|
Konya-Karaman Plain
The Konya-Karaman Plain is a plain in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey, associated with the Konya and Karaman Provinces. It is a flat plain (a height of 900–1050 m) that covers the majority of Konya Basin and constitutes the main part of the Central Anatolian Plateau. The plain is one of the driest areas in Turkey. To alleviate it, a major irrigational Konya Plain Project was launched in 2012. The project includes 14 irrigation, three potable water and one energy investments, including the Blue Tunnel Project and the Bagbasi Dam. The plain is dominated by the Çarşamba river, which forms a delta in its centre. History The Konya-Karaman Plain did not possess resources which prehistoric and early historic human communities there required, such as timber, metal, chipped stone, and ground stone, which pushed its inhabitants to develop procurement networks in as early as the 9th millennium BC, with these networks continuing to exist in the Bronze and Iron Ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konya Plain Topographic Map-blank
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it Darü'l-Mülk, meaning "seat of government". In 19th-century accounts of the city in English its name is usually spelt Konia or Koniah. As of 2021, the population of the Metropolitan Province was 2,277,017, making it the sixth most populous city in Turkey, and second most populous of the Central Anatolia Region, after Ankara . Of this, 1,390,051 lived in the three urban districts of Meram, Selçuklu and Karatay. Konya is served by TCDD high-speed train ( YHT) services from Istanbul and Ankara. The local airport ( Konya Havalimanı, KYA) is served by flights from Istanbul. Etymology of Iconium Konya was known in classical antiquity and during the medieval period as (''Ikónion'') in Greek (with regular Medieval Greek apheresis ''Kón ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). Lumber has many uses beyond home building. Lumber is sometimes referred to as timber as an archaic term and still in England, while in most parts of the world (especially the United States and Canada) the term timber refers specifically to unprocessed wood fiber, such as cut logs or standing trees that have yet to be cut. Lumber may be supplied either rough- sawn, or surfaced on one or more of its faces. Beside pulpwood, ''rough lumber'' is the raw material for furniture-making, and manufacture of other items requiring cutting and shaping. It is available in many species, including hardwoods and softwoods, such as white pine and red pine, because of their low cost. ''Finished lumber'' is supplied in standard sizes, mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
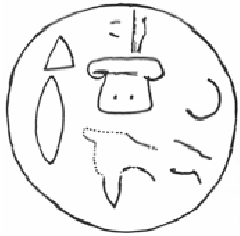
Anatolian Hieroglyphs
Anatolian hieroglyphs are an indigenous logographic script native to central Anatolia, consisting of some 500 signs. They were once commonly known as Hittite hieroglyphs, but the language they encode proved to be Luwian, not Hittite, and the term Luwian hieroglyphs is used in English publications. They are typologically similar to Egyptian hieroglyphs, but do not derive graphically from that script, and they are not known to have played the sacred role of hieroglyphs in Egypt. There is no demonstrable connection to Hittite cuneiform. History Individual Anatolian hieroglyphs are attested from the second and early first millennia BC across Anatolia and into modern Syria. A biconvex bronze personal seal was found in the Troy VIIb level (later half of the 12th century BC) inscribed with Luwian Hieroglyphs. The earliest examples occur on personal seals, but these consist only of names, titles, and auspicious signs, and it is not certain that they represent language. Most actual text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartapu
Hartapu was an Anatolian king in the 8th century BCE. He is known from Hieroglyphic Luwian inscriptions from Kizildağ, Mount Karadağ, Burunkaya near Aksaray, and most recently Türkmen-Karahöyük, site of a monumental stele in which he claimed victory over the kingdom of Phrygia, ruled around that time by King Midas. Hartapu, who bore the titles Great king, and Hero, states himself to be the son of another Great King and Hero named Mursili. If Hartapu is the son of Mursili III, he may have succeeded his uncle Kurunta, the younger brother of Mursili III as king of Tarḫuntašša in the 2nd half of the 13th century BC. Hartapu's use of royal titulation may have been similar to its use by to Kurunta, who also bore the titles Great King and Hero to demonstrate his right to the throne of Hattusa, still occupied by the descendants of the usurper Ḫattušili III. Those descendants were Tudhaliya IV during Kurunta's reign, and Suppiluliuma II during Hartapu's reign. It is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarḫuntašša
''Tarḫuntašša ( ''dIM-ta-aš-ša'' "City of Tarhunt"; Hieroglyphic Luwian: ''(DEUS)TONITRUS-hu-ta-sá'') was a Hittite Bronze Age city in south-central Anatolia mentioned in Hittite documents. Its location is unknown. In 2019, a previously little-researched site at Türkmen-Karahöyük, near Çumra on the Konya Plain, was investigated and put forward as the site of Tarḫuntassa by Michele Massa, James Osborne and Christoph Bachhuber. Previously proposed locations include Konya, Sirkeli Höyük in Cilicia, the Göksu valley, the vicinity of Kayseri, Kilise Tepe (near Mut, formerly known as Maltepe), and Kızıldağ (north of Karaman). New Hittite capital In the early 13th century BC, Muwatalli II moved the Hittite capital from Hattusa to Tarhuntassa. The reasons for this move remain unclear. Official records postdating Muwatalli II's death state that he moved the capital as the result of an omen. Generally, archaeologists explain the move as a military strategy, in order t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Liverpool
, mottoeng = These days of peace foster learning , established = 1881 – University College Liverpool1884 – affiliated to the federal Victoria Universityhttp://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukla/2004/4 University of Manchester Act 2004. legislation.gov.uk (4 July 2011). Retrieved on 14 September 2011.1903 – royal charter , type = Public , endowment = £190.2 million (2020) , budget = £597.4 million (2020–21) , city = Liverpool , country = England , campus = Urban , coor = , chancellor = Colm Tóibín , vice_chancellor = Dame Janet Beer , head_label = Visitor , head = The Lord President of the Council '' ex officio'' , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , colours = The University , affiliations = Russell Group, EUA, N8 Group, NWUA, AACSB, AMBA, EQUIS, EASN, Universities UK , website = , logo = Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Çatalhöyük
Çatalhöyük (; also ''Çatal Höyük'' and ''Çatal Hüyük''; from Turkish ''çatal'' "fork" + ''höyük'' "tumulus") is a tell of a very large Neolithic and Chalcolithic proto-city settlement in southern Anatolia, which existed from approximately 7500 BC to 6400 BC, and flourished around 7000 BC. In July 2012, it was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Çatalhöyük is located overlooking the Konya Plain, southeast of the present-day city of Konya (ancient Iconium) in Turkey, approximately 140 km (87 mi) from the twin-coned volcano of Mount Hasan. The eastern settlement forms a mound that would have risen about 20 m (66 ft) above the plain at the time of the latest Neolithic occupation. There is also a smaller settlement mound to the west and a Byzantine settlement a few hundred meters to the east. The prehistoric mound settlements were abandoned before the Bronze Age. A channel of the Çarşamba River once flowed between the two mounds, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Site
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology and represents a part of the archaeological record. Sites may range from those with few or no remains visible above ground, to buildings and other structures still in use. Beyond this, the definition and geographical extent of a "site" can vary widely, depending on the period studied and the theoretical approach of the archaeologist. Geographical extent It is almost invariably difficult to delimit a site. It is sometimes taken to indicate a settlement of some sort although the archaeologist must also define the limits of human activity around the settlement. Any episode of deposition such as a hoard or burial can form a site as well. Development-led archaeology undertaken as cultural resources management has the disadvantage (or the ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)