|
Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern * : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." * : "Near the end of the 19th century V.F. Miller (1886, 1887) theorized that the Scythians and their kindred, the Sauromatians, were Iranian-speaking peoples. This has been a popular point of view and continues to be accepted in linguistics and historical science .. * : "From the end of the 7th century B.C. to the 4th century B.C. the Central- Eurasian steppes were inhabited by two large groups of kin Iranian-speaking tribes – the Scythians and Sarmatians .. * : "All contemporary historians, archeologists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
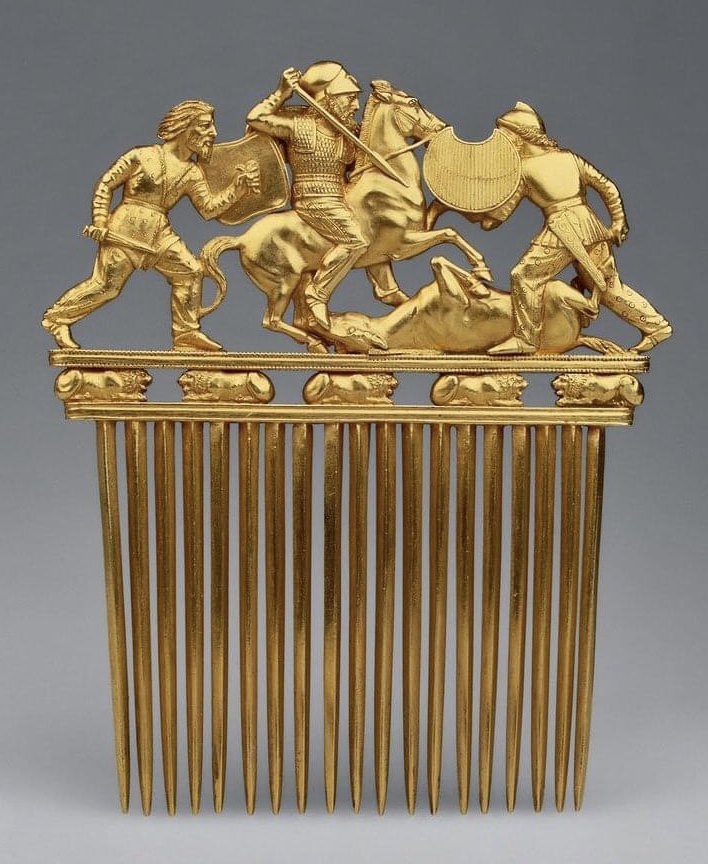
Scythian Comb
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern * : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." * : "Near the end of the 19th century V.F. Miller (1886, 1887) theorized that the Scythians and their kindred, the Sauromatians, were Iranian-speaking peoples. This has been a popular point of view and continues to be accepted in linguistics and historical science .. * : "From the end of the 7th century B.C. to the 4th century B.C. the Central- Eurasian steppes were inhabited by two large groups of kin Iranian-speaking tribes – the Scythians and Sarmatians .. * : "All contemporary historians, archeologists and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Culture
The Scythian culture was an Iron Age archaeological culture which flourished on the Pontic-Caspian steppe in Eastern Europe from about 700 BC to 200 AD. It is associated with the Scythians and other peoples inhabiting the region of Scythia, and was part of the wider Scytho-Siberian world. Chronology The Scythian Culture can be divided into three stages: * Early Scythian – from the mid-8th or the late 7th century BC to about 500 BC * Mid-Scythian or Classical Scythian – from about 500 BC to about 200 BC * Late Scythian – from about 200 BC to the mid-3rd century AD, in the Crimea and the Lower Dnipro, by which time the population was settled. Development Early Scythian The Early Scythian Culture emerged during the 8th century BC. Since the Scythians were nomads who did not create permanent settlements, the Early Scythian culture is known primarily from Scythian funerary sites. The earliest Scythians had belonged to the Srubnaya culture in its Srubnaya-Khvalynsk form, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Religion
The Scythian religion refers to the mythology, ritual practices and beliefs of the Scythian cultures, a collection of closely related ancient Iranian peoples who inhabited Central Asia and the Pontic–Caspian steppe in Eastern Europe throughout Classical Antiquity, spoke the Scythian language (itself a member of the Eastern Iranian language family), and which included the Scythians proper, the Cimmerians, the Sarmatians, the Alans, the Sindi, the Massagetae and the Saka. The Scythian religion is assumed to have been related to the earlier Proto-Indo-Iranian religion as well as to contemporary Eastern Iranian and Ossetian traditions, and to have influenced later Slavic, Hungarian and Turkic mythologies. Development The Scythian religion was of Iranian origin. The religion was influenced by that of the populations whom the Scythians had conquered, such as the sedentary Thracian populations of the western Pontic steppe. Due to this, many of the Scythian male deities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who historically inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin. "Modern scholars have mostly used the name Saka to refer specifically to Iranians of the Eastern Steppe and Tarim Basin" "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." The Sakas were closely related to the European Scythians, and both groups formed part of the wider Scythian cultures and ultimately derived from the earlier Andronovo culture, and the Saka language formed part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into West Asia. Although the Cimmerians were culturally Scythian, they formed an ethnic unit separate from the Scythians proper, to whom the Cimmerians were related and who displaced and replaced the Cimmerians.: "As the Cimmerians cannot be differentiated archeologically from the Scythians, it is possible to speculate about their Iranian origins. In the Neo-Babylonian texts (according to D’yakonov, including at least some of the Assyrian texts in Babylonian dialect) and similar forms designate the Scythians and Central Asian Saka, reflecting the perception among inhabitants of Mesopotamia that Cimmerians and Scythians represented a single cultural and economic group" The Cimmerians themselves left no written records, and most information abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massagetae
The Massagetae or Massageteans (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Sakā tigraxaudā (Old Persian: , "wearer of pointed caps") or Orthocorybantians (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ),: As for the term “Orthocorybantii”, this is a translation of Iranian “wearers of pointed caps”: "The (who wear pointed caps) were known to Greek authors as the , a direct translation of the Old Persian name" were an ancient Eastern Iranian Saka people who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia and were part of the wider Scythian cultures. The Massagetae rose to power in the 8th to 7th centuries BCE, when they kickstarted a series of events with wide-reaching consequences by expelling the Scythians out of Central Asia and into the Caucasian and Pontic Steppes. The Massagetae are most famous for their queen Tomyris's defeating and killing of Cyrus, the founder of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The Massagetae declined after the 3rd century BCE, after which they merged with some other trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; grc, Σαρμαται, Sarmatai; Latin: ) were a large confederation of ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples of classical antiquity who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th century AD. Originating in the central parts of the Eurasian Steppe, the Sarmatians were part of the wider Scythian cultures. They started migrating westward around the fourth and third centuries BC, coming to dominate the closely related Scythians by 200 BC. At their greatest reported extent, around 100 BC, these tribes ranged from the Vistula River to the mouth of the Danube and eastward to the Volga, bordering the shores of the Black and Caspian seas as well as the Caucasus to the south. In the first century AD, the Sarmatians began encroaching upon the Roman Empire in alliance with Germanic tribes. In the third century AD, their dominance of the Pontic Steppe was broken by the Germanic Goths. With the Hunnic invasions of the fourth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities. The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe, from the Great Hungarian Plain in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the steppes and the wooded steppes and even the semi-deserts from the Great Hungarian Plain to the Ordos in northern China." T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Iranian Peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities. The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe, from the Great Hungarian Plain in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the steppes and the wooded steppes and even the semi-deserts from the Great Hungarian Plain to the Ordos in northern China." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to the Scythians. Name The name () is the Hellenized form of a Scythian name whose original form is not attested. The linguist Alexis Manaster Ramer has reconstructed it as or , or as or , meaning "prospering the friend/socius", with the final part modified into , referring to the composite vegetal wand of Bacchus, in Greek because the ancient Greeks associated Scythian peoples with Bacchic rites. Location At the time when the Greek historian Herodotus described them, in the 5th century BC, the Agathyrsi occupied the region around the source of the Maris river, in the mountainous part of ancient Dacia now known as Transylvania in what in the present-day is the state of Romania, as well as in the regions corresponding to moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Languages
The Scythian languages are a group of Eastern Iranian languages of the classical and late antique period (the Middle Iranian period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descendants. The dominant ethnic groups among the Scythian-speakers were nomadic pastoralists of Central Asia and the Pontic–Caspian steppe. Fragments of their speech known from inscriptions and words quoted in ancient authors as well as analysis of their names indicate that it was an Indo-European language, more specifically from the Iranian group of Indo-Iranian languages. Most of the Scythian languages eventually became extinct, except for modern Ossetian (which descends from the Alanian dialect of Scytho-Sarmatian), Wakhi (which descends from the Khotanese and Tumshuqese forms of Scytho-Khotanese), and Yaghnobi (which descends from Sogdian). Alexander Lubotsky summarizes the known linguistic landscape as follows: Classif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetians
The Ossetians or Ossetes (, ; os, ир, ирæттæ / дигорӕ, дигорӕнттӕ, translit= ir, irættæ / digoræ, digorænttæ, label=Ossetic) are an Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the northern and southern sides of the Caucasus Mountains. They natively speak Ossetic, an Eastern Iranian language of the Indo-European language family, with most also being fluent in Russian as a second language. Ossetic, a remnant of the Scytho-Sarmatian dialect group which was once spoken across the Pontic–Caspian Steppe, is one of the few Iranian languages remaining inside Europe. Currently, the Ossetian homeland of Ossetia is politically divided between North Ossetia–Alania in Russia, and the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Their closest historical and linguistic relatives, the Jász people, live in the Jászság region withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |