|
Károly Kamermayer
Károly Kamermayer (14 May 1829 – 5 June 1897) was a Hungarian jurist and councillor, who served as the first mayor of Budapest between 1873 and 1896. During his tenure, the city grew into the country's administrative, political, economic, trade, and cultural hub, and Budapest had become one of the cultural centers of Europe. Early life Also referred to as ''Kammermayer'', he came from a bourgeois family of German origin, which had settled in Kingdom of Hungary (1526–1867), Hungary in the 18th century. He was born in Pest, Hungary, Pest on 14 May 1829, the son of wealthy industrialist József Kammermayer, who worked as operations manager at Count György Károlyi's glassworks in Parád. His mother, Anna Emmerling, was a descendant of a patrician family in Pest. Károly Kamermayer (who initially also wrote his name with double "m") finished his secondary studies in Gyöngyös. He attended the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Eger, Archbishopric Lyceum of Eger, then studied law at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayor Of Budapest
The Mayor of Budapest ( hu, Budapest főpolgármestere) is the head of the General Assembly in Budapest, Hungary, elected directly for 5-year term since 2014 (previously municipal elections were held quadrennially). Until 1994 the mayor was elected by the General Assembly. The office was called Chairman of the Council of Budapest ( hu, Budapest tanácselnöke) between 1950 and 1990, during the Communist period. Since 1990, the position is domestically known as Lord Mayor ( hu, főpolgármester) to distinguish the office from that of the mayors that lead each of Budapest's 23 districts. Between 1873 and 1945, the Lord Mayor of Budapest was representative of the Hungarian government as head of the capital's municipal authority, similarly to the Lord-Lieutenants of Counties. History Austria-Hungary The newly elected 400-member General Assembly of Budapest held its inaugural session on 25 October 1873, as a major step in the unification process of Buda and Óbuda on the west ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sapper
A sapper, also called a pioneer (military), pioneer or combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparing field defenses, and road and airfield construction and repair. They are also trained and equipped to serve as provisional infantry, fighting as such as a secondary mission. A sapper's duties facilitate and support movement, defense, and survival of allied forces and impede those of enemies. The term "sapper" is used in the British Army and Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth nations and the U.S. military. The word "sapper" comes from the French word ''sapeur'', itself being derived from the verb ''saper'' (to undermine, to dig under a wall or building to cause its collapse). Historical origin Sapping A sapper, in the sense first used by the French military, was one who dug trenches to allow besieging forces to advance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
György Klapka
György (Móric) Klapka (german: Georg Klapka; 7 April 182017 May 1892) was a Hungarian general. He was one of the most important Hungarian generals of the Hungarian War of Independence of 1848–1849, politician, member of the Hungarian Parliament, and deputy War Minister. Early life Klapka was born at Temesvár, Kingdom of Hungary on 7 April 1820 in a German-speaking Roman-Catholic family of Moravian origin. His ancestors migrated there from Moravia during the reign of Joseph II (1780-1790) his grandfather founding military pharmacies during the Austro-Turkish War of 1787–1791.Zsolt Vesztrócz125 éve hunyt el Klapka György, Komárom hős védője (2017) In the following decades the families prestige grew, and György Klapka's father, József Klapka, became the mayor of Temesvár for nearly 15 years, being elected for two times deputy in the Hungarian Diet, being later ennobled by the king. His mother was Júlia Kehrer.Szinnyei József: Magyar írók élete és munkái ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Győr
Győr ( , ; german: Raab, links=no; names of European cities in different languages: E-H#G, names in other languages) is the main city of northwest Hungary, the capital of Győr-Moson-Sopron County and Western Transdanubia, Western Transdanubia region, and – halfway between Budapest and Vienna – situated on one of the important roads of Central Europe. It is the sixth largest city in Hungary, and one of its seven main regional centres. The city has City with county rights, county rights. History The area along the Danube River has been inhabited by varying cultures since ancient times. The first large settlement dates back to the 5th century BCE; the inhabitants were Celts. They called the town ''Ara Bona'' "Good altar", later contracted to ''Arrabona'', a name which was used until the eighth century. Its shortened form is still used as the German (''Raab'') and Slovak (''Ráb'') names of the city. Roman merchants moved to Arrabona during the 1st century BCE. Around 10 CE, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pered
The Battle of Pered, fought on 20–21 June 1849, was one of the battles which took place in the Summer Campaign of the Hungarian War of Independence from 1848 to 1849, fought between the Hungarian Revolutionary Army and the Habsburg Empire helped by Russian troops. The Hungarian army was led by General Artúr Görgei, while the imperial army by Lieutenant field marshal Julius Jacob von Haynau. After several preliminary minor battles of the Hungarian and Austrian troops along the Vág river, in which the attacking Hungarians could not achieve success, Görgei took the command of his troops, and after receiving reinforcements, on 20 June, put his troops to attack again towards West. Although the II. Hungarian army corps occupied in heavy fights the village of Pered, the other two corps (the III. and the VIII.) were unsuccessful, and could not advance. The angered Görgei removed the commander of the III. corps, General Károly Knezić because of his inactivity, and Colonel Lajos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russian Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian Army consisted of more than 900,000 regular soldiers and nearly 250,000 irregulars (mostly Cossacks). Precursors: Regiments of the New Order Russian tsars before Peter the Great maintained professional hereditary musketeer corps known as '' streltsy''. These were originally raised by Ivan the Terrible; originally an effective force, they had become highly unreliable and undisciplined. In times of war the armed forces were augmented by peasants. The regiments of the new order, or regiments of the foreign order (''Полки нового строя'' or ''Полки иноземного строя'', ''Polki novovo (inozemnovo) stroya''), was the Russian term that was used to describe military units that were formed in the Tsardom of Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komárom
Komárom (Hungarian: ; german: Komorn; la, Brigetio, later ; sk, Komárno) is a city in Hungary on the south bank of the Danube in Komárom-Esztergom County. Komárno, Slovakia, is on the northern bank. Komárom was formerly a separate village called . In 1892 Komárom and Újszőny were connected with an iron bridge and in 1896 the two towns were united under the name city of Komárom. The fortress played an important role in the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 and many contemporary English sources refer to it as the Fortress of Comorn. History Following the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries, Prince Árpád gave Komárom and the Komárom county vicinity to tribal chieftain Ketel. Ketel was the first known ancestor of the famous Koppán (genus) clan. At the beginning of the 12th century, this tribe founded the town's Benedictine Monastery in honor of the Blessed Virgin, mentioned in 1222 by the name of Monostorium de Koppán. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lajos Aulich
Lajos Aulich (25 August 1793 – 6 October 1849) was the third Minister of War of Hungary. A professional soldier and lieutenant colonel in the Austrian Army, he fought against Habsburg oppression. At them time of the War of Hungarian Independence (1848–1849) during the Spring Campaign, Aulich commanded an army, who gathered, and prepared for the great Battle of Isaszeg. He became a honvédség (Hungarian Army) colonel on 2 October 1848, and was named General at the Battle of Kápolna. He was a stickler for the rules: when Lajos Kossuth sent him requests, he answered: "please work through Görgey." Due to his gout, he was relieved of field duty and appointed Minister of War on 14 July 1849. He was executed less than three months later as one of the 13 Martyrs of Arad The Thirteen Martyrs of Arad ( hu, aradi vértanúk) were the thirteen Hungarian rebel generals who were executed by the Austrian Empire on 6 October 1849 in the city of Arad, then part of the Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Buda (1849)
The siege of Buda took place at Buda castle (called ''Festung Ofen'' in German), part of the twin capital cities of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian revolutionary army was led by General Artúr Görgei during the Hungarian War of Independence. Part of the Spring Campaign, the siege began on 4 May 1849, ending with the Hungarian capture of the castle by assault on 21 May. Buda Castle was the only fortress throughout the entire war to be taken by storm by the besiegers on either side. All other fortresses capitulated following agreements between besiegers and besieged. The siege of Buda was also the shortest siege of the war (18 days). The senseless bombardment of Pest by Austrian commander Major General Heinrich Hentzi caused destruction of classic buildings on the shores of the Danube. Other regions of the capitals also suffered heavy damage due to the artillery duels between the two sides. The capture of Buda Castle completed the liberation of the Hungarian capital cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Bridge (Budapest)
Chain bridges are suspension bridges built with chains. Some chain bridge built using this design have retained the name Chain Bridge. Thus as a proper noun, it may refer to: In Hungary: * Chain Bridge (Budapest), a bridge over the Danube in Budapest, Hungary (completed 1849) In Germany: * Chain Bridge (Nuremberg), a pedestrian bridge over the river Pegnitz in Nuremberg, Bavaria (opened 1924) In the United Kingdom: * Union Bridge (Tweed), a bridge over the River Tweed between England and Scotland (opened 1820) * Chain Bridge, a bridge over the River Usk in Monmouthshire, Wales (opened 1829) * Chain Bridge (Berwyn), a bridge over the River Dee at Berwyn, Llangollen, Denbighshire, North Wales (completed 1818) In the United States: * Chain Bridge (Easton, Pennsylvania), a historic change bridge spanning the Lehigh River (completed 1857) * Chain Bridge (Potomac River) The Chain Bridge is a viaduct which crosses the Potomac River at Little Falls in Washington, D.C. The steel g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artúr Görgei
Artúr Görgei de Görgő et Toporc (born Arthur Görgey; hu, görgői és toporci Görgei Artúr, german: Arthur Görgey von Görgő und Toporc; 30 January 181821 May 1916) was a Hungarian military leader renowned for being one of the greatest generals of the Hungarian Revolutionary Army. In his youth, Görgei was a talented chemist, with his work in the field of chemistry being recognized by many renowned Hungarian and European chemists. However, now he is more widely known for his role in the Hungarian Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849. As the most successful general and greatest military genius of the Hungarian Revolutionary Army, he was the leader of the victorious Spring Campaign and liberated almost all of Western Hungary from Austrian occupation. In recognition of his military successes, he was awarded by the Hungarian Government and was appointed Minister of War. In the last days of the revolution, he was appointed the "dictator" of Hungary. On 13 Au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
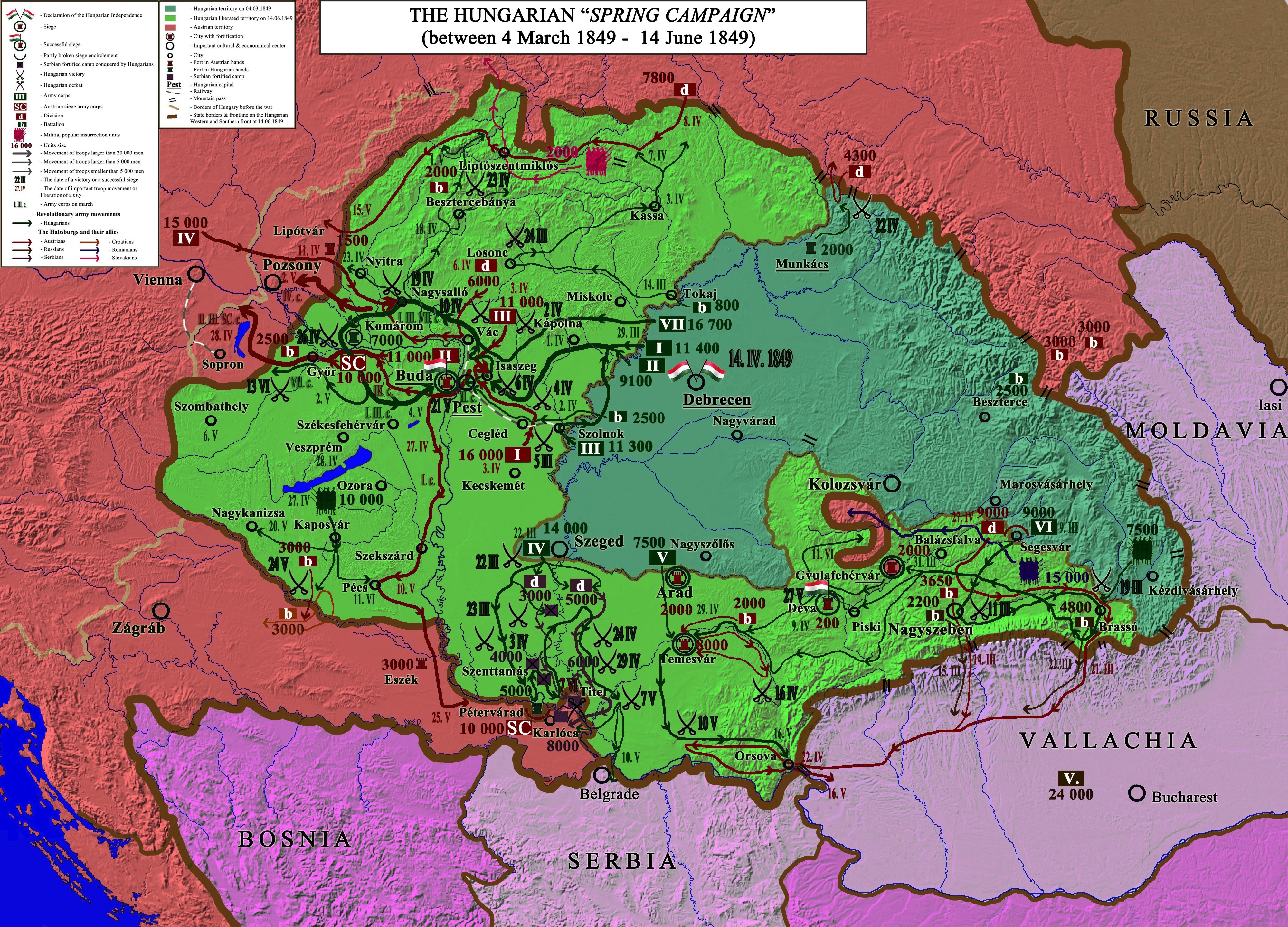
Spring Campaign
The Spring CampaignIstván Lázár, An illustrated history of Hungary, Corvina, 1999, p. 90, ( hu, tavaszi hadjárat), named also the ''Glorious Spring Campaign''Tarján Tamás1849. április 26. , A komáromi csata Rubicon ( hu, dicsőséges tavaszi hadjárat) is the military campaign of the Hungarian Revolutionary Army against the forces of the Habsburg Empire in Middle and Western Hungary during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 between 2 April and 21 May 1849, which resulted in the liberation of almost the whole territory of Hungary from the Habsburg forces. The spring campaign's commander-in-chief was General Artúr Görgey, whose army (47 500 men, 198 cannons) defeated the numerically, technologically and tactically superior (55 000 soldiers and 214 cannons and rockets) imperial armies led by Alfred I, Prince of Windisch-Grätz and after his dismissal, Ludwig von Welden, in a series of victories. The Hungarians won the battles of Hatvan (2nd of April), Tápióbicske (4th of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |