|
List Of AMD CPU Microarchitectures
The following is a list of AMD CPU microarchitectures. Nomenclature Historically, AMD's CPU families were given a "K-number" (which originally stood for Kryptonite, an allusion to the Superman comic book character's fatal weakness) starting with their first internal x86 CPU design, the K5, to represent generational changes. AMD has not used K-nomenclature codenames in official AMD documents and press releases since the beginning of 2005, when ''K8'' described the Athlon 64 processor family. AMD now refers to the codename K8 processors as the ''Family 0Fh'' processors. 10h and 0Fh refer to the main result of the CPUID x86 processor instruction. In hexadecimal numbering, 0F(h) (where the ''h'' represents hexadecimal numbering) equals the decimal number 15, and 10(h) equals the decimal number 16. (The "K10h" form that sometimes pops up is an improper hybrid of the "K" code and ''Family XXh'' identifier number.) The Family hexadecimal identifier number can be determined for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Micro Devices
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactured its own processors, the company later outsourced its manufacturing, a practice known as going fabless, after GlobalFoundries was spun off in 2009. AMD's main products include microprocessors, motherboard chipsets, embedded processors, graphics processors, and FPGAs for servers, workstations, personal computers, and embedded system applications. History First twelve years Advanced Micro Devices was formally incorporated by Jerry Sanders, along with seven of his colleagues from Fairchild Semiconductor, on May 1, 1969. Sanders, an electrical engineer who was the director of marketing at Fairchild, had, like many Fairchild executives, grown frustrated with the increasing lack of support, opportunity, and flexibility within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bobcat (microarchitecture)
The AMD Bobcat Family 14h is a microarchitecture created by AMD for its AMD APUs, aimed at a low-power/low-cost market. It was revealed during a speech from AMD executive vice-president Henri Richard in Computex 2007 and was put into production Q1 2011. One of the major supporters was executive vice-president Mario A. Rivas who felt it was difficult to compete in the x86 market with a single core optimized for the 10–100 W range and actively promoted the development of the simpler core with a target range of 1–10 W. In addition, it was believed that the core could migrate into the hand-held space if the power consumption can be reduced to less than 1 W. ''Bobcat'' cores are used together with GPU cores in accelerated processing units (APUs) under the "''Fusion''" brand. A simplified architecture diagram was released at AMD's Analyst Day in November 2009. This is similar in concept with earlier AMD research in 2003,AMD 2003 Microprocessor Forum SlidesSlide 11an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeware
Freeware is software, most often proprietary, that is distributed at no monetary cost to the end user. There is no agreed-upon set of rights, license, or EULA that defines ''freeware'' unambiguously; every publisher defines its own rules for the freeware it offers. For instance, modification, redistribution by third parties, and reverse engineering are permitted by some publishers but prohibited by others. Unlike with free and open-source software, which are also often distributed free of charge, the source code for freeware is typically not made available. Freeware may be intended to benefit its producer by, for example, encouraging sales of a more capable version, as in the freemium and shareware business models. History The term ''freeware'' was coined in 1982 by Andrew Fluegelman, who wanted to sell PC-Talk, the communications application he had created, outside of commercial distribution channels. Fluegelman distributed the program via a process now termed '' shareware''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen 4
Zen 4 is the codename for a CPU microarchitecture by AMD, released on September 27, 2022. It is the successor to Zen 3 and uses TSMC's N5 process for CCDs. Zen 4 powers Ryzen 7000 mainstream desktop processors (codenamed "Raphael") and will be used in high-end mobile processors (codenamed "Dragon Range"), thin & light mobile processors (codenamed "Phoenix"), as well as Epyc 9004 server processors (codenamed "Genoa" and "Bergamo"). Features Like its predecessor, Zen 4 in its Desktop Ryzen variants features one or two Core Complex Dies (CCDs) built on TSMC's 5 nm process and one I/O die built on 6 nm. Previously, the I/O die on Zen 3 was built on GlobalFoundries' 14 nm process. Zen 4's I/O die includes integrated RDNA 2 graphics for the first time on any Zen architecture. Zen 4 marks the first utilization of the 5 nm process for x86-based desktop processors. On desktop and server platforms, Zen 4 has moved from DDR4 to DDR5 memory; DDR4 is not supported. Addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
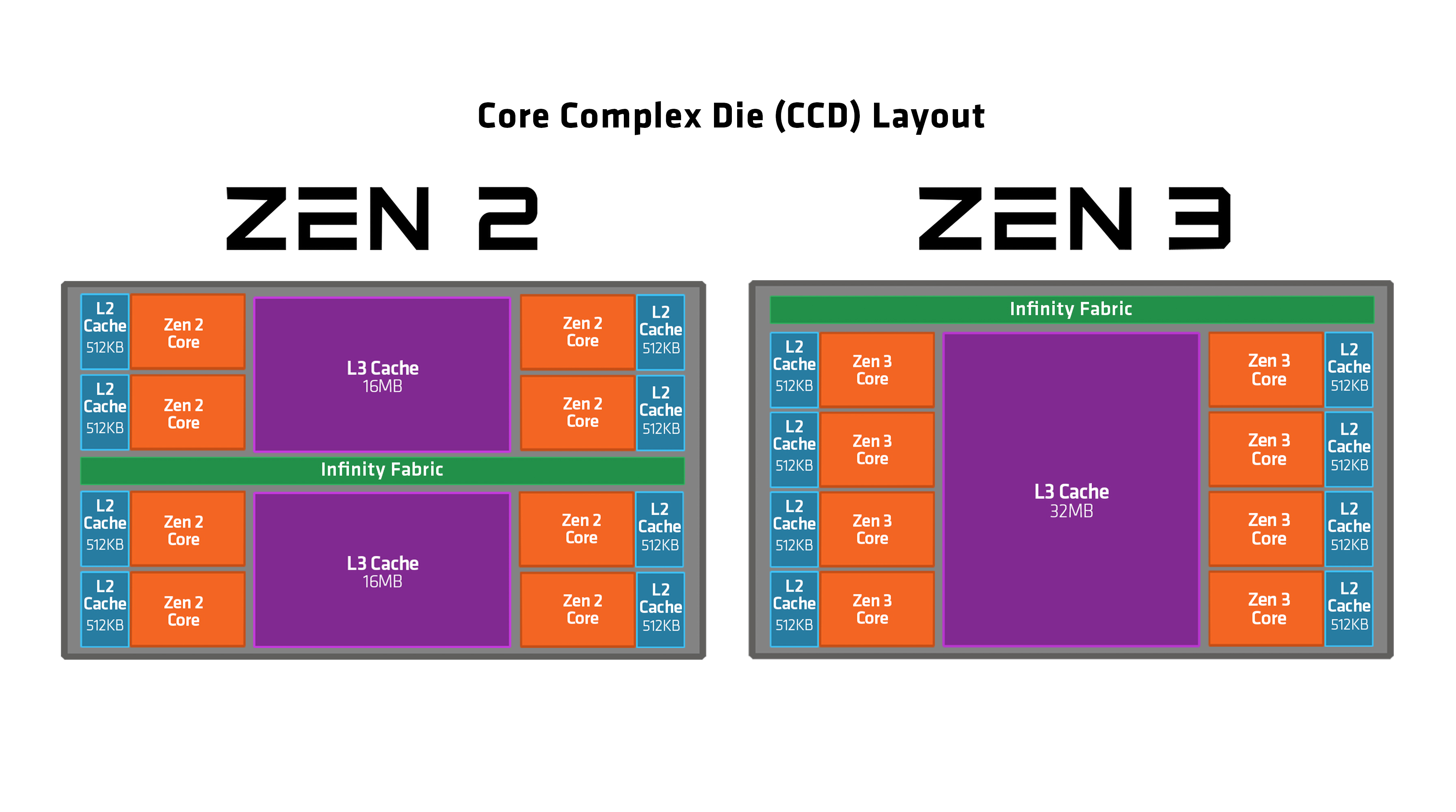
Zen 3
Zen 3 is the codename for a CPU microarchitecture by AMD, released on November 5, 2020. It is the successor to Zen 2 and uses TSMC's 7 nm process, 7 nm process for the chiplets and GlobalFoundries's 14 nm process, 14 nm process for the I/O die on the server chips and 12 nm for desktop chips. Zen 3 powers Ryzen 5000 mainstream desktop processors (codenamed "Vermeer") and Epyc server processors (codenamed "Milan"). Zen 3 is supported on motherboards with List of AMD chipsets#AM4 chipsets, 500 series chipsets; 400 series boards also saw support on select B450 / X470 motherboards with certain BIOSes. Zen 3 is expected to be the last microarchitecture before AMD switches to DDR5 memory and new sockets. According to AMD, Zen 3 has a 19% higher instructions per cycle (IPC) on average than Zen 2. On April 1, 2022, AMD released the new Ryzen 6000 series for the laptop, using an improved "Zen 3+" architecture, bringing RDNA 2 graphics integrated in a APU to the PC for the first time. On Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygon Dhyana
Epyc is a brand of multi-core x86-64 microprocessors designed and sold by AMD, based on the company's Zen microarchitecture. Introduced in June 2017, they are specifically targeted for the server and embedded system markets. Epyc processors share the same microarchitecture as their regular desktop-grade counterparts, but have enterprise-grade features such as higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, and larger cache memory. They also support multi-chip and dual-socket system configurations by using the Infinity Fabric interconnect. History In March 2017, AMD announced plans to re-enter the server market with a platform based on the Zen microarchitecture, codenamed Naples, and officially revealed it under the brand name Epyc in May. That June, AMD officially launched Epyc 7001 series processors, offering up to 32 cores per socket, and enabling performance that allowed Epyc to be competitive with the competing Intel Xeon product line. Two years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen 2
Zen 2 is a computer processor microarchitecture by AMD. It is the successor of AMD's Zen and Zen+ microarchitectures, and is fabricated on the 7 nanometer MOSFET node from TSMC. The microarchitecture powers the third generation of Ryzen processors, known as Ryzen 3000 for the mainstream desktop chips (codename "Matisse"), Ryzen 4000U/H (codename "Renoir") and Ryzen 5000U (codename "Lucienne") for mobile applications, as Threadripper 3000 for high-end desktop systems, and as Ryzen 4000G for accelerated processing units (APUs). The Ryzen 3000 series CPUs were released on 7 July 2019, while the Zen 2-based Epyc server CPUs (codename "Rome") were released on 7 August 2019. An additional chip, the Ryzen 9 3950X, was released in November 2019. At CES 2019, AMD showed a Ryzen third-generation engineering sample that contained one chiplet with eight cores and 16 threads. AMD CEO Lisa Su also said to expect more than eight cores in the final lineup. At Computex 2019, AMD revealed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen+
Zen+ is the codename for a computer processor microarchitecture by AMD. It is the successor to the first gen Zen microarchitecture, first released in April 2018, powering the second generation of Ryzen processors, known as Ryzen 2000 for mainstream desktop systems, Threadripper 2000 for high-end desktop setups and Ryzen 3000G (instead of 2000G) for accelerated processing units (APUs). Features Zen+ uses GlobalFoundries' 12 nm fabrication process, an optimization of the 14 nm process used for Zen, with only minor design rule changes. This means that the die sizes between Zen and Zen+ are identical as AMD chose to use the new smaller transistors to increase the amount of empty space, or "dark silicon", between the various features on the die. This was done to improve power efficiency & reduce thermal density to allow for higher clock speeds, rather than design an entirely new floorplan for a physically smaller die (which would have been significantly more work and thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zen (microarchitecture)
Zen is the codename for a family of computer processor microarchitectures from AMD, first launched in February 2017 with the first generation of its Ryzen CPUs. It is used in Ryzen (desktop and mobile), Ryzen Threadripper (workstation/high end desktop), and Epyc (server). Comparison History First generation The first generation Zen was launched with the Ryzen 1000 series of CPUs (codenamed Summit Ridge) in February 2017. The first Zen-based preview system was demonstrated at E3 2016, and first substantially detailed at an event hosted a block away from the Intel Developer Forum 2016. The first Zen-based CPUs reached the market in early March 2017, and Zen-derived Epyc server processors (codenamed "Naples") launched in June 2017 and Zen-based APUs (codenamed "Raven Ridge") arrived in November 2017. This first iteration of Zen utilized Global Foundries' 14 nm manufacturing process. First generation refresh Zen+ was first released in April 2018, powering the second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puma (microarchitecture)
The Puma Family 16h is a low-power microarchitecture by AMD for its APUs. It succeeds the Jaguar as a second-generation version, targets the same market, and belongs to the same AMD architecture Family 16h. The ''Beema'' line of processors are aimed at low-power notebooks, and ''Mullins'' are targeting the tablet sector. Design The Puma cores use the same microarchitecture as Jaguar, and inherits the design: * Out-of-order execution and Speculative execution, up to 4 CPU cores * Two-way integer execution * Two-way 128-bit wide floating-point and packed integer execution * Integer hardware divider * Puma does not feature clustered multi-thread (CMT), meaning that there are no "modules" * Puma does not feature Heterogeneous System Architecture or zero-copy * 32 KiB instruction + 32 KiB data L1 cache per core * 1–2 MiB unified L2 cache shared by two or four cores * Integrated single channel memory controller supporting 64bit DDR3L * 3.1 mm2 area per core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaguar (microarchitecture)
The AMD Jaguar Family 16h is a low-power microarchitecture designed by AMD. It is used in APUs succeeding the Bobcat Family microarchitecture in 2013 and being succeeded by AMD's Puma architecture in 2014. It is two-way superscalar and capable of out-of-order execution. It is used in AMD's Semi-Custom Business Unit as a design for custom processors and is used by AMD in four product families: ''Kabini'' aimed at notebooks and mini PCs, ''Temash'' aimed at tablets, ''Kyoto'' aimed at micro-servers, and the ''G-Series'' aimed at embedded applications. Both the PlayStation 4 and the Xbox One use chips based on the Jaguar microarchitecture, with more powerful GPUs than AMD sells in its own commercially available Jaguar APUs. Design * 32 KiB instruction + 32 KiB data L1 cache per core, L1 cache includes parity error detection * 16-way, 1–2 MiB unified L2 cache shared by two or four cores, L2 cache is protected from errors by the use of error correcting code * Out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Excavator (microarchitecture)
AMD Excavator Family 15h is a microarchitecture developed by Advanced Micro Devices, AMD to succeed Steamroller (microarchitecture), Steamroller Family 15h for use in AMD APU processors and normal CPUs. On October 12, 2011, AMD revealed Excavator to be the code name for the fourth-generation Bulldozer (microarchitecture), Bulldozer-derived core. The Excavator-based Accelerated processing unit, APU for mainstream applications is called ''Carrizo'' and was released in 2015. The ''Carrizo'' APU is designed to be Heterogeneous System Architecture, HSA 1.0 compliant. An Excavator-based APU and CPU variant named ''Toronto'' for server and enterprise markets was also produced. Excavator was the final revision of the Bulldozer (microarchitecture)#Revisions, "Bulldozer" family, with two new microarchitectures replacing Excavator a year later. Excavator was succeeded by the x86-64 Zen (first generation microarchitecture), Zen architecture in early 2017. Architecture Excavator added hardwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |