|
Lithobolos
A lithobolos () refers to any mechanical Greek and Roman artillery, artillery weapon used and/or referred to as a stone thrower in ancient warfare. Typically this referred to engines that propel a stone along a flat track with two rigid bow arms powered by torsion (twisted cord), in particular all sizes of palintonon. However, Charon of Magnesia referred to his flexion (bow) stone-thrower engine, a gastraphetes shooting 5–6 Mina (unit), mina (), as a lithobolos; Isidoros of Abydos reportedly built a larger version shooting . Also, the euthytonon, a single-arm torsion catapult, was referred to by contemporaries as a stone-thrower, as was its Roman evolution the onager (weapon), onager. Stone-throwers of the same class looked alike, with their stone capacity scaling mostly with overall size. Machine dimensions can be approximated mathematically based on the equivalent spring diameter. History Buddhist texts record that King Ajatashatru of Magadha as having commissioned stone-t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek And Roman Artillery
The Greeks and Romans both made extensive use of artillery for shooting large arrows, bolts or spherical stones or metal balls. Occasionally they also used ranged early thermal weapons. There was heavy siege artillery, but more mobile and lighter field artillery was already known and used in pitched battles, especially in Roman imperial period. The technology was developed quite rapidly, from the earliest gastraphetes in about 399 BC to the most advanced torsion artillery in about 300 BC at the time of Demetrius Polyiorcetes. No improvement, except in details, was ever made upon the catapults of Demetrius. The Romans obtained their knowledge from the Greeks, and employed the Greek specialists. Five Greek and Roman sources have survived: two treatises by Heron of Alexandria, ''Belopoeika'' and ''Cheiroballistra''; and the books by Biton of Pergamon, Philo of Byzantium and Vitruvius File:Gastraphetes - Biton's catapult - catapulta di Bitone.jpg, Greek non-torsion siege crossbow (' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the Roman conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year, which eliminated the last major Hellenistic kingdom. Its name stems from the Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás''), which was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the modern historiographical term ''Hellenistic'' was derived. The term "Hellenistic" is to be distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all the ancient territories of the period that had come under significant Greek influence, particularly the Hellenized Middle East, after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian conquest of the Achaemenid Empire in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zopyrus Of Tarentum
Zopyrus (; ) (died 484/3 BC) was a Persian nobleman mentioned in Herodotus' ''Histories''. He was son of Megabyzus I, who helped Darius I in his ascension. According to Herodotus, when Babylon revolted against the rule of Darius I, Zopyrus devised a plan to regain control of the vital city. By cutting off his own nose and ears, and then having himself whipped, he arrived at the court of Darius. Upon presenting himself to Darius, the king stood up from his throne, shocked at the state of Zopyrus, and asked who had done this to him. Zopyrus then said that he had mutilated himself. Darius asked "Are you fool enough to think that the mutilation of your body can hasten our victory? When you did that to yourself you must have taken leave of your senses." At this Zopyrus explained his plan, he would go before the people of Babylon and proclaim himself an exile and deserter of the Persian army punished by Darius himself. Seeing that the mutilation had already been done, Darius agreed an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attic Talent
The Attic talent (a talent of the Attic standard), also known as the Athenian talent or Greek talent (, ''talanton''), is an ancient unit of weight equal to about , as well as a unit of value equal to this amount of pure silver.The exact mass of a talent was 25.992kg. Herodotus, Robin Waterfield and Carolyn Dewald, ''The Histories'' (1998), p. 593. A talent was originally intended to be the mass of water required to fill an amphora, about .Talent (Biblical Hebrew), Unit of Measure ''unitconversion.org''. History The earliest known Athenian coins range between the years of 545 BC to 515 BC. However, Athenians had already adopted the |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenistic Sicily, Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, based on his surviving work, he is considered one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity, and one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and mathematical analysis, analysis by applying the concept of the Cavalieri's principle, infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove many geometry, geometrical theorem, theorems, including the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Archimedes' other math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Syracuse (214–212 BCE)
A siege () . is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy. A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender (military), surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment (military), investment"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engines, artillery bombardment, mining (military), mining (also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
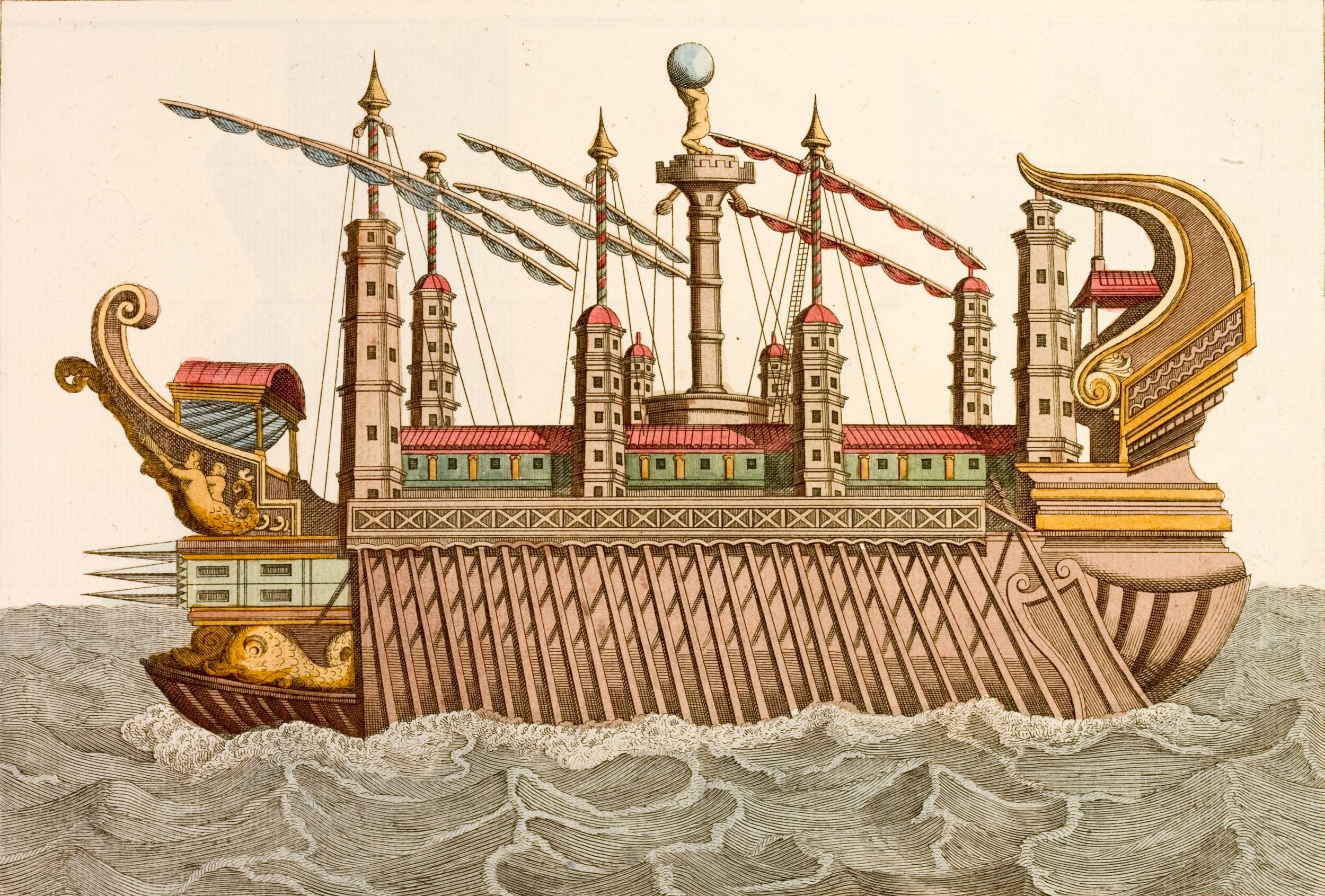
Syracusia
''Syracusia'' (, ''syrakousía'', literally "of Syracuse") was an ancient Greek ship sometimes claimed to be the largest transport ship of antiquity. She was reportedly too big for any port in Sicily, and thus only sailed once from Syracuse in Sicily to Alexandria in the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, whereupon she was given as a present to Ptolemy III Euergetes. The exact dimension of Syracusia is unknown; Michael Lahanas put it at 55 m long, 14 m wide, and 13 m high. General characteristics ''Syracusia'' was designed by Archimedes and built around 240 BC by Archias of Corinth on the orders of Hieron II of Syracuse. The historian Moschion of Phaselis said that ''Syracusia'' could carry a cargo of some 1600 to 1800 tons and a capacity of 1,942 passengers. She reputedly bore more than 200 soldiers, as well as a catapult. She sailed only once to berth in Alexandria, where she was later given to Ptolemy (Ptolemaios) III Euergetes of Egypt and renamed ''Alexandreia'' (, literally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Salamis (306 BCE)
The naval Battle of Salamis in 306 BC took place off Salamis, Cyprus between the fleets of Ptolemy I of Egypt and Antigonus I Monophthalmus, two of the Diadochi, the generals who, after the death of Alexander the Great, fought each other for control of his empire. Cyprus had been seized by Ptolemy, and was used as a base for operations against the Antigonid territories in Asia Minor and the Levant. In 306 BC, Antigonus sent his son Demetrius to invade the island, which was defended by Ptolemy's brother Menelaus. After landing on the northeastern part of the island, Demetrius marched to Salamis, defeated Menelaus in a battle, and laid siege to the city. This was the first time where Demetrius demonstrated his flair for siege warfare, which would later earn him the sobriquet Poliorcetes, "the Besieger". Nevertheless, Menelaus was able to hold off Demetrius' attacks until the arrival of reinforcements. Ptolemy led a large-scale rescue expedition in person, hoping to catch Demetriu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissance as the first book on architectural theory, as well as a major source on the canon of classical architecture. It is not clear to what extent his contemporaries regarded his book as original or important. He states that all buildings should have three attributes: , , and ("strength", "utility", and "beauty"), principles reflected in much Ancient Roman architecture. His discussion of perfect proportion in architecture and the human body led to the famous Renaissance drawing of the ''Vitruvian Man'' by Leonardo da Vinci. Little is known about Vitruvius' life, but by his own descriptionDe Arch. Book 1, preface. section 2. he served as an artilleryman, the third class of arms in the Roman military offices. He probably served as a senior of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; ), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greece, ancient Greek city in Aeolis. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north side of the river Caicus (modern-day Bakırçay) and northwest of the modern city of Bergama, Turkey. During the Hellenistic period, it became the capital of the Kingdom of Pergamon in 281–133 BC under the Attalid dynasty, who transformed it into one of the major cultural centres of the Greek world. Many remains of its monuments can still be seen and especially the masterpiece of the Pergamon Altar. Pergamon was the northernmost of the seven churches of Asia cited in the New Testament Book of Revelation. The city is centered on a mesa of andesite, which formed its acropolis. This mesa falls away sharply on the north, west, and east sides, but three natural terraces on the south side provide a route up to the top. To the west of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. It became the capital city of the civilization of Ancient Carthage and later Roman Carthage. The city developed from a Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic people, Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Elissa, Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, Lebanon, Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. In the myth, Dido asked for land from a local tribe, which told her that she could get as much land as an oxhide could cover. She cut the oxhide into strips and laid out the perimeter of the new city. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Rhodes (305 BC)
Siege of Rhodes may refer to one of the following sieges of the island of Rhodes: * Siege of Rhodes (305–304 BC), by Demetrius I of Macedon * Siege of Rhodes (88 BC), siege by Mithridates VI of Pontus in the First Mithridatic War * Hospitaller conquest of Rhodes (1306–1310), the Knights Hospitaller invade Rhodes except for the city of Rhodes * Siege of Rhodes (1444), unsuccessful attempt by the Mamluks under Aynal Gecut to expel the Knights Hospitaller from the island * Siege of Rhodes (1480), first, unsuccessful attempt by the Ottoman Empire to expel the Knights Hospitaller from the island * Siege of Rhodes (1522) The siege of Rhodes of 1522 was the second and ultimately successful attempt by the Ottoman Empire to expel the Knights of Rhodes from their island stronghold and thereby secure Ottoman control of the Eastern Mediterranean. The first siege i ..., second, successful attempt by the Ottoman Empire to expel the Knights Hospitaller from the island * Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |