|
Keny (game)
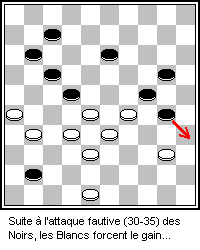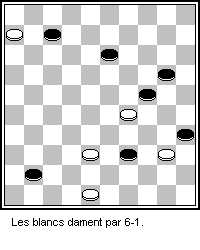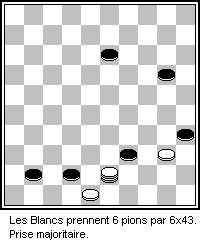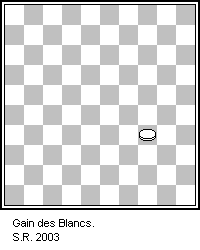
Keny (Russian: Кены) is a draughts game played in the Caucasus and nearby areas of Turkey. Keny is actually the Ossetian name for the game as it is most popular in Ossetia, a region in the Caucasus. In Armenia, it is called Vayut tama (Russian: вают тама). The game is also known as Caucasian checkers (Russian: кавказские шашки). There may be slight variations of the game, but the rules described here are from Nikita Sokolov (Никита Соколов) from his article "A long time ago, we did not take checkers into our hands ..." ("Давненько не брали мы в руки шашек...") (2005). Rules The game resembles both Turkish and Armenian draughts in that all these games use an 8 x 8 uncheckered square board, have 16 men or checkers (an unpromoted man is called a "ken", or Russian: кен) initially placed in each player's second and third ranks, and allow for men and kings to move orthogonally (a king is called a "pepper", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically been considered as a natural barrier between Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Mount Elbrus in Russia, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands, part of which is in Turkey. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is occupied by several independent states, mostly by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetians
The Ossetians or Ossetes (, ; os, ир, ирæттæ / дигорӕ, дигорӕнттӕ, translit= ir, irættæ / digoræ, digorænttæ, label=Ossetic) are an Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the northern and southern sides of the Caucasus Mountains. They natively speak Ossetic, an Eastern Iranian language of the Indo-European language family, with most also being fluent in Russian as a second language. Ossetic, a remnant of the Scytho-Sarmatian dialect group which was once spoken across the Pontic–Caspian Steppe, is one of the few Iranian languages remaining inside Europe. Currently, the Ossetian homeland of Ossetia is politically divided between North Ossetia–Alania in Russia, and the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Their closest historical and linguistic relatives, the Jász people, live in the Jászság region withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
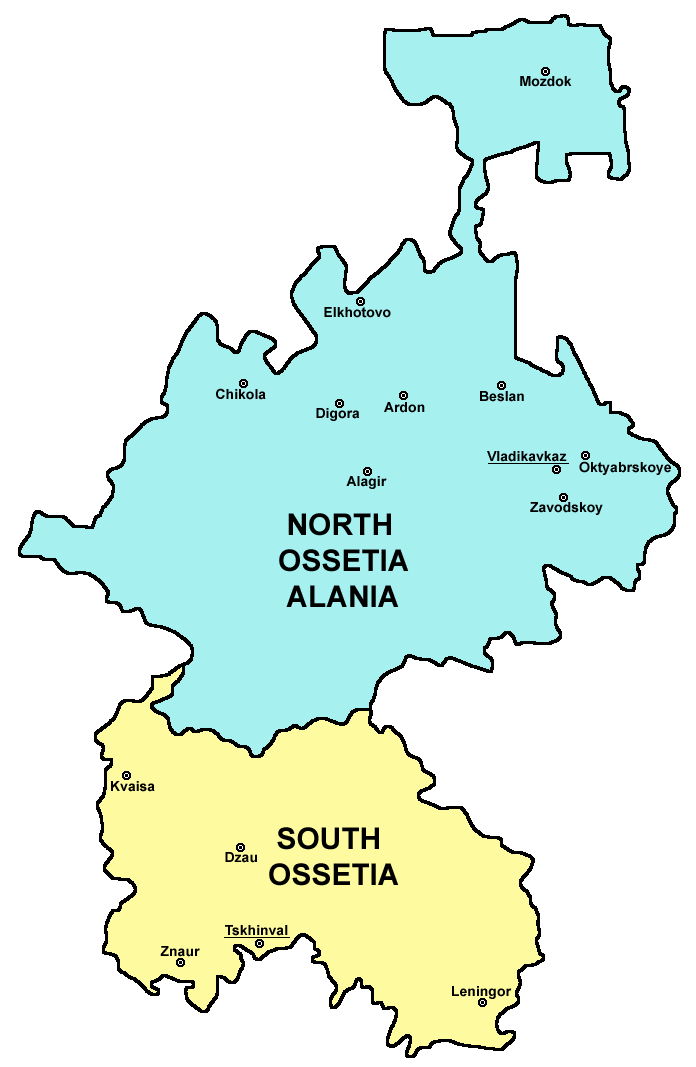
Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; os, Ирыстон or , or ; russian: Осетия, Osetiya; ka, ოსეთი, translit. ''Oseti'') is an ethnolinguistic region located on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia, but it has come under the control of the ''de facto'' government of the Russian-backed Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania within the Russian Federation. Recent history * 1774 — North Ossetia becomes part of the Russian Empire. * 1922 — Creation of the South Ossetian autonomous oblast. North Ossetia remains a part of Russian SFSR, South Ossetia remains a part of Georgian SSR. * 20 September 1990 — South Osse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halma
Halma (from the Greek word ἅλμα meaning "jump") is a strategy board game invented in 1883 or 1884 by George Howard Monks, an American thoracic surgeon at Harvard Medical School. His inspiration was the English game ''Hoppity'' which was devised in 1854. The gameboard is checkered and divided into 16×16 squares. Pieces may be small checkers or counters, or wooden or plastic cones or men resembling small chess pawns. Piece colors are typically black and white for two-player games, and various colors or other distinction in games for four players. Overview The game is played by two or four players seated at opposing corners of the board. The game is won by being first to transfer all of one's pieces from one's own camp into the camp in the opposing corner. For four-player games played in teams, the winner is the first team to race both sets of pieces into opposing camps. On each turn, a player either moves a single piece to an adjacent open square, or jumps over one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ugolki
Ugolki (, russian: уголки}, English: ''corners'') is a two-player board game, similar to halma, that is typically played on an 8×8 grid board with 16 game pieces per player. It is said to have been invented in Europe in the late 18th century. Variations on the size of the board and the number of game pieces also exist. Game rules Both players start off with square arrangements of 16 game pieces in opposing corners of the gameboard. Each player's goal is to move all their pieces from the starting corner to the corner occupied by the opponent at the start of the game. Players take turns moving one game piece. A piece may move only away from the starting location into a destination that is empty, provided either of the following conditions are met: * the destination square is adjacent to the starting square * the destination square can be reached by consecutive {{Short pages monitor [Baidu] |
Conspirateurs
''Conspirateurs'' () is a two- or four-player strategy board game said to have been invented in 18th-century France. Robert Charles Bell believes the game to date from after 1789, following the French Revolutionary Wars, "a period of feverish political activity with factions conspiring against each other". ''Conspirateurs'' resembles other games such as Halma, Ugolki, Chinese Checkers, and Salta Salta () is the capital and largest city in the Argentine province of the same name. With a population of 618,375 according to the 2010 census, it is also the 7th most-populous city in Argentina. The city serves as the cultural and economic ce ... in that pieces jump without capturing over friendly or enemy pieces, to move more quickly to their destinations. Equipment The gameboard comprises 17×17 gridded lines. At the centre is a specially marked or coloured area comprising 5×9 intersection ''points'' representing a "secret meeting place". On the board's perimeter, 39 points a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salta
Salta () is the capital and largest city in the Argentine province of the same name. With a population of 618,375 according to the 2010 census, it is also the 7th most-populous city in Argentina. The city serves as the cultural and economic center of the Valle de Lerma Metropolitan Area (Spanish: ''Área Metropolitana del Valle de Lerma'', AMVL), which is home to over 50.9% of the population of Salta Province and also includes the municipalities of La Caldera, Vaqueros, Campo Quijano, Rosario de Lerma, Cerrillos, La Merced and San Lorenzo. Salta is the seat of the Capital Department, the most populous department in the province. History Salta was founded on April 16, 1582 by the Spanish conquistador Hernando de Lerma, who intended the settlement to be an outpost between Lima, Peru and Buenos Aires. The origin of the name ''Salta'' is a matter of conjecture, with several theories being advanced to explain it. During the war of independence, the city became a commercial an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draughts
Checkers (American English), also known as draughts (; British English), is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Checkers is developed from alquerque. The term "checkers" derives from the checkered board which the game is played on, whereas "draughts" derives from the verb "to draw" or "to move". The most popular forms of checkers in Anglophone countries are American checkers (also called English draughts), which is played on an 8×8 checkerboard; Russian draughts, Turkish draughts both on an 8x8 board, and International draughts, played on a 10×10 board – the latter is widely played in many countries worldwide. There are many other variants played on 8×8 boards. Canadian checkers and Singaporean/Malaysian checkers (also locally known as ''dum'') are played on a 12×12 board. American checkers was weakly solved in 2007 by a team of Canadian computer s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Draughts
Turkish draughts (Turkish: Dama)(Armenian: շաշկի)(Arabic: دامە)(Kurmanji: دامە) is a variant of draughts (checkers) played in Turkey, Greece, Egypt, Kuwait, Lebanon, Syria, Jordan and several other locations around the Mediterranean Sea and Middle East. Rules On an 8×8 board, 16 ' are lined up on each side, in two rows. The back rows are vacant. A traditional Turkish draughts is mono-coloured. White moves first. Men move orthogonally forwards or sideways one square, capturing by means of a jump; they cannot move or capture backwards or diagonally. When a man reaches the back row, it promotes to a ''king''. Kings can move any number of empty squares orthogonally forwards, backwards or sideways. A king captures by jumping over a single piece any number of empty squares away, landing on any open square beyond the captured piece along a straight line. If a jump is available it must be taken. If there is more than one way to jump, the one capturing the most number of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Draughts
Armenian draughts, or Tama, is a variant of draughts (or checkers) played in Armenia. The rules are similar to Turkish draughts, Dama. Armenian draughts, however, allows for diagonal movement. Rules On an 8×8 board, 16 men are lined up on each side in two rows, skipping the first and last row. From a player's point of view, the second and third rows are filled with men of his own color, and the sixth and seventh rows are filled with the opponent's men. Players alternate turns with each making one move per turn. Pieces initially consist of men only. When reaching the opposite side of the board, men are "crowned" to pieces called kings. A man can move forwards, straight ahead or diagonally, or sideways to an orthogonally adjacent field if that field is empty. Kings may move in all directions (up, down, left, right, or diagonally), as long as the path is clear of pieces. In other words, the king moves like a Chess#Moves, Chess queen. If a man is orthogonally adjacent to an oppone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)