
* Shallow layers of ''sand'' and ''gravel'' are associated with areas of heathland, including at Headley Headley may refer to:
Places
* Headley, Basingstoke and Deane in the civil parish of Ashford Hill with Headley
* Headley, East Hampshire
** Headley Grange, Hampshire
* Headley, Surrey
Other uses
* Headley (surname)
* Baron Headley, a title in t ...
and Netley Heaths in Surrey. These deposits have their origin in the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
and indicate the position of the sea shore during this period.
* ''Clay-with-Flints
In geology, clay-with-flints was the name given by William Whitaker in 1861 to a peculiar deposit of stiff red, brown or yellow clay containing unworn whole flints as well as angular shattered fragments, also with a variable admixture of rounded ...
'', a sandy clay with many flints is found on higher ground. The origins of this layer are uncertain, however the clay is thought to have been formed during several periods of glaciation and was produced by cryoturbation
In gelisols ( permafrost soils), cryoturbation (frost churning) refers to the mixing of materials from various horizons of the soil down to the bedrock due to freezing and thawing.
Cryoturbation occurs to varying degrees in most gelisols. The c ...
and decalcification of the chalk. This hypothesis is supported by the presence of flint, which is also found in the underlying strata.
 * The ''
* The ''Chalk Group
The Chalk Group (often just called the Chalk) is the lithostratigraphic unit (a certain number of rock strata) which contains the Upper Cretaceous limestone succession in southern and eastern England. The same or similar rock sequences occur acr ...
'', composed almost entirely of chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk ...
, a soft, fine-grained limestone. These strata have their origins in the late Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
(approximately 100 – 66 million years ago). For the entirety of this period, south east England was covered by a warm, shallow sea in which coccolithophores
Coccolithophores, or coccolithophorids, are single celled organisms which are part of the phytoplankton, the autotrophic (self-feeding) component of the plankton community. They form a group of about 200 species, and belong either to the kingdo ...
, single-celled alga
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mi ...
e with small calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
skeletons, thrived. As the phytoplankton died, their calcium-rich shells were deposited on the sea bed and, over time were compressed to form rock. The chalk of the North Downs is generally divided into three distinct stata: The ''Upper Chalk'', which has many flints; the ''Middle Chalk'', with fewer flints; and the ''Lower Chalk'' or ''Coombe Rock'', greyish, with few flints. The chalk is most commonly exposed on slopes or as cliffs, where the overlying acidic strata have been quarried or washed away. The buried upper surface of the chalk beneath the acidic strata is often eroded into pipes, gulleys and pinnacles, sometimes visible in road cuttings and quarries.
* The ''Upper Greensand
Greensand or green sand is a sand or sandstone which has a greenish color. This term is specifically applied to shallow marine sediment that contains noticeable quantities of rounded greenish grains. These grains are called ''glauconies'' and c ...
Formation'', a whitish, limy sandstone, often used for building, for which it has been mined from beneath the chalk (for example from the Godstone Baby Mines). The Upper Greensand of the North Downs is a thin bed of one or two metres thickness, and it is rarely visible at the surface (it is much thicker elsewhere).
Wealden uplift and erosion
anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the ...
which stretched across the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" (Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), (Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Kana ...
to the Artois region of northern France. Initially an island, this dome-like structure was drained by the ancestors of the rivers which today cut through the North and South Downs. The dome was eroded away over the course of the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
, exposing the strata beneath and resulting in the escarpments of the Downs.
Chalk is a relatively soft rock that may be eroded or weathered in a number of different ways. It is porous, absorbing up to 20% of its dry weight in water, and is therefore highly susceptible to weathering by freeze-thaw action, which may occur over repeated annual or diurnal cycles. This frost weathering produces a mix of rubble and viscous mud, which may be washed downhill, further eroding the landscape (a process known as solifluction
Solifluction is a collective name for gradual processes in which a mass moves down a slope ("mass wasting") related to freeze-thaw activity. This is the standard modern meaning of solifluction, which differs from the original meaning given to it ...
). Since chalk contains a very high percentage of calcium carbonate, it can be dissolved by both groundwater and rainwater.
