|
Kōkei (monk)
Kōkei (also Kogei; 皇慶: 977?–1049), the author of the ''Enoshima Engi'', was an eminent Japanese Buddhist monk. He is said to have commenced his career as a monk at the age of seven, when he climbed Mt. Hiei to Enryakuji Monastery, one of the centers of Japanese Buddhism. Kōkei is credited with the building of the Enryuji (円隆寺) Temple in Tango (丹後; ancient name for region to the north of Kyoto on the Sea of Japan) during the period 995-998. In the year 1003 AD, he boarded a vessel in an attempt to travel to Song Dynasty China to study Buddhism, however, the vessel was unable to depart, and he gave up that ambition. Around 1026, he left Enryakuji and built a thatched hermitage in the Tanba region north of Kyoto at Ikegami (池上). It is said to have been the predecessor of the Ikegami-in (池上院) sub-temple. In reference to this hermitage, he was also known as "Ikegami Ajari" (池上阿闍梨: "The Master-teacher of Ikegami"). He remained at Ikegami until he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enoshima Engi
The ''Enoshima Engi'' (江嶋縁起) is a history of the temples and shrines on Enoshima Island in Sagami Bay. It was written in Chinese language, Chinese, the scholarly language of the time, by the Japanese Buddhist monk Kōkei (monk), Kōkei in 1047 AD. The ''Enoshima Engi'' consists of two parts. The first tells the story of the tribulations of prehistoric villagers who lived in the vicinity of Enoshima. The villagers were plagued for a period of a thousand-some years by a destructive, five-headed dragon (Gozuryu:w:ja:五頭竜, 五頭竜) that had its lair in a nearby lake. Aware of their suffering, on May 31, 552 AD, the Goddess Benzaiten caused the island of Enoshima to arise from the bottom of the bay to serve as her abode. She then descended onto the island amidst a series of spectacular terrestrial and aerial phenomena. The dragon fell in love with the beautiful goddess and asked her to be his consort. Benzaiten, who was widely known for her persuasive eloquence, rejected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese People
The are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Japanese archipelago."人類学上は,旧石器時代あるいは縄文時代以来,現在の北海道〜沖縄諸島(南西諸島)に住んだ集団を祖先にもつ人々。" () Japanese people constitute 97.9% of the population of the country of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 129 million people are of Japanese descent; of these, approximately 122.5 million are residents of Japan. People of Japanese ancestry who live outside Japan are referred to as , the Japanese diaspora. Depending on the context, the term may be limited or not to mainland Japanese people, specifically the Yamato (as opposed to Ryukyuan and Ainu people). Japanese people are one of the largest ethnic groups in the world. In recent decades, there has also been an increase in the number of multiracial people with both Japanese and non-Japanese roots, including half Japanese people. History Theories of origins Archaeological evidence indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia via the Silk Road. It is the world's fourth-largest religion, with over 520 million followers (Buddhists) who comprise seven percent of the global population. The Buddha taught the Middle Way, a path of spiritual development that avoids both extreme asceticism and hedonism. It aims at liberation from clinging and craving to things which are impermanent (), incapable of satisfying ('), and without a lasting essence (), ending the cycle of death and rebirth (). A summary of this path is expressed in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind with observance of Buddhist ethics and meditation. Other widely observed practices include: monasticism; " taking refuge" in the Buddha, the , and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enryakuji
is a Tendai monastery located on Mount Hiei in Ōtsu, overlooking Kyoto. It was first founded in 788 during the early Heian period (794–1185) by Saichō (767–822), also known as Dengyō Daishi, who introduced the Tendai sect of Mahayana Buddhism to Japan from China. The temple complex has undergone several reconstruction efforts since then, with the most significant (that of the main hall) taking place in 1642 under Tokugawa Iemitsu. Enryaku-ji is the headquarters of the Tendai sect and one of the most significant monasteries in Japanese history. As such, it is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Historic Monuments of Ancient Kyoto (Kyoto, Uji and Otsu Cities)". The founders of Jōdo-shū, Jōdo Shinshū, Sōtō Zen, and Nichiren Buddhism all spent time at the monastery. Enryaku-ji is also the center for the practice of kaihōgyō (aka the "marathon monks"). History With the support of Emperor Kanmu, the Buddhist monk Saichō ordained a hundred disciples in 807. Main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Buddhism
Buddhism has been practiced in Japan since about the 6th century CE. Japanese Buddhism () created many new Buddhist schools, and some schools are original to Japan and some are derived from Chinese Buddhist schools. Japanese Buddhism has had a major influence on Japanese society and culture and remains an influential aspect to this day.Asia SocietBuddhism in Japan accessed July 2012 According to the Japanese Government's Agency for Cultural Affairs estimate, , with about 84 million or about 67% of the Japanese population, Buddhism was the religion in Japan with the second most adherents, next to Shinto, though a large number of people practice elements of both. According to the statistics by the Agency for Cultural Affairs in 2021, the religious corporation under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology in Japan had 135 million believers, of which 47 million were Buddhists and most of them were believers of new schools of Buddh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the city had a population of 1.46 million. The city is the cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Kyoto, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 3.8 million people. Kyoto is one of the oldest municipalities in Japan, having been chosen in 794 as the new seat of Japan's imperial court by Emperor Kanmu. The original city, named Heian-kyō, was arranged in accordance with traditional Chinese feng shui following the model of the ancient Chinese capital of Chang'an/Luoyang. The emperors of Japan ruled from Kyoto in the following eleven centuries until 1869. It was the scene of several key events of the Muromachi period, Sengoku period, and the Boshin War, such as the Ōnin War, the Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
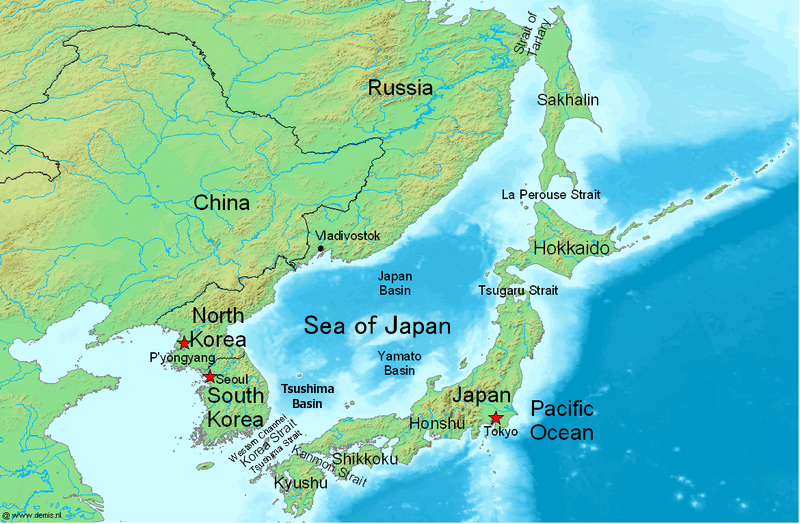
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Song Dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, ending the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. The Song often came into conflict with the contemporaneous Liao, Western Xia and Jin dynasties in northern China. After retreating to southern China, the Song was eventually conquered by the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The dynasty is divided into two periods: Northern Song and Southern Song. During the Northern Song (; 960–1127), the capital was in the northern city of Bianjing (now Kaifeng) and the dynasty controlled most of what is now Eastern China. The Southern Song (; 1127–1279) refers to the period after the Song lost control of its northern half to the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in the Jin–Song Wars. At that time, the Song court retreated south of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ennin
, better known in Japan by his posthumous name, Jikaku Daishi (), was a priest of the Tendai school of Buddhism in Japan, and its third . Ennin was instrumental in expanding the Tendai Order's influence, and bringing back crucial training and resources from China, particularly esoteric Buddhist training and Pure Land teachings. Birth and origin He was born into the Mibu () family in present-day Tochigi Prefecture, Japan and entered the Buddhist priesthood at Enryaku-ji on Mt. Hiei (Hieizan) near Kyoto at the age of 14. Trip to China In 838, Ennin was in the party which accompanied Fujiwara no Tsunetsugu's diplomatic mission to the Tang dynasty Imperial court. The trip to China marked the beginning of a set of tribulations and adventures which he documented in his journal. The journal describes an account of the workings of the government of China, which saw strong and able administrative control of the state and its provinces, even at a time of a supposed decline of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendai
, also known as the Tendai Lotus School (天台法華宗 ''Tendai hokke shū,'' sometimes just "''hokke shū''") is a Mahāyāna Buddhist tradition (with significant esoteric elements) officially established in Japan in 806 by the Japanese monk Saichō ( posthumously known as Dengyō Daishi). The Tendai school, which has been based on Mount Hiei since its inception, rose to prominence during the Heian period (794-1185). It gradually eclipsed the powerful ''Hossō'' school and competed with the rival Shingon school to become the most influential sect at the Imperial court. By the Kamakura period (1185-1333), Tendai had become one of the dominant forms of Japanese Buddhism, with numerous temples and vast landholdings. During the Kamakura period, various monks left Tendai (seeing it as corrupt) to establish their own "new" or "Kamakura" Buddhist schools such as Jōdo-shū, Nichiren-shū and Sōtō Zen. The destruction of the head temple of Enryaku-ji by Oda Nobunaga in 1571, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzaiten
Benzaiten (''shinjitai'': 弁才天 or 弁財天; ''kyūjitai'': 辯才天, 辨才天, or 辨財天, lit. "goddess of eloquence"), also simply known as Benten (''shinjitai'': 弁天; ''kyūjitai'': 辯天 / 辨天), is a Japanese Buddhist goddess who originated mainly from Saraswati, the Hindu goddess of speech, the arts, and learning, with certain traits deriving from the warrior goddess Durga. Worship of Benzaiten arrived in Japan during the sixth through eighth centuries, mainly via Classical Chinese translations of the ''Golden Light Sutra'' (Sanskrit: ''Suvarṇaprabhāsa Sūtra''), which has a section devoted to her. During the medieval period onwards, Benzaiten came to be associated or even conflated with a number of Buddhist and local deities, which include the goddess Kisshōten (the Buddhist version of the Hindu Lakshmi, whose role as goddess of fortune eventually became ascribed to Benzaiten in popular belief), the snake god Ugajin (the combined form of the two bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |