|
Kunkus Yantaq
Kunkus Yantaq ( Ancash Quechua ''kunkush'' ''Puya raimondii'', ''llamt'a, llant'a, yanta'' firewood, ''-q'' a suffix, Hispanicized spelling ''Cuncusyantac'') is a mountain in the Paryaqaqa mountain range in the Andes of Peru. It is located in the Lima Region, Huarochirí Province, San Mateo District. Kunkus Yantaq lies southeast of Qullqayuq. The Yuraqmayu ("white river") originates southeast of Kunkus Yantaq. It is a left tributary of the Rimac The Recreation, Intramural, and Athletic Complex (RIMAC, ) is a sports complex at the University of California San Diego comprising an arena, a weight room and various other event and athletic facilities. It is one of the largest college athleti ... River. References Mountains of Peru Mountains of Lima Region {{LimaRegion-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paryaqaqa Mountain Range
The Pariacaca mountain range (possibly from Quechua ''parya'' reddish, sparrow, ''qaqa'' rock, Paryaqaqa or Parya Qaqa, a regional deity, a mountain god ( apu)), also called Huarochirí mountain range lies in the Andes of Peru. It is located in the Junín Region, in the provinces of Jauja and Yauli, and in the Lima Region, in the provinces of Huarochirí and Yauyos. It is part of the '' Cordillera Central'' of Peru. Mountains The highest mountain in the range is Pariacaca at . Other peaks are listed below: * Tunshu, * Colquepucro, * Carhuachuco, * Paka, * Suyruqucha, * Huallacancha, * Antachaire, * Nina Ukru, * Pachanqutu, * Paqcha, * Wayllakancha, * Kunkus Yantaq, * Wararayuq, * Tuku Mach'ay, * Putka, * Qayqu, * Tata Qayqu, * Yantayuq, * Chumpi, * Ch'uspi, * Quriwasi, * Uqhu, * Ukhu Qhata, * Wiqu, * Wamanripa, * Kiwyu Waqanan, * Qayqu, * Chhuqu P'ukru, * Parya Chaka, * Kunkus, * Kunkus (Yauli), * Suyuq, * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg , other_symbol = Great Seal of the State , other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal , national_motto = "Firm and Happy for the Union" , national_anthem = "National Anthem of Peru" , march = "March of Flags" , image_map = PER orthographic.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Lima , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = Peruvian Spanish, Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages = , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2017 , demonym = Peruvians, Peruvian , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Semi-presidential system, semi-presidential republic , leader_title1 = President of Peru, President ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lima Region
The Department of Lima () is a department and region located in the central coast of Peru, the ''seat of the Regional Government'' is Huacho. Lima Province, which contains the city of Lima, the country's capital, is located west of the Department of Lima; this province is autonomous and not under the jurisdiction of the Regional Government. Geography The department of Lima is bordered by the departments of Ancash on the north, Huánuco, Pasco, and Junín on the east, Huancavelica on the southeast, Ica on the south, and the Pacific Ocean and the Lima Province on the west. The department has a coastal and an Andean zone, and has a great diversity of natural regions: the Coast or ''Chala'' (0 to 500 meters above sea level) up to the ''Janka'' or ''Mountain range'' ( es, Cordillera, over 4800 meters). The predominating regions are the ''Yunga'' (500 to 2300 meters above sea level) and ''Quechua'' (2300 to 3500 meters) Points of interest Lachay National Reserve The Lachay Natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancash Quechua
Ancash Quechua, or Huaylay (Waylay), is a Quechua variety spoken in the Peruvian department of Ancash by approximately 1,000,000 people. Like Wanka Quechua, it belongs to Quechua I (according to Alfredo Torero). Classification The Ancash Quechua varieties belong to the Quechua I branch of the homonymous language family, belonging to a dialectal continuum extended in the central Peruvian Sierra from Ancash in the north to the provinces of Castrovirreyna and Yauyos in the south. Some varieties bordering this continuum partially share morphological characteristics that distinguish the Ancash group from the other central Quechua, so it is difficult to establish a discrete limit. Among these nearby varieties are the Quechua of Bolognesi, Ocros and Cajatambo and that of the Alto Marañón region in the department of Huánuco. See also * Quechuan and Aymaran spelling shift In recent years, Peru has revised the official spelling for place-names originating from Aymara and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
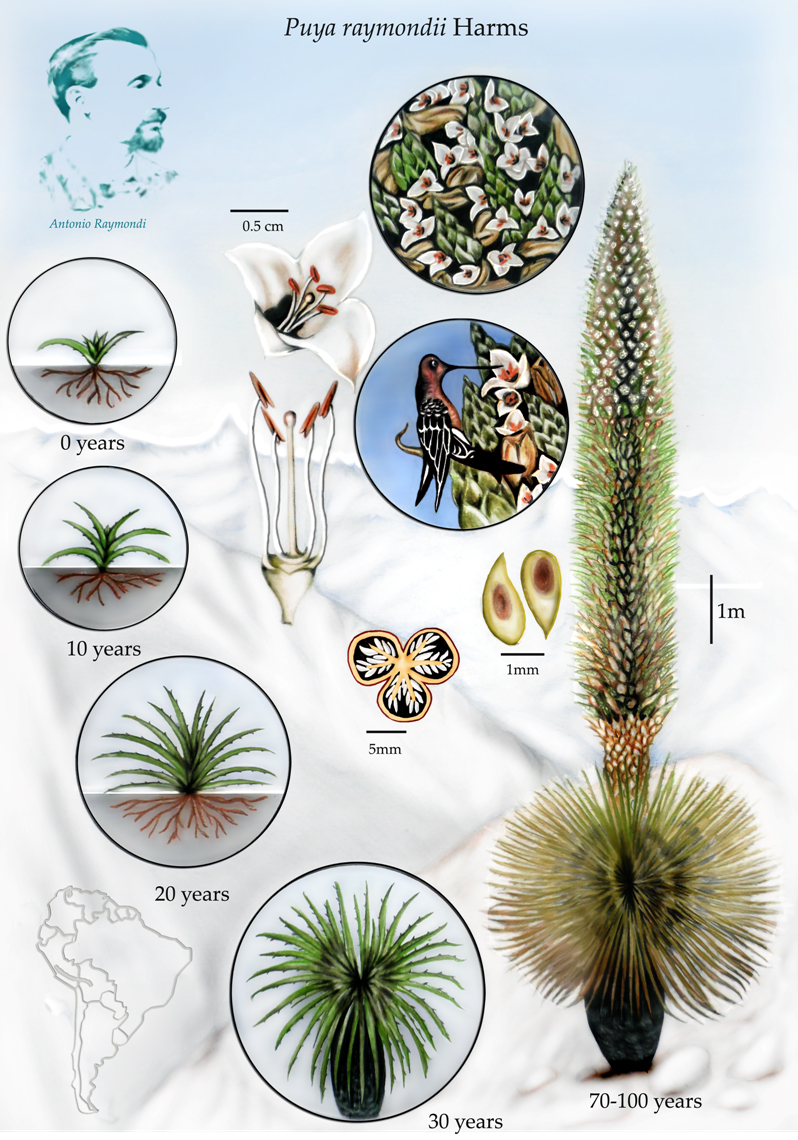
Puya Raimondii
''Puya raimondii'', also known as queen of the Andes (English), titanka (Quechua) or puya de Raimondi (Spanish), is the largest species of bromeliad, its inflorescences reaching up to in height. It is native to the high Andes of Bolivia and Peru. It was once hypothesized to be a ''Protocarnivorous plant''. Taxonomy The first scientific description of this species was made in 1830 by the French scientist Alcide d'Orbigny after he encountered it in the region of Vacas, Cochabamba, in Bolivia at an altitude of . However, as the plants he saw were immature and not yet flowering, he could not classify them taxonomically. The species name of ''raimondii'' commemorates the 19th-century Italian scientist Antonio Raimondi, who immigrated to Peru and made extensive botanical expeditions there. He encountered this species in the region of Chavín de Huantar and published it as new to science under the name ''Pourretia gigantea'' in his 1874 book ''El Perú'' In 1928, the name was cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns, adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs. Suffixes can carry grammatical information (inflectional suffixes) or lexical information ( derivational/lexical suffixes'').'' An inflectional suffix or a grammatical suffix. Such inflection changes the grammatical properties of a word within its syntactic category. For derivational suffixes, they can be divided into two categories: class-changing derivation and class-maintaining derivation. Particularly in the study of Semitic languages, suffixes are called affirmatives, as they can alter the form of the words. In Indo-European studies, a distinction is made between suffixes and endings (see Proto-Indo-European root). Suffixes can carry grammatical information or lexical information. A word-final segment that is somewhere between a free morpheme and a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huarochirí Province
Huarochirí Province (in hispanicized spelling) or Waruchiri is located in the Lima Region of Peru. Its capital is Matucana. The western section is part of the Lima Metropolitan Area. Geography The La Viuda and Paryaqaqa or Waruchiri mountain ranges and the ''Cordillera de la Corte'' traverse the province. One of the highest peaks of the province is Paryaqaqa at above sea level. Other mountains are listed below:escale.minedu.gob.pe - UGEL map of the Huarochirí Province (Lima Region) Political division The province is divided into thirty-two districts. * Matucana ( Matucana) (seat) * Antioquia ( Antioquia) * Callahuanca ( Callahuanca) * Carampoma ( Carampoma) * Chicla ( Chicla) * Cuenca ( San José de los Chorillos) * Huachupampa ( San Lorenzo de Huachupampa) * Huanza ( Huanza) * Huarochirí ( Huarochirí) * Lahuaytambo ( Lahuaytambo) * Langa ( Langa) * Laraos (Laraos) * Mariatana ( Mariatana) * Ricardo Palma (Ricardo Palma) * San Andrés de Tupicocha ( San A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Mateo District, Huarochirí
San Mateo District is one of thirty-two districts of the Huarochirí Province, located in the Department of Lima in Peru. Instituto Nacional de Estadística e Informática. Banco de Información Distrital''. Retrieved April 11, 2008. It was one of eleven districts that formed the Huarochirí Province after it was created by decree on August 4, 1821, during the Protectorate of San Martín. Geography The La Viuda and the Paryaqaqa Pariacaca, Paria Caca'','' Paryaqaqa, Parya Qaqa, (possibly from Quechua ''parya'' reddish; copper; sparrow, ''qaqa'' rock) or Tullujuto (possibly from Quechua ''tullu'' bone, ''qutu'' heap, "bone heap") is the highest mountain in the Pariacac ... or Waruchiri mountain ranges traverse the district. Some of the highest mountains of the district are listed below:escale.minedu.gob.pe - UGEL map of the Huarochirí Province (Lima Region) See also * Yuraqmayu References {{coord, 11.7586, S, 76.3000, W, source:wikidata-and-enwiki-cat-tree_r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qullqayuq
Qullqayuq (Quechua ''qullqa'', deposit, storehouse, ''-yuq'' a suffix to indicate ownership, "the one with a deposit", Hispanicized spelling ''Culcayoc'') is a mountain in the Cordillera Central in the Andes of Peru, about high. It is situated in the Lima Region, Huarochiri Province, San Mateo District. Qullqayuq lies south of Quri, southwest of the lake named Wallaqucha and northwest of Qarwachuku of the Paryaqaqa Pariacaca, Paria Caca'','' Paryaqaqa, Parya Qaqa, (possibly from Quechua ''parya'' reddish; copper; sparrow, ''qaqa'' rock) or Tullujuto (possibly from Quechua ''tullu'' bone, ''qutu'' heap, "bone heap") is the highest mountain in the Pariacaca ... or Waruchiri mountain range. References Mountains of Peru Mountains of Lima Region {{LimaRegion-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuraqmayu (Lima)
The Yuraqmayu (Quechua ''yuraq'' white, ''mayu'' river, "white river", hispaniciced spelling ''Yuracmayo'') or Río Blanco (Spanish for "white river") is a 36.2 km long river in Peru located in the Lima Region, Huarochirí Province, in the districts of Chicla and San Mateo. It is a left tributary of the Rimac River which empties into the Pacific Ocean. The river originates in the San Mateo District, southeast of Kunkus Yantaq. Its direction is mainly to the northwest. Upstream it is the natural border between the districts of Chicla and San Mateo. The confluence with the Rimac River is south of Chicla. The Yuraqmayu dam which was erected near the village of Yuraqmayu at was erected in 1995. It is high and long. It is operated by Edegel. The reservoir A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimac River
The Recreation, Intramural, and Athletic Complex (RIMAC, ) is a sports complex at the University of California San Diego comprising an arena, a weight room and various other event and athletic facilities. It is one of the largest college athletic facilities in the country. RIMAC Arena is the home arena of the UC San Diego Tritons men's and women's basketball, volleyball, and fencing teams, and Triton Soccer Stadium on the adjacent RIMAC Field hosts Triton men's and women's soccer matches. History In 1990, UC San Diego proposed a fee increase of $70 per student to fund a new athletic and event complex. Advocates of the project argued that the existing Main Gym did not have enough aerobic or weight-lifting space to support a rapidly growing university. In addition, Main Gym only seated 2,200 and was rarely available for concerts. The referendum narrowly passed with 51% of the votes, but the results were contested for years. In September 1991, the Regents of the University of Cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)