Across much of the North Downs, the chalk dips below the London Clay
The London Clay Formation is a marine geological formation of Ypresian (early Eocene Epoch, c. 56–49 million years ago) age which crops out in the southeast of England. The London Clay is well known for its fossil content. The fossils from t ...
at a relatively shallow angle (c. 18° near Dorking), however at the far west of the range, local faulting has produced a much steeper angle (up to 55°), resulting in the distinctive Hog's Back
The Hog's Back is a hilly ridge, part of the North Downs in Surrey, England. It runs between Farnham in the west and Guildford in the east.
Name
Compared with the main part of the Downs to the east of it, it is a narrow elongated ridge, hence ...
between Farnham and Guildford.
Ecology
The North Downs support several important habitats includingchalk grassland
Calcareous grassland (or alkaline grassland) is an ecosystem associated with thin basic soil, such as that on chalk and limestone downland. Plants on calcareous grassland are typically short and hardy, and include grasses and herbs such as clove ...
, scrub, woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the ''plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
and chalk heath
Chalk heath is a rare habitat, in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome, formed of a paradoxical mixture of shallow-rooted calcifuge ("calcium-hating") and deeper-rooted calcicole ("calcium-loving") plants, growing on a thin lay ...
.
Chalk grassland
Chalk grassland
Calcareous grassland (or alkaline grassland) is an ecosystem associated with thin basic soil, such as that on chalk and limestone downland. Plants on calcareous grassland are typically short and hardy, and include grasses and herbs such as clove ...
is found on the steep south-facing scarp slopes and the more gently graded north-facing dip slopes, where woodland is absent. The alkaline soils are thin and nutrient poor, which prevents deeper-rooted lush grasses (with a high water demand) from dominating. Each square metre of chalk downland may support up to 40 different species. This semi-natural habitat is maintained through sheep, cattle and rabbit grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and other ...
which prevents scrub encroachment. Chalk grassland to the west of the Medway Valley is dominated by upright brome
''Bromus erectus'', commonly known as erect brome, upright brome or meadow brome, is a dense, course, tufted perennial grass. It can grow to . Like many brome grasses the plant is hairy. The Botanical name#Components of plant names, specific epit ...
and fescue
''Festuca'' (fescue) is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the grass family Poaceae (subfamily Pooideae). They are evergreen or herbaceous perennial tufted grasses with a height range of and a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on every ...
, whilst grassland to the east is dominated by tor-grass
''Brachypodium pinnatum'', the heath false brome or tor-grass, is a species of grass with a widespread distribution in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. It typically grows in calcareous grassland, and reaches tall. The flowerhead is ...
. Owing to the close proximity of the North Downs to the European continent, the warm climate and the south-facing escarpment, several plant species survive on the chalk grassland which are scarce or not found elsewhere in the British Isles.
The nationally rare late spider orchid
''Ophrys holosericea'', the late spider orchid, is a species of flowering plant in the family Orchidaceae, native to western and central Europe and the Mediterranean region. There has been considerable confusion about the identity of this species ...
is limited within the British Isles to chalk grassland between Folkestone
Folkestone ( ) is a port town on the English Channel, in Kent, south-east England. The town lies on the southern edge of the North Downs at a valley between two cliffs. It was an important harbour and shipping port for most of the 19th and 20t ...
and Wye. One of the two native British sites for the nationally rare monkey orchid is on the North Downs. The nationally scarce man orchid
''Orchis anthropophora'' (formerly ''Aceras anthropophorum''), the man orchid, is a European species of orchid whose flowers resemble a human figure. The head is formed by the petals and sepals, and the suspended torso and limbs by the lobes of ...
is not uncommon on chalk grassland on the Downs in Surrey and Kent. Other scarce plant species such as early gentian, dwarf milkwort and bedstraw broomrape also occur on chalk grassland in the North Downs.
Chalk grassland also supports a rich fauna, particularly insects. Notable butterfly species include Adonis blue
The Adonis blue (''Lysandra bellargus'', also known as ''Polyommatus bellargus'') is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It inhabits the Palearctic realm (Western Europe, Central Europe, Southern Europe, Southern Russia, Iraq, Iran, Caucasus, T ...
and silver-spotted skipper, which may be found on warm, sheltered, south-facing slopes. The chalk downland above the Stour Valley is the only British site for the black-veined moth. Other notable moth species that occur on the North Downs include the fiery clearwing moth and the straw belle moth.
Quarries and chalk cliffs
On the summit of the cliffs betweenDeal
A deal, or deals may refer to:
Places United States
* Deal, New Jersey, a borough
* Deal, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* Deal Lake, New Jersey
Elsewhere
* Deal Island (Tasmania), Australia
* Deal, Kent, a town in England
* Deal, ...
and Folkestone the early spider orchid
''Ophrys sphegodes'', commonly known as the early spider-orchid, is a species of sexually-deceptive orchid native to Europe and the Middle East. It is a very varied species with many subspecies recognised.
Description
Plant height varies with l ...
occurs in large numbers, as well as the rare oxtongue broomrape. Naturally exposed chalk is rare inland with the exception of the river cliffs formed by the River Mole
The River Mole is a tributary of the River Thames in southern England. It rises in West Sussex near Gatwick Airport and flows northwest through Surrey for to the Thames at Hampton Court Palace. The river gives its name to the Surrey district ...
on the west face of Box Hill and at Ham Bank in Norbury Park
Norbury Park is a swathe of mixed wooded and agricultural land associated with its Georgian manor house near Leatherhead and Dorking, Surrey, which appears in the Domesday Book of 1086. It occupies mostly prominent land reaching into a bend in th ...
. However, quarry lakes within chalk pits provide habitats for great crested newt
The northern crested newt, great crested newt or warty newt (''Triturus cristatus'') is a newt species native to Great Britain, northern and central continental Europe and parts of Western Siberia. It is a large newt, with females growing up to ...
. The scarce musk orchid
''Herminium monorchis'', the musk orchid, is a commonly occurring species of orchid. It is widespread across much of Europe and northern Asia from France to Japan, including China, Siberia, Mongolia, Ukraine, Germany, Italy, Scandinavia, etc.
It ...
has colonised disused chalk pits near Hollingbourne
Hollingbourne is a village and civil parish in the borough of Maidstone in Kent, England. The parish is located on the southward slope of the North Downs to the east of the county town, Maidstone. The parish population is around 900 and has th ...
in Kent.
Woodland
Woodland was far more extensive on the North Downs prior to human clearance 5000 to 4000 years ago. Fragments still remain particularly where the layer ofclay-with-flints
In geology, clay-with-flints was the name given by William Whitaker in 1861 to a peculiar deposit of stiff red, brown or yellow clay containing unworn whole flints as well as angular shattered fragments, also with a variable admixture of rounded ...
overlying the chalk has inhibited clearance. Where this is the case species such as pedunculate oak
''Quercus robur'', commonly known as common oak, pedunculate oak, European oak or English oak, is a species of flowering plant in the beech and oak family, Fagaceae. It is a large tree, native to most of Europe west of the Caucasus. It is widel ...
predominate, although much woodland has been replanted with conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single ...
and sweet chestnut
''Castanea sativa'', the sweet chestnut, Spanish chestnut or just chestnut, is a species of tree in the family Fagaceae, native to Southern Europe and Asia Minor, and widely cultivated throughout the temperate world. A substantial, long-lived ...
.
dip slope
A dip slope is a topographic (geomorphic) surface which slopes in the same direction, and often by the same amount, as the true dip or apparent dip of the underlying strata.Jackson, JA, J Mehl and K Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology.'' Amer ...
. Calcaerous woodland is typically dominated by beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
, hornbeam
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the flowering plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The 30–40 species occur across much of the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Origin of names
The common English name ''hornbeam' ...
, yew and ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
. Box Hill has one of the largest areas of native box
A box (plural: boxes) is a container used for the storage or transportation of its contents. Most boxes have flat, parallel, rectangular sides. Boxes can be very small (like a matchbox) or very large (like a shipping box for furniture), and can ...
woodland in England. One notable species characteristic of calcaerous woodland is the nationally scarce lady orchid
''Orchis purpurea'', the lady orchid, is a herbaceous plant belonging to the genus ''Orchis'' of the family Orchidaceae.
Description
''Orchis purpurea'' reaches on average of height. The leaves are broad and oblong-lanceolate, forming a ros ...
, which is found in more than 100 sites on the Kent stretch of the North Downs, but is confined to just two sites elsewhere in the UK.
Scrub
Although its spread is often considered undesirable, scrub provides valuable habitat for a range of invertebrates, including theRoman snail
''Helix pomatia'', common names the Roman snail, Burgundy snail, or escargot, is a species of large, edible, air-breathing land snail, a pulmonate gastropod terrestrial mollusc in the family Helicidae.MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. ...
, rufous grasshopper and the dark green fritillary
The dark green fritillary (''Speyeria aglaja'') is a species of butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. The insect has a wide range in the Palearctic realm - Europe, Morocco, Iran, Siberia, Central Asia, China, Korea, and Japan.
Description in Seit ...
.
Chalk heath
In Surrey,superficial deposits
Superficial deposits (or surficial deposits) refer to geological deposits typically of Quaternary age (less than 2.6 million years old). These geologically recent unconsolidated sediments may include stream channel and floodplain deposits, beach ...
from the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
are found overlying the chalk. These sands and gravels indicate the position of a former sea shore. Where these deposits occur, they are thin and the chalk also comes to the surface in the same areas (e.g. Headley Heath on the north east side of Box Hill), allowing acid-loving plants to thrive alongside those that prefer alkaline conditions, producing the rare chalk heath
Chalk heath is a rare habitat, in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome, formed of a paradoxical mixture of shallow-rooted calcifuge ("calcium-hating") and deeper-rooted calcicole ("calcium-loving") plants, growing on a thin lay ...
habitat.
History
Worked flints and human and animal remains dating from theLower Paleolithic
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in ...
, about 400,000 years ago, were discovered at Barnfield Pit
Swanscombe Skull Site or Swanscombe Heritage Park is a geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Swanscombe in north-west Kent, England. It contains two Geological Conservation Review sites and a National Nature Reserve. The park lies ...
near Swanscombe
Swanscombe Help:IPA/English, /ˈswɒnzkəm/ is a village in the Borough of Dartford in Kent, England, and the civil parish of Swanscombe and Greenhithe. It is 4.4 miles west of Gravesend and 4.8 miles east of Dartford.
History
Prehistory
B ...
; this provides the earliest evidence of human occupation in the North Downs. It is suggested that human activity at that time coincided with intermittent warm phases during the last glacial period and that continuous occupation of the Downs did not occur until warming after the glaciation. Flint axes have also been found on river terraces at Farnham, on Walton Walton may refer to:
People
* Walton (given name)
* Walton (surname)
* Susana, Lady Walton (1926–2010), Argentine writer
Places
Canada
* Walton, Nova Scotia, a community
** Walton River (Nova Scotia)
*Walton, Ontario, a hamlet
United Kingdo ...
and Banstead Heaths and on the crest of the escarpment above Folkestone. There is considerable evidence of Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
activity in the Surrey Downs through the discovery of ''pit-dwellings'' at Weston Woods near Albury
Albury () is a major regional city in New South Wales, Australia. It is located on the Hume Highway and the northern side of the Murray River. Albury is the seat of local government for the council area which also bears the city's name – the ...
and the quantity of discarded tools, microliths
A microlith is a small stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 35,000 to 3,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Australia. The ...
and other implements discovered.
 In about 3000 BC the emergence of
In about 3000 BC the emergence of Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
culture saw the lifestyle of the Mesolithic hunter-gatherers shift to a more sedentary and communal lifestyle that relied upon the keeping of livestock and the growing of crops. There is substantial evidence of Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
activity within the North Downs, notably the long barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material repres ...
s concentrated in the Medway and Stour valleys. The Medway long barrows, which include Kit's Coty House
Kit's Coty House or Kit's Coty is a chambered long barrow near the village of Aylesford in the southeastern English county of Kent. Constructed ''circa'' 4000 BCE, during the Early Neolithic period of British prehistory, today it survives in a ...
and Coldrum Stones, are constructed of sarsen stone
Sarsen stones are silicified sandstone blocks found in quantity in Southern England on Salisbury Plain and the Marlborough Downs in Wiltshire; in Kent; and in smaller quantities in Berkshire, Essex, Oxfordshire, Dorset, and Hampshire.
Geology ...
, locally found on Blue Bell Hill and in the valleys of the dip slope, whilst the Stour Valley long barrows are constructed of earth.
Agriculture and industry
 The landscape of the Downs has been greatly shaped by man. There has been
The landscape of the Downs has been greatly shaped by man. There has been deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
of the Downs for centuries. The woodland that remains today is largely located where deforestation has been inhibited by steep slopes or by the layer of clay with flints, which is difficult to plough. Because of the many small farms that have survived on the Downs, a network of narrow lanes and minor roads has developed. This has resulted in a landscape similar to that found in Normandy known as ''bocage
Bocage (, ) is a terrain of mixed woodland and pasture characteristic of parts of Northern France, Southern England, Ireland, the Netherlands and Northern Germany, in regions where pastoral farming is the dominant land use.
''Bocage'' may als ...
''. The predominant type of farming on the Downs is arable farming; this increased greatly during the 20th century. Pastoral farming also occurs but to a lesser extent. Human settlements within the Downs have generally formed in sheltered valleys and at the foot of the scarp slope (known as spring line settlements). In recent years vineyards have been planted along the southern slopes of the Downs, in particular the Denbies Wine Estate
Denbies Wine Estate, near Dorking, Surrey, has the largest vineyard in England, with under vines, representing more than 10 per cent of the plantings in the whole of the United Kingdom. It has a visitors' centre that attracts around 300,000 vis ...
, Dorking
Dorking () is a market town in Surrey in South East England, about south of London. It is in Mole Valley District and the council headquarters are to the east of the centre. The High Street runs roughly east–west, parallel to the Pipp Br ...
, which is the largest vineyard in the country, accounting for 10% of the country's vines. The chalky soils are similar to those of the Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
region.
There is plenty of evidence of chalk extraction on the Downs, particularly along the scarp slope. Oil has been drilled at the foot of the Downs in several locations in Surrey. The Kent Coalfield was established in the late 19th century after coal was found in 1890. Four successful collieries continued to be worked through much of the 20th century: Betteshanger
Betteshanger is a village near Deal in East Kent, England. It gave its name to the largest of the four chief collieries of the Kent coalfield. The population of the village is included in the civil parish of Northbourne.
Before the coal mine
...
, Snowdown
Snowdown is a hamlet near Dover in Kent, England. It was the location of one of the four chief collieries of the Kent coalfield, which closed in 1987.
The population of the village is included in the civil parish
In England, a civil pari ...
, Tilmanstone
Tilmanstone is a small village and civil parish in Kent, in the South East of England, near Eastry, a much bigger and more developed area. Tilmanstone no longer has a village school; however, the independent Northbourne Park School is close to the ...
and Chislet
Chislet is an English village and civil parish in northeast Kent between Canterbury and the Isle of Thanet. The parish is the second largest in the district. A former spelling, 'Chistlet', is seen in 1418. The population of the civil parish incl ...
; Bettershanger was the last to close in 1989. The east to west ridge of the Downs has provided a natural transport route for centuries. Much of the historic Pilgrims' Way
The Pilgrims' Way (also Pilgrim's Way or Pilgrims Way) is the historical route supposedly taken by pilgrims from Winchester, Hampshire, Winchester in Hampshire, England, to the shrine of Thomas Becket at Canterbury in Kent. This name, of compa ...
still survives at the foot of the scarp slope, and this has been joined much more recently by the M20 motorway
The M20 is a motorway in Kent, England. It follows on from the A20 at Swanley, meeting the M25, and continuing on to Folkestone, providing a link to the Channel Tunnel and the ports at Dover. It is long. Although not signposted in England, ...
. The scarp slope has also been used for fortification; many examples of this still exist, such as Thurnham Castle and on Castle Hill, Folkestone Castle Hill near Folkestone.
Places of interest
Many beauty spots on the North Downs are owned by theNational Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
, for instance Box Hill and Langdon Cliffs. Other areas of interest are Newland's Corner, Wye Downs
Wye and Crundale Downs is a biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in a number of separate areas east of Ashford in Kent. It is a Special Area of Conservation and a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I. and it is pa ...
and the Hog's Back
The Hog's Back is a hilly ridge, part of the North Downs in Surrey, England. It runs between Farnham in the west and Guildford in the east.
Name
Compared with the main part of the Downs to the east of it, it is a narrow elongated ridge, hence ...
. Much chalk grassland and ancient woodland on the Downs is open-access, and there are also many historic sites such as Kit's Coty House
Kit's Coty House or Kit's Coty is a chambered long barrow near the village of Aylesford in the southeastern English county of Kent. Constructed ''circa'' 4000 BCE, during the Early Neolithic period of British prehistory, today it survives in a ...
(near Maidstone) and Dover Castle
Dover Castle is a medieval castle in Dover, Kent, England and is Grade I listed. It was founded in the 11th century and has been described as the "Key to England" due to its defensive significance throughout history. Some sources say it is the ...
.
Hills
The topography of the North Downs means there are relatively few summits with topographic prominence. Below is a list of summits on the North Downs which are more than 180 metres in height with 30 metres of topographic prominence (a commonly used threshold in Britain). The summits are arranged in order along the range, from west to east.Photo gallery
Wye Downs
Wye and Crundale Downs is a biological and geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in a number of separate areas east of Ashford in Kent. It is a Special Area of Conservation and a Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I. and it is pa ...
National Nature Reserve
File:View over Hollingbourne Downs(SSSI), Kent, UK.jpg, The North Downs above Hollingbourne
Hollingbourne is a village and civil parish in the borough of Maidstone in Kent, England. The parish is located on the southward slope of the North Downs to the east of the county town, Maidstone. The parish population is around 900 and has th ...
.
Image:NorthDownsWayStoneSign9948.JPG, A marker on the North Downs Way
The North Downs Way National Trail is a long-distance path in southern England, opened in 1978. It runs from Farnham to Dover, past Guildford, Dorking, Merstham, Otford and Rochester, along the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty ...
, Ranscombe Farm, Medway, Ranscombe Farm, Cuxton, Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
Image:BluebellWood9923Ranscombe.JPG, Bluebell wood, Bluebells at Ranscombe Farm
Image:Downs with Cloud 0177.JPG, Looking East, typical downland scenery in the Medway Gap, Ranscombe Farm
Image:Dry Valley, Hucking 1.jpg, A dry valley
A dry valley may develop on many kinds of permeable rock, such as limestone and chalk, or sandy terrains that do not regularly sustain surface water flow. Such valleys do not hold surface water because it sinks into the permeable bedrock.
There ...
on the dip slope
A dip slope is a topographic (geomorphic) surface which slopes in the same direction, and often by the same amount, as the true dip or apparent dip of the underlying strata.Jackson, JA, J Mehl and K Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology.'' Amer ...
of the North Downs near Hucking
Image:North Downs woodland at Hucking.JPG, Woodland on the North Downs at the Hucking Estate
Image:NorthDownsWayTrail.jpg, Typical chalk downland trail near Hollingbourne
Hollingbourne is a village and civil parish in the borough of Maidstone in Kent, England. The parish is located on the southward slope of the North Downs to the east of the county town, Maidstone. The parish population is around 900 and has th ...
Image:North Downs Way.jpg, A modern metal trail marker near Harrietsham
Image:WealdfromDowns.JPG, A view South across the Kent Weald from the North Downs Way near Detling
See also
*Chalk figures in the United Kingdom *Geology of the United Kingdom *North Downs Way
The North Downs Way National Trail is a long-distance path in southern England, opened in 1978. It runs from Farnham to Dover, past Guildford, Dorking, Merstham, Otford and Rochester, along the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty ...
*Downland
Downland, chalkland, chalk downs or just downs are areas of open chalk hills, such as the North Downs. This term is used to describe the characteristic landscape in southern England where chalk is exposed at the surface. The name "downs" is deriv ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * *External links
KentDowns AONB site
{{coord, 51, 16, N, 0, 30, W, display=title, region:GB_type:mountain_source:GNS-enwiki Geology of England Hills of Kent Hills of Surrey Hills of Hampshire Borough of Ashford Natural regions of England Chalk landforms