|
Lactobacilli
The ''Lactobacillaceae'' are a family of lactic acid bacteria. It is the only family in the lactic acid bacteria which includes homofermentative and heterofermentative organisms; in the ''Lactobacillaceae,'' the pathway used for hexose fermentation is a genus-specific trait. ''Lactobacillaceae'' include the homofermentative lactobacilli ''Lactobacillus'', ''Holzapfelia'', ''Amylolactobacillus'', ''Bombilactobacillus'', ''Companilactobacillus'', ''Lapidilactobacillus'', ''Agrilactobacillus'', ''Schleiferilactobacillus'', ''Loigolactobacillus'', ''Lacticaseibacillus'', ''Latilactobacillus'', ''Dellaglioa'', ''Liquorilactobacillus'', ''Ligilactobacillus'', and ''Lactiplantibacillus''; the heterofermentative lactobacilli ''Furfurilactobacillus'', ''Paucilactobacillus'', ''Limosilactobacillus'', ''Fructilactobacillus'', ''Acetilactobacillus'', ''Apilactobacillus'', ''Levilactobacillus'', ''Secundilactobacillus'', and ''Lentilactobacillus,'' which were previously classified in the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactobacillus
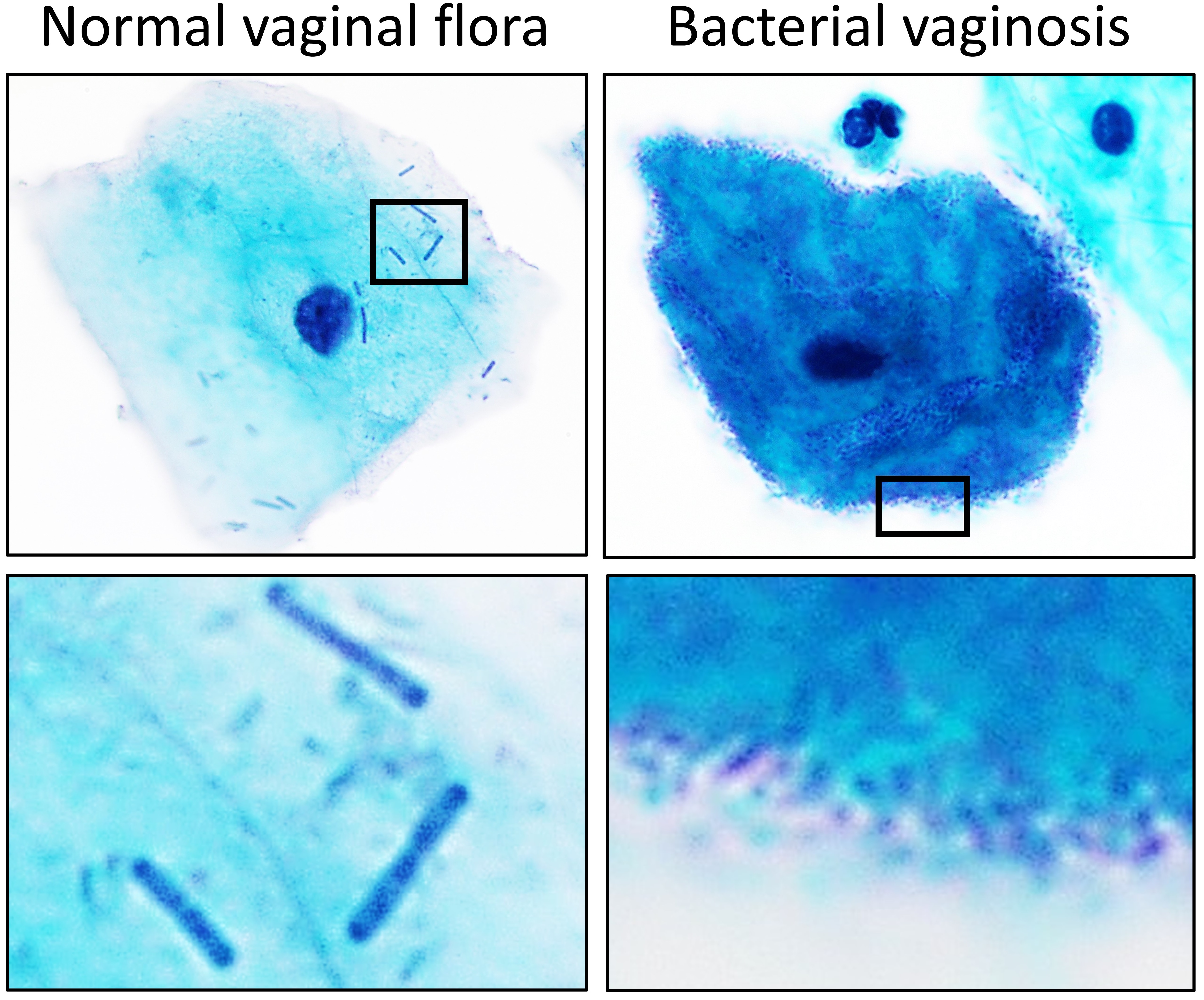
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of Gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system, and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist during harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleiferilactobacillus
''Schleiferilactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature and the phylogeny is based on whole-genome sequences. References Lactobacillaceae Bacteria genera {{Lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holzapfelia
''Holzapfelia floricola'' is a species of lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped ( bacilli) or spherical ( cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bact .... References Lactobacillaceae {{Lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paucilactobacillus
''Paucilactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical ... and the phylogeny is based on whole-genome sequences. References Lactobacillaceae Bacteria genera {{Lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralactobacillus
''Paralactobacillus selangorensis'' is a species of lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillales are an order of gram-positive, low-GC, acid-tolerant, generally nonsporulating, nonrespiring, either rod-shaped ( bacilli) or spherical ( cocci) bacteria that share common metabolic and physiological characteristics. These bact .... References Lactobacillaceae {{Lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oenococcus
''Oenococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive bacteria, placed within the family Lactobacillaceae. The only species in the genus was ''Oenococcus oeni'' (which was known as ''Leuconostoc oeni'' until 1995). In 2006, the species '' Oenococcus kitaharae'' was identified. As its name implies, ''Oenococcus oeni'' holds major importance in the field of oenology, where it is the primary bacterium involved in completing malolactic fermentation Malolactic conversion (also known as malolactic fermentation or MLF) is a process in winemaking in which Tart (flavor), tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation .... References Lactobacillaceae Bacteria genera {{Lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loigolactobacillus
''Loigolactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical ... and the phylogeny is based on whole-genome sequences. References Lactobacillaceae Bacteria genera {{Lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquorilactobacillus
''Liquorilactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria. Species The genus comprises the following species: * '' Liquorilactobacillus aquaticus'' (Mañes-Lázaro ''et al''. 2009) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus cacaonum'' (De Bruyne ''et al''. 2009) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus capillatus'' (Chao ''et al''. 2008) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus ghanensis'' (Nielsen ''et al''. 2007) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus hordei'' (Rouse ''et al''. 2008) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus mali'' (Carr and Davies 1970) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus nagelii'' (Edwards ''et al''. 2000) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus oeni'' (Mañes-Lázaro ''et al''. 2009) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus satsumensis'' (Endo and Okada 2005) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus sicerae'' (Puertas ''et al''. 2014) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Liquorilactobacillus sucico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligilactobacillus
''Ligilactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria associated with vertebrate hosts, formed through the 2020 division of the ''Lactobacillus'' genus. Most of these homofermentative species are motile and express urease to survive gastric acids, making them popular choices for probiotics. The G/C content of this genus varies between 32.5-43.3%. Species The genus ''Ligilactobacillus'' comprises the following species: * '' Ligilactobacillus acidipiscis'' (Tanasupawat ''et al''. 2000) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Ligilactobacillus agilis'' (Weiss ''et al''. 1982) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Ligilactobacillus animalis'' (Dent and Williams 1983) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Ligilactobacillus apodemi'' (Osawa ''et al''. 2006) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Ligilactobacillus araffinosus'' (Fujisawa ''et al''. 1986) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Ligilactobacillus aviarius'' (Fujisawa ''et al''. 1985) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Ligilactobacillus ceti'' (Vela ''et al''. 2008) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levilactobacillus
''Levilactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria. Species The genus ''Levilactobacillus'' comprises the following species: * ''Levilactobacillus acidifarinae'' (Vancanneyt ''et al''. 2005) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus angrenensis'' (Long ''et al''. 2020) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus bambusae'' (Guu ''et al''. 2018) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * '' Levilactobacillus brevis'' (Orla-Jensen 1919) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus cerevisiae'' (Koob ''et al''. 2017) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus enshiensis'' (Zhang ''et al''. 2020) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus fujinensis'' (Long and Gu 2019) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus fuyuanensis'' (Long and Gu 2019) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus hammesii'' (Valcheva ''et al''. 2005) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus huananensis'' (Long and Gu 2019) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Levilactobacillus koreensis'' (Bui ''et al''. 2011) Zheng ''et al'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lentilactobacillus
''Lentilactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria. Species The genus ''Lentilactobacillus'' comprises the following species: * ''Lentilactobacillus buchneri'' (Henneberg 1903) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus curieae'' (Lei ''et al''. 2013) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus diolivorans'' (Krooneman ''et al''. 2002) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus farraginis'' (Endo and Okada 2007) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus hilgardii'' (Douglas and Cruess 1936) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus kefiri'' (Kandler and Kunath 1983) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus kisonensis'' (Watanabe ''et al''. 2009) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus kribbianus'' Bai ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus otakiensis'' (Watanabe ''et al''. 2009) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus parabuchneri'' (Farrow ''et al''. 1989) Zheng ''et al''. 2020 * ''Lentilactobacillus parafarraginis'' (Endo and Okada 2007) Zheng '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latilactobacillus
''Latilactobacillus'' is a genus of lactic acid bacteria. Phylogeny The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) is an online database that maintains information on the naming and taxonomy Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification. A taxonomy (or taxonomical ... and the phylogeny is based on whole-genome sequences. References Lactobacillaceae Bacteria genera {{Lactobacilli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |