Ossetians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ossetians or Ossetes (, ; os, ир, ирæттæ / дигорӕ, дигорӕнттӕ, translit= ir, irættæ / digoræ, digorænttæ, label=
 *
*

 In more-recent history, the Ossetians participated in the
In more-recent history, the Ossetians participated in the
 Stavropol Krai — 7,700
*
Stavropol Krai — 7,700
*

 Rostov Oblast — 2,600
*
Rostov Oblast — 2,600
*
File:Osetino komXXjc.jpg, Ossetian woman in traditional clothes, early years of the 20th century
File:Osetia woman working.jpg, Ossetian women working (19th century)
File:Ramonov vano ossetin northern caucasia dress 18 century.jpg, Ossetian Northern Caucasia dress of the 18th century, Ramonov Vano (19th century)
File:Three ossetian teachers.jpg, Three Ossetian teachers (19th century)
File:Ossetian girl 1883.jpg, Ossetian girl in 1883
File:Gazdanov-192?.jpg,
Ossetians.com – a site about famous Ossetians
{{Authority control Alans Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Turkey Ethnic groups in Syria Iranian ethnic groups Iranian peoples in the Caucasus Peoples of the Caucasus
Ossetic
Ossetian (, , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete (), is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Greater Caucasus. It is the native language of the Ossetia ...
) are an Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
who are indigenous to Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; os, Ирыстон or , or ; russian: Осетия, Osetiya; ka, ოსეთი, translit. ''Oseti'') is an ethnolinguistic region located on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. ...
, a region situated across the northern and southern sides of the Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains,
: pronounced
* hy, Կովկասյան լեռներ,
: pronounced
* az, Qafqaz dağları, pronounced
* rus, Кавка́зские го́ры, Kavkázskiye góry, kɐfˈkasːkʲɪje ˈɡorɨ
* tr, Kafkas Dağla ...
. They natively speak Ossetic
Ossetian (, , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete (), is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Greater Caucasus. It is the native language of the Ossetia ...
, an Eastern Iranian language
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages emerging in Middle Iranian times (from c. the 4th century BC). The Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle Western Iranian dial ...
of the Indo-European language family
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
, with most also being fluent in Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
as a second language. Ossetic, a remnant of the Scytho-Sarmatian
The Scythian languages are a group of Eastern Iranian languages of the classical and late antique period (the Middle Iranian period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descend ...
dialect group which was once spoken across the Pontic–Caspian Steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
, is one of the few Iranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are groupe ...
remaining inside Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
.
Currently, the Ossetian homeland of Ossetia is politically divided between North Ossetia–Alania in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, and the ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' country of South Ossetia
South Ossetia, ka, სამხრეთი ოსეთი, ( , ), officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated populat ...
(recognized by the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' part of Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
). Their closest historical and linguistic relatives, the Jász people, live in the Jászság region within the northwestern part of the Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County
Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok ( hu, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok megye, ) is the name of an administrative county ( comitatus or ''megye'') in Hungary. It lies in central Hungary and shares borders with the Hungarian counties Pest, Heves, Borsod-Abaúj-Zempl ...
of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
. A third group descended from the medieval Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
are the Asud
The Asud (Mongolian Cyrillic: , IPA: //) were a military group of Alani origin. The Mongol clan Asud is the plural of As, the Arabic name for the Alans.
Against the Alans and the Cumans (Kipchaks), the Mongols used divide and conquer tactics by ...
of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
. Both the Jász and the Asud have long been assimilated; only the Ossetians have preserved a form of the Alanic language.
The majority of Ossetians are Eastern Orthodox Christians
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
, with sizable minorities professing the Ossetian ethnic religion of Uatsdin
Assianism (, ''Watsdin'') is a modern Pagan religion derived from the traditional mythology of the Ossetians, modern descendants of the Scythians of the Alan tribes, believed to be a continuation of the ancient Scythian religion. The religion is ...
as well as Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
.
Etymology
The Ossetians and Ossetia received their name from the Russians, who had adopted theGeorgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
designations ''Osi'' (ოსი, pl. ''Osebi'', ოსები) and ''Oseti'' ('the land of the Osi', ოსეთი), used since the Middle Ages for the single Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
-speaking population of the Central Caucasus and probably based on an old Alan
Alan may refer to:
People
*Alan (surname), an English and Turkish surname
* Alan (given name), an English given name
**List of people with given name Alan
''Following are people commonly referred to solely by "Alan" or by a homonymous name.''
*A ...
self-designation ''As'', which is cognate with the Jassic self-designation Jasz, both probably being based on the Scytho-Sarmatian
The Scythian languages are a group of Eastern Iranian languages of the classical and late antique period (the Middle Iranian period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descend ...
name of the Iazyges
The Iazyges (), singular Ἰάζυξ. were an ancient Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In BC, they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Dacian steppe between th ...
, or ''Yazigi'' as they called themselves. Since Ossetian speakers lacked any single inclusive name for themselves in their native language beyond the traditional Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
– Digoron subdivision, these terms came to be accepted by the Ossetians as an endonym already before their integration into the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.
This practice was put into question by the new Ossetian nationalism in the early 1990s, when the dispute between the Ossetian subgroups of Digoron and Iron over the status of the Digor dialect
Digor or Digorian (''дигорон digoron'') is a dialect of the Ossetian language spoken by the Digor people. It is less widely spoken than Iron, the other extant Ossetian dialect. The two are distinct enough to sometimes be considered separ ...
made Ossetian intellectuals search for a new inclusive ethnic name. This, combined with the effects of the Georgian–Ossetian conflict, led to the popularization of '' Alania'', the name of the medieval Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
confederation, to which the Ossetians traced their origin and to the inclusion of this name into the official republican title of North Ossetia in 1994.
The root ''os/as''- could also stem from an earlier *''ows''/''aws''-, whose meaning is unknown. This is suggested by the archaic Georgian root ''ovs''- (cf. ''Ovsi'', ''Ovseti''), documented in the ''Georgian Chronicles
''The Georgian Chronicles'' is a conventional English name for the principal compendium of medieval Georgian historical texts, natively known as ''Kartlis Tskhovreba'' ( ka, ქართლის ცხოვრება), literally "Life of Ka ...
''; the long length of the initial vowel or the gemination
In phonetics and phonology, gemination (), or consonant lengthening (from Latin 'doubling', itself from ''gemini'' 'twins'), is an articulation of a consonant for a longer period of time than that of a singleton consonant. It is distinct from s ...
of the consonant ''s'' in some forms ( NPers. ''Ās'', ''Āṣ''; Lat
Lat or LAT may refer to:
Places
* Lat, Fuman, village in Gilan Province, Iran
* Lat, Rasht, village in Gilan Province, Iran
* Lat, Mazandaran, village in Iran
* Lat-e Disar, village in Mazandaran Province, Iran
* Lat, Qazvin, village in I ...
. ''Aas'', ''Assi''); and by the Armenian ethnic name *''Awsowrk (''Ōsur''-), referring to an Alan tribe dwelling near modern Georgia by the time of Anania Shirakatsi
Anania Shirakatsi ( hy, Անանիա Շիրակացի, ''Anania Širakac’i'', anglicized: Ananias of Shirak) was a 7th-century Armenian polymath and natural philosopher, author of extant works covering mathematics, astronomy, geography, chronol ...
(7th century AD).
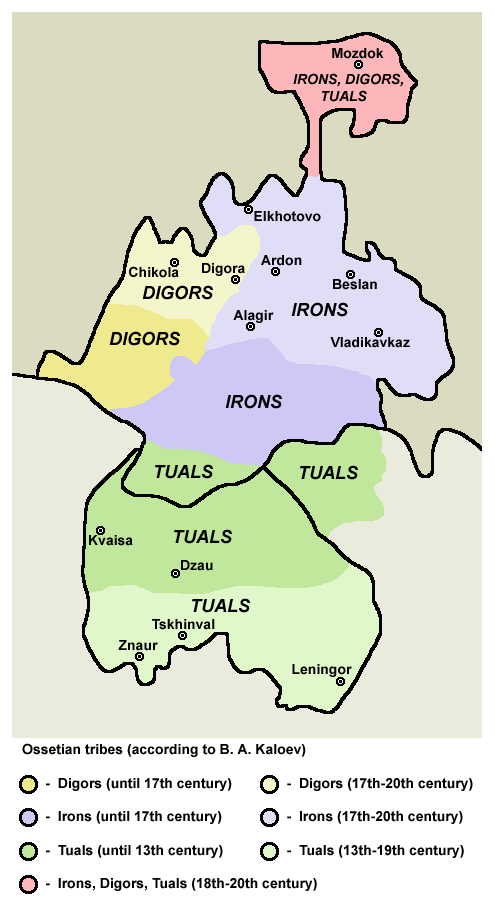
Subgroups
 *
*Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
in the east and south form a larger group of Ossetians. They speak Iron dialect
Iron (Ossetic: Ирон, ''Iron'' or Ирон ӕвзаг, ''Iron evzag'') is one of the two main dialects of the Ossetic language along with DigorThordarson, Fridrik. 1989. Ossetic. Compendium Linguarum Iranicarum, ed. by Rudiger Schmitt, 456-7 ...
. Irons are divided into several subgroups: Alagirs, Kurtats, Tagaurs, Kudar, Tual, Urstual and Chsan.
** Kudar are the southern group of Ossetians.
**Tual are in the central part of Ossetia (see also Dvals
The Dvals ( ka, დვალები, ''Dvalebi''; os, Туалтæ, ''Twaltæ'') were a ethnographic group of Georgians, their lands lying on both sides of the central Greater Caucasus mountains, somewhere between the Darial and Mamison gorge ...
).
**Chsan are in the east of South Ossetia.
* Digoron in the west. Digors live in Digora district, Iraf district and some settlements in Kabardino-Balkaria
The Kabardino-Balkarian Republic (russian: Кабарди́но-Балка́рская Респу́блика, ''Kabardino-Balkarskaya Respublika''; kbd, Къэбэрдей-Балъкъэр Республикэ, ''Ķêbêrdej-Baĺķêr Respublik� ...
and Mozdok district. They speak Digor dialect
Digor or Digorian (''дигорон digoron'') is a dialect of the Ossetian language spoken by the Digor people. It is less widely spoken than Iron, the other extant Ossetian dialect. The two are distinct enough to sometimes be considered separ ...
.
* Iasi, who settled in the Jászság
Jászság ("Jaszygia", la, Jazigia) is a historical, ethnographical and geographical region in Hungary. Its territory is situated in the north-western part of the Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. The main town in the region is Jászberény. Já ...
region in Hungary during the 13th century. They spoke the extinct Jassic dialect
Jassic ( hu, jász) is an extinct dialect of the Ossetian language once spoken in Hungary, named after the Jasz people, a nomadic tribe that settled in Hungary in the 13th century.
History
The Jasz (Jassic) people came to Hungary together with ...
.
Culture
Mythology
The native beliefs of the Ossetian people are rooted in theirSarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
origin, which have been syncretized with a local variant of Folk Orthodoxy
Folk Orthodoxy (russian: народное православие; sr, народно православље; lv, narodno pravoslavlje) refers to the folk religion and Religious syncretism, syncretic elements present in the Eastern Orthodox commun ...
, in which some pagan gods having been converted into Christian saints. The Narts
The Nart sagas ( Abkhaz: Нарҭаа ражәабжьқәа; ''Nartaa raƶuabƶkua''; ady, Нарт тхыдэжъхэр, translit=Nart txıdəĵxər; os, Нарты кадджытæ; ''Narty kaddžytæ''; ''Nartı kadjıtæ'') are a series of ...
, the Daredzant, and the Tsartsiat, serve as the basic literature of folk mythology in the region.
Music
Genres
Ossetian folk songs are divided into 10 uniquegenres
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other for ...
:
* Historic songs
* War songs
* Heroic songs
* Work songs
* Wedding songs
* Drinking songs
* Humorous songs
* Dance songs
* Romantic songs
* Lyrical songs
Instruments
Ossetians use the following Instruments in their music: * String Instruments: ** Plucked strings: *** ''Dyuuadæstænon'' - a twelve-stringed Harp *** ''Fændyr'' - an Harp with two or three plucked strings ** Bowed strings *** ''Hysyn'' - two or three string Fiddle *** ''Hyyrnæg'' - is a double-bridged instrument, a kind ofCello
The cello ( ; plural ''celli'' or ''cellos'') or violoncello ( ; ) is a Bow (music), bowed (sometimes pizzicato, plucked and occasionally col legno, hit) string instrument of the violin family. Its four strings are usually intonation (music), t ...
* Wind instruments
A wind instrument is a musical instrument that contains some type of resonator (usually a tube) in which a column of air is set into vibration by the player blowing into (or over) a mouthpiece set at or near the end of the resonator. The pitc ...
** ''Uadyndz'' - Flute
** Khyozyn - Reed Flute
** Lalym - Bagpipes
** Udaevdz - Double-reeds
** Fidiuæg - some kind of instrument made from a bull's horn
* Percussion instruments
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a beater including attached or enclosed beaters or rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Ex ...
** Kartsgænæg - Rattles
** Gymsæg - Drum
** Dala - Tambourine
The tambourine is a musical instrument in the percussion family consisting of a frame, often of wood or plastic, with pairs of small metal jingles, called "zills". Classically the term tambourine denotes an instrument with a drumhead, though ...
History

Pre-history (Early ''Alans'')
The Ossetians descend from theIazyges
The Iazyges (), singular Ἰάζυξ. were an ancient Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In BC, they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Dacian steppe between th ...
tribe of the Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
, a Sarmatian
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
sub-tribe, which in turn is a Scythian
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
subgroup itself. The Alans were the only branch of the Sarmatians to keep their culture in the face of a Gothic invasion (c. 200 AD) and those who remained built a great kingdom between the Don and Volga Rivers, according to Coon
Coon may refer to:
Fauna Butterflies
* Coon, common name of the butterfly ''Astictopterus jama''
* Coon, species group of the butterfly genus ''Atrophaneura'', now genus ''Losaria''
* Coon, common name of the butterfly '' Psolos fuligo''
Ma ...
, ''The Races of Europe''. Between 350 and 374 AD, the Huns destroyed the Alan kingdom and the Alan people were split in half. One half fled to the west, where they participated in the Barbarian Invasions of Rome, established short-lived kingdoms in Spain and North Africa and settled in many other places such as Orléans, France, Iași, Romania, Alenquer, Portugal and Jászberény, Hungary. The other half fled to the south and settled on the plains of the North Caucasus, where they established their medieval kingdom of Alania.
Middle Ages
In the 8th century a consolidated Alan kingdom, referred to in sources of the period as Alania, emerged in the northern Caucasus Mountains, roughly in the location of the latter-dayCircassia
Circassia (; also known as Cherkessia in some sources; ady, Адыгэ Хэку, Адыгей, lit=, translit=Adıgə Xəku, Adıgey; ; ota, چرکسستان, Çerkezistan; ) was a country and a historical region in the along the northeast ...
and the modern North Ossetia–Alania. At its height, Alania was a centralized monarchy with a strong military force and had a strong economy that benefited from the Silk Road.
After the Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
invasions of the 1200s, the Alans were forced out of their medieval homeland south of the River Don in present-day Russia. Due to this, the Alans migrated toward the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
Mountains, where they would form three ethnographical groups; the Iron, the Digoron and the Kudar. The Jassic people
The Jász (''Latin'': Jazones) are an Eastern Iranic ethnic group who have lived in Hungary since the 13th century. They live mostly in a region known as ''Jászság'', which comprises the north-western part of Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. ...
were a fourth group that migrated in the 13th century to Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
.
Modern history
 In more-recent history, the Ossetians participated in the
In more-recent history, the Ossetians participated in the Ossetian–Ingush conflict
The East Prigorodny conflict, also referred to as the Ossetian–Ingush conflict, was an inter-ethnic conflict in the eastern part of the Prigorodny District in the Republic of North Ossetia–Alania, which started in 1989 and developed, in 1992 ...
(1991–1992) and Georgian–Ossetian conflicts ( 1918–1920, early 1990s) and in the 2008 South Ossetia war between Georgia and Russia.
Key events:
*1774 — Ossetia becomes part of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.
*1801 — After Russian annexation of the east Georgian kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti
The Kingdom of Kartli-Kakheti ( ka, ქართლ-კახეთის სამეფო, tr) (1762–1801
) was created in 1762 by the unification of two eastern Georgian kingdoms of Kartli and Kakheti. From the early 16th century, accord ...
, the modern-day territory of South Ossetia becomes part of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
.
*1922 — Creation of the South Ossetian autonomous oblast
The South Ossetian Autonomous Oblast (russian: Юго-Осетинская автономная область, ka, სამხრეთ ოსეთის ავტონომიური ოლქი, os, Хуссар Ирыстоны ав� ...
. North Ossetia remains a part of the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
, while South Ossetia
South Ossetia, ka, სამხრეთი ოსეთი, ( , ), officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated populat ...
remains a part of the Georgian SSR
The Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic (Georgian SSR; ka, საქართველოს საბჭოთა სოციალისტური რესპუბლიკა, tr; russian: Грузинская Советская Соц� ...
.
*20 September 1990 – The independent Republic of South Ossetia is formed. Though it remained unrecognized, it detached itself from Georgia ''de facto''. In the last years of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, ethnic
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
tensions between Ossetians and Georgians in Georgia's former Autonomous Oblast of South Ossetia (abolished in 1990) and between Ossetians and Ingush in North Ossetia evolved into violent clashes that left several hundred dead and wounded and created a large tide of refugees on both sides of the border.
Ever since ''de facto'' independence, there have been proposals in South Ossetia of joining Russia and uniting with North Ossetia.
Language
The Ossetian language belongs to theEastern Iranian
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages emerging in Middle Iranian times (from c. the 4th century BC). The Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle Western Iranian dial ...
(Alanic
Alanic is a sports and fitness clothing brand headquartered in North Hollywood, California, USA. Alanic corporate offices are located at 1/49 Lemana lane, Sydney, Australia. It has been the official supplier of the Miami Marathon USA, Vancouve ...
) branch of the Indo-European language family
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
.
Ossetian is divided into two main dialect groups: Ironian ( os. – Ирон) in North and South Ossetia and Digorian ( os. – Дыгурон) in Western North Ossetia. In these two groups are some subdialects, such as Tualian, Alagirian and Ksanian. The Ironian dialect is the most widely spoken.
Ossetian is among the remnants of the Scytho-Sarmatian
The Scythian languages are a group of Eastern Iranian languages of the classical and late antique period (the Middle Iranian period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descend ...
dialect group, which was once spoken across the Pontic–Caspian Steppe. The Ossetian language is not mutually intelligible with any other Iranian language.
Religion
Prior to the 10th century, Ossetians were strictly pagan, though they were partiallyChristianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
by Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
missionaries in the beginning of the 10th century. By the 13th, gradually most of the urban population of Ossetia became Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
as a result of Georgian
Georgian may refer to:
Common meanings
* Anything related to, or originating from Georgia (country)
** Georgians, an indigenous Caucasian ethnic group
** Georgian language, a Kartvelian language spoken by Georgians
**Georgian scripts, three scrip ...
missionary work.
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
was introduced shortly after during the 1500s and 1600s, when the members of the Digor first encountered Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
of the Kabarday
The Kabardians ( Highland Adyghe: Къэбэрдей адыгэхэр; Lowland Adyghe: Къэбэртай адыгэхэр; russian: Кабардинцы) or Kabardinians are one of the twelve major Circassian tribes, representing one of t ...
tribe in Western Ossetia, who themselves had been introduced to the religion by Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
during the 1400s.
According to a 2013 estimate, up to 15% of North Ossetia’s population practice Islam.
In 1774, Ossetia became part of the in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, which only went on to strengthen Orthodox Christianity
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Chur ...
considerably, by having sent Russian Orthodox
Russian Orthodoxy (russian: Русское православие) is the body of several churches within the larger communion of Eastern Orthodox Christianity, whose liturgy is or was traditionally conducted in Church Slavonic language. Most ...
missionaries there. However, most of the missionaries chosen were churchmen from Eastern Orthodox communities living in Georgia, including Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
and Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, oth ...
, as well as ethnic Georgians. Russian missionaries themselves were not sent, as this would have been regarded by the Ossetians as too intrusive.
Today, the majority of Ossetians from both North and South Ossetia follow Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
.
Assianism
Assianism (, ''Watsdin'') is a modern Pagan religion derived from the traditional mythology of the Ossetians, modern descendants of the Scythians of the Alan tribes, believed to be a continuation of the ancient Scythian religion. The religion ...
(''Uatsdin'' or ''Aesdin'' in Ossetian), the Ossetian folk religion, is also widespread among Ossetians, with ritual traditions like animal sacrifices, holy shrines, annual festivities, etc. There are temples, known as ''kuvandon,'' in most villages. According to the research service ''Sreda'', North Ossetia is the primary center of Ossetian Folk religion and 29% of the population reported practicing the Folk religion in a 2012 survey. Assianism has been steadily rising in popularity since the 1980s.
Economy
The Northern Ossetians export lumber and cultivate various crops, mainly corn. The Southern Ossetians are chiefly pastoral, herding sheep, goats and other cattle. Traditional manufactured products include leather goods, fur headgear, daggers and metalware.Demographics
Outside ofSouth Ossetia
South Ossetia, ka, სამხრეთი ოსეთი, ( , ), officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated populat ...
, there are also a significant number of Ossetians living in Trialeti
Trialeti ( ka, თრიალეთი) is a mountainous area in central Georgia. In Georgian, its name means "a place of wandering". The Trialeti Range
Trialeti Range ( ka, თრიალეთის ქედი) is an east-west mountain ...
, in North-Central Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. A large Ossetian diaspora lives in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, Ossetians have also settled in Belgium, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
(primarily New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
), Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
(Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
), Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
(Sydney
Sydney ( ) is the capital city of the state of New South Wales, and the most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Located on Australia's east coast, the metropolis surrounds Sydney Harbour and extends about towards the Blue Mountain ...
) and other countries all around the world.
Russian Census of 2002
The vast majority of Ossetians live in Russia (according to theRussian Census (2002)
The Russian Census of 2002 (russian: Всеросси́йская пе́репись населе́ния 2002 го́да) was the first census of the Russian Federation since the dissolution of the Soviet Union, carried out on October 9 through Oc ...
):
* North Ossetia–Alania — 445,300
* Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
— 10,500
* Kabardino-Balkaria
The Kabardino-Balkarian Republic (russian: Кабарди́но-Балка́рская Респу́блика, ''Kabardino-Balkarskaya Respublika''; kbd, Къэбэрдей-Балъкъэр Республикэ, ''Ķêbêrdej-Baĺķêr Respublik� ...
— 9,800
*
Krasnodar Krai
Krasnodar Krai (russian: Краснода́рский край, r=Krasnodarsky kray, p=krəsnɐˈdarskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the North Caucasus region in Southern Russia and administratively a part of ...
— 4,100
* Karachay–Cherkessia
The Karachay-Cherkess Republic (russian: Карача́ево-Черке́сская Респу́блика, ''Karachayevo-Cherkesskaya Respublika''; krc, Къарачай-Черкес Республика, ''Qaraçay-Çerkes Respublika''; Cir ...
— 3,200
*Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
— 2,800
*Moscow Oblast
Moscow Oblast ( rus, Моско́вская о́бласть, r=Moskovskaya oblast', p=mɐˈskofskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ), or Podmoskovye ( rus, Подмоско́вье, p=pədmɐˈskovʲjə, literally "under Moscow"), is a federal subject of Rus ...
— 2,400
Genetics
The Ossetians are a unique ethnic group of the Caucasus, speaking an Indo-Iranian language surrounded mostly by Vainakh-Dagestani and Abkhazo-Circassian ethnolinguistic groups, as well as Turkic tribes such as theKarachays
The Karachays ( krc, Къарачайлыла, Qaraçaylıla or таулула, , 'Mountaineers') are an indigenous Caucasian Turkic ethnic group in the North Caucasus. They speak Karachay-Balkar, a Turkic language. They are mostly situa ...
and the Balkars
The Balkars ( krc, Малкъарлыла, Malqarlıla or Таулула, , 'Mountaineers') are a Turkic people of the Caucasus region, one of the titular populations of Kabardino-Balkaria. Their Karachay-Balkar language is of the Ponto-Ca ...
.
The Y-haplogroup data indicate that North Ossetians are more similar to other North Caucasian groups, and South Ossetians to other South Caucasian groups, than the two are to each other. With respect to mtDNA, Ossetians are significantly more similar to some Iranian groups than to Caucasian groups. It is thus suggested that there is a common origin of Ossetians from the Proto-Iranian Urheimat, followed by subsequent male-mediated migrations from their Caucasian neighbours.
Gallery
Gaito Gazdanov
Gaito Gazdanov (russian: Гайто́ (Гео́ргий) Ива́нович Газда́нов, ''Gaito'' 'Georgii'Ivanovich Gazdanov''; os, Гæздæнты Бæппийы фырт Гайто, ''Gæzdænty Bæppijy fyrt Gajto''; 5 December ...
, writer
File:Sergei Guriev.jpg, Sergei Guriev
Sergey Maratovich Guriyev (russian: Серге́й Мара́тович Гури́ев, os, Гуриаты Мараты фырт Сергей / Gwyriaty Maraty fyrt Sergej) is a Russian economist, who is Provost and a professor of economics at t ...
, economist
File:Bagraev.jpg, Nikolay Bagrayev, politician
File:South Ossetian performers.JPG, South Ossetian performers
File:Barry (capitaine). F. 17. Ossèthe (Ossète), Koban. Mission scientifique de Mr Ernest Chantre. 1881.jpg, Ossetian man in 1881
File:Soslan Ramonov 2015.jpg, Soslan Ramonov, wrestler
File:Shota Bibilov 2011.jpg, Shota Bibilov
Shota Gennadyevich Bibilov (russian: Шота Геннадьевич Бибилов; born 6 August 1990) is a Russian former professional footballer of Ossetian descent.
Club career
He made his professional debut in the Russian First Divisio ...
, professional footballer
File:Ruslan Karaev.JPG, Ruslan Karaev
Ruslan Savelyevich Karaev (Karayev) (russian: Русла́н Саве́льевич Кара́ев, Ruslan Savelyevich Karayev; os, Хъараты Савелийы фырт Руслан, Qaraty Savelijy fyrt Ruslan; born May 19, 1983) is a Russ ...
, professional kickboxer
File:Gabulov.JPG, Vladimir Gabulov
Vladimir Borisovich Gabulov ( rus, Владимир Борисович Габулов, p=vlɐˈdʲimɪr bɐˈrʲisəvʲɪtɕ gɐˈbuləf, os, Гæбулты Борисы фырт Владимир, ''Gabulte Boriše fert Vlâdimir'', born 19 Oct ...
, Ossetian goalkeeper
File:Valery Gergiev David Shankbone 2010.jpg, Valery Gergiev
Valery Abisalovich Gergiev (russian: Вале́рий Абиса́лович Ге́ргиев, ; os, Гергиты Абисалы фырт Валери, Gergity Abisaly fyrt Valeri; born 2 May 1953) is a Russian conductor and opera company d ...
, conductor
See also
*Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
*Asud
The Asud (Mongolian Cyrillic: , IPA: //) were a military group of Alani origin. The Mongol clan Asud is the plural of As, the Arabic name for the Alans.
Against the Alans and the Cumans (Kipchaks), the Mongols used divide and conquer tactics by ...
* Digor (people)
*Iazyges
The Iazyges (), singular Ἰάζυξ. were an ancient Sarmatian tribe that traveled westward in BC from Central Asia to the steppes of modern Ukraine. In BC, they moved into modern-day Hungary and Serbia near the Dacian steppe between th ...
* Iron (people)
*Jassic people
The Jász (''Latin'': Jazones) are an Eastern Iranic ethnic group who have lived in Hungary since the 13th century. They live mostly in a region known as ''Jászság'', which comprises the north-western part of Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. ...
* Alexander Kubalov
* Ossetians in Trialeti
*Ossetians in Turkey
Ossetians in Turkey are citizens and denizens of Turkey who are, or descend from, ethnic Ossetians who originate in Ossetia in the Caucasus.
History
An estimated 50,000 Ossetes left the Russian Caucasus during the early 1860s as part of a greater ...
* Peoples of the Caucasus
*Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th cen ...
*Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
*Terek Cossacks
The Terek Cossack Host (russian: Терское казачье войско, ''Terskoye kazach'ye voysko'') was a Cossack host created in 1577 from free Cossacks who resettled from the Volga to the Terek River. The local aboriginal Terek Cossack ...
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
Ossetians.com – a site about famous Ossetians
{{Authority control Alans Ethnic groups in Russia Ethnic groups in Turkey Ethnic groups in Syria Iranian ethnic groups Iranian peoples in the Caucasus Peoples of the Caucasus