|
Ljubomir Micić
Ljubomir Micić ( sr-cyr, Љубомир Мицић, 15 November 1895 – 14 June 1971) was a Serbian poet, writer, critic, editor and actor. He was the founder of the avant-garde movement Zenitism and its magazine ''Zenit''. Both he and his brother, Branko Ve Poljanski became prominent ''avant-garde'' artists. Biography He studied philosophy at University of Zagreb. He founded the review ''Zenit'', set up a Zenit Gallery and published his own writings and other authors under the Zenit imprint. Zenit was active from February 1921 until April 1924 in Zagreb, and afterward in Belgrade from 1924 until late 1926 with a total of 43 editions. The first artist to collaborate with Micić and to contribute to Zenit's orientation towards Expressionism was Vilko Gecan. Micić's Zenitism was supported by a small number of younger Yugoslav artists, namely Mihajlo Petrov, Vasa Pomorišac, Jovan Bijelić, Petar Dobrović, Ivan Radović. Micić worked on collecting and exhibiting avant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jastrebarsko
Jastrebarsko (; hu, Jaska), colloquially known as Jaska, is a town in Zagreb County, Croatia. History Antiquity In 1865, remnants of a Roman settlement were uncovered in Repišće, Klinča Sela, a village in Jastrebarsko metropolitan area. Further archeological investigation in the late 20th century classified them as a villa rustica and a necropolis consisting of six tumuli, both dating to the early Roman Empire period. The remnants are deemed to be the westernmost group of Noric-Pannonian tumuli and they make a very rare occasion of tombstones located directly on top of tumuli, which is in the rest of Croatia recorded only in Donji Čehi. The location of this archeological site on the fluvial terraces of the local Konjava stream is attributed to the peaceful state of the central Roman Empire, which in turn led to formation of settlements in river valleys. PDF, 121 KB Sveta Marija pod Okićem ( en, Saint Mary under Okić) (locally nicknamed Grič), an archeological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jovan Bijelić
Jovan Bijelić ( sr-cyr, Јован Бијелић ( – 12 March 1964) was a painter and academic. Bijelić is one of the most important representatives of color expressionism in Yugoslavia. The Department of Fine Arts and Music of the Serbian Academy of Sciences in Belgrade elected Bijelić as a full member on 5 December 1963.Review of international affairs: Volume 5; Volume 5 Savez novinara Jugoslavije, Socijalistički savez radnog naroda Jugoslavije, Savez udruženja novinara – 1954 "the teacher of the "middle generation", Jovan Bijelic, with his rich palette." Bijelić is included on The 100 most prominent Serbs ''The 100 most prominent Serbs'' ( sr-Cyrl, 100 најзнаменитијих Срба) is a book containing the biographies of the hundred most important Serbs compiled by a committee of academicians at the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts. ... list. Gallery Jovan Bijelić 1969 Yugoslavia stamp.jpg, Jovan Bijelić 2009 Serbian stamp.jpg, Jovan Bijelić ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constructivism (art)
Constructivism is an early twentieth-century art movement founded in 1915 by Vladimir Tatlin and Alexander Rodchenko. Abstract and austere, constructivist art aimed to reflect modern industrial society and urban space. The movement rejected decorative stylization in favor of the industrial assemblage of materials. Constructivists were in favour of art for propaganda and social purposes, and were associated with Soviet socialism, the Bolsheviks and the Russian avant-garde. Constructivist architecture and art had a great effect on modern art movements of the 20th century, influencing major trends such as the Bauhaus and De Stijl movements. Its influence was widespread, with major effects upon architecture, sculpture, graphic design, industrial design, theatre, film, dance, fashion and, to some extent, music. Beginnings Constructivism was a post-World War I development of Russian Futurism, and particularly of the 'counter reliefs' of Vladimir Tatlin, which had been exhibited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Avant-garde
The Russian avant-garde was a large, influential wave of avant-garde modern art that flourished in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union, approximately from 1890 to 1930—although some have placed its beginning as early as 1850 and its end as late as 1960. The term covers many separate, but inextricably related, art movements that flourished at the time; including Suprematism, Constructivism, Russian Futurism, Cubo-Futurism, Zaum and Neo-primitivism. Many of the artists who were born, grew up or were active in what is now Belarus and Ukraine (including Kazimir Malevich, Aleksandra Ekster, Vladimir Tatlin, Wassily Kandinsky, David Burliuk, Alexander Archipenko), are also classified in the Ukrainian avant-garde. The Russian avant-garde reached its creative and popular height in the period between the Russian Revolution of 1917 and 1932, at which point the ideas of the avant-garde clashed with the newly emerged state-sponsored direction of Socialist Realism. Artists and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Filippo Tommaso Marinetti
Filippo Tommaso Emilio Marinetti (; 22 December 1876 – 2 December 1944) was an Italian poet, editor, art theorist, and founder of the Futurist movement. He was associated with the utopian and Symbolist artistic and literary community Abbaye de Créteil between 1907 and 1908. Marinetti is best known as the author of the first ''Futurist Manifesto'', which was written and published in 1909, and as a co-author of the Fascist Manifesto, in 1919. Childhood and adolescence Emilio Angelo Carlo Marinetti (some documents give his name as "Filippo Achille Emilio Marinetti") spent the first years of his life in Alexandria, Egypt, where his father (Enrico Marinetti) and his mother (Amalia Grolli) lived together ''more uxorio'' (as if married). Enrico was a lawyer from Piedmont, and his mother was the daughter of a literary professor from Milan. They had come to Egypt in 1865, at the invitation of Khedive Isma'il Pasha, to act as legal advisers for foreign companies that were taking part i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Futurism
Futurism ( it, Futurismo, link=no) was an artistic and social movement that originated in Italy, and to a lesser extent in other countries, in the early 20th century. It emphasized dynamism, speed, technology, youth, violence, and objects such as the car, the airplane, and the industrial city. Its key figures included the Italians Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, Umberto Boccioni, Carlo Carrà, Fortunato Depero, Gino Severini, Giacomo Balla, and Luigi Russolo. Italian Futurism glorified modernity and according to its doctrine, aimed to liberate Italy from the weight of its past. Important Futurist works included Marinetti's 1909 ''Manifesto of Futurism'', Boccioni's 1913 sculpture ''Unique Forms of Continuity in Space'', Balla's 1913–1914 painting '' Abstract Speed + Sound'', and Russolo's ''The Art of Noises'' (1913). Although Futurism was largely an Italian phenomenon, parallel movements emerged in Russia, where some Russian Futurists would later go on to found groups of their o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
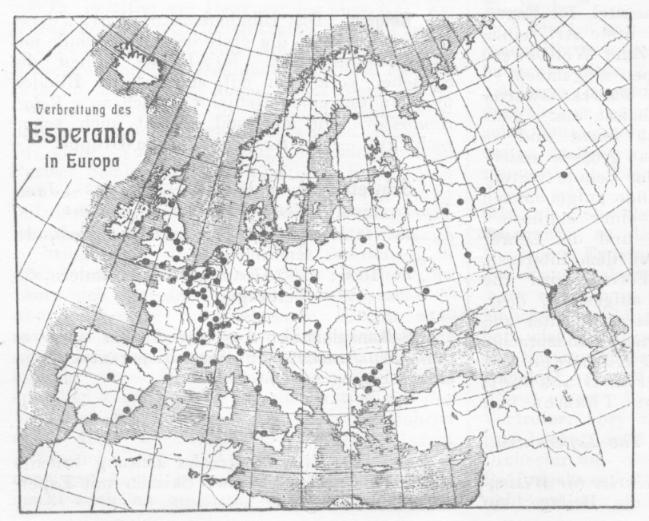
Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communication, or "the international language" (). Zamenhof first described the language in '' Dr. Esperanto's International Language'' (), which he published under the pseudonym . Early adopters of the language liked the name ''Esperanto'' and soon used it to describe his language. The word translates into English as "one who hopes". Within the range of constructed languages, Esperanto occupies a middle ground between "naturalistic" (imitating existing natural languages) and ''a'priori'' (where features are not based on existing languages). Esperanto's vocabulary, syntax and semantics derive predominantly from languages of the Indo-European group. The vocabulary derives primarily from Romance languages, with substantial contributions from Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dušan Matić
Dušan Matić (Serbian Cyrillic: Душан Матић; 31 August 1898 – 12 September 1980) was a Serbian poet who was active as part of the Belgrade surrealist group. Biography Early life Dušan Matić was born on 31 August 1898 in Ćuprija. His father was a civil servant from Jagodina, and his mother was from Kruševac. Due to his father's occupation, the Matić family moved frequently, spending time in Pirot, Čačak, Niš and Šabac. Just as he had started attending school in Šabac in 1912, the First Balkan War erupted. His family home was destroyed in the early days of World War I, after which the Matić family moved to Kruševac to stay with the family of Dušan's mother. At the age of 16, Matić published his first poetry in the Serbian Social Democratic Party aligned ''Radničke novine'' (The Workers' Journal) under the ''nom de plume'' Uroš Jovanović. In 1915, Matić followed his father in the Great Retreat, eventually departing from Durrës. Moving from Messina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastko Petrović
Rastko Petrović (1898-1949) was a Serbian poet and writer. After serving in the Serbian Army in World War I, he studied law in Paris and became a diplomat. Based at the Yugoslav embassy in Washington, D.C. during World War II, he remained in the United States after the war and died there in 1949. In 1986, after official recognition, his remains were brought to Belgrade Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a .... Works * ''Burleska gospodina Peruna, boga groma'' (A burlesque of Lord Perun, god of thunder), 1921. * ''Otkrovenje'' (Revelation), 1922. * ''Afrika'', 1930. * ''Ljudi Govore'' (The people speak), 1931. * ''Dan šesti'' (The sixth day), 1961. References External linksTranslated works by Rastko Petrović 1898 births 1949 deaths Photographers from Belgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanislav Vinaver
Stanislav Vinaver ( sr-Cyrl, Станислав Винавер; 1 March 1891 – 1 August 1955) was a Serbian writer, poet, translator and journalist. Vinaver was born to affluent Ashkenazi Jews, Ashkenazi Jewish parents that had immigrated to Serbia from Poland in the late 19th century. He studied at the University of Paris, volunteered to fight in the Balkan Wars and later took part in World War I as an officer in the Royal Serbian Army. In 1915, he lost his father to typhus. He travelled to France and the United Kingdom the following year, delivering lectures about Serbia and its people. In 1917, he was assigned to the Serbian consulate in Saint Petersburg, Petrograd, where he was to witness the Russian Revolution and its aftermath. Following World War I, Vinaver briefly worked for the Ministry of Education of the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (later Kingdom of Yugoslavia, Yugoslavia). In the 1930s, he worked for Radio Belgrade and was appointed chief of Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_by_Wassily_Kandinsky.jpg)