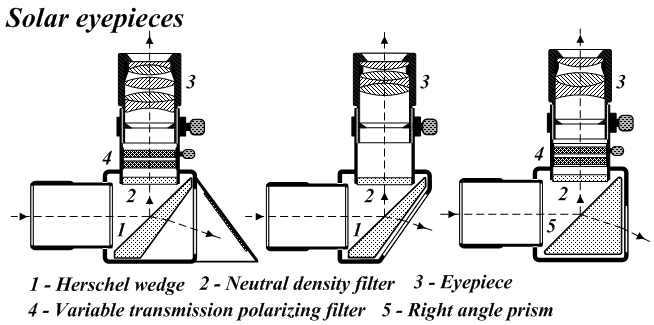
|
Karl-Otto Kiepenheuer
Karl-Otto Kiepenheuer (10 November 1910 – 23 May 1975) was a German astronomer and astrophysicist. His research focused on the Sun, and for that purpose he initiated construction of several solar telescopes and founded the Kiepenheuer Institute for Solar Physics. Life and work Kiepenheuer was born in 1910 in Weimar, Germany, as a son of the publisher Gustav Kiepenheuer. After the divorce of his parents in 1923 he stayed with his mother. In 1929, he began his studies of physics, astronomy and mathematics at the Berlin Institute of Technology and the University of Berlin. He spent one semester in Paris where he visited the Paris Observatory, Meudon observatory. He later worked at the Göttingen Observatory where he tried to develop a method to measure the UV radiation of the Sun. After an unsuccessful attempt at Jungfraujoch, he realized that the elevation of 3,454 meters was insufficient for this measurement. The balloon-borne instruments of Erich Regener proved to be more useful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouring cities of Erfurt and Jena, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia, with approximately 500,000 inhabitants. The city itself has a population of 65,000. Weimar is well known because of its large cultural heritage and its importance in German history. The city was a focal point of the German Enlightenment and home of the leading figures of the literary genre of Weimar Classicism, writers Johann Wolfgang von Goethe and Friedrich Schiller. In the 19th century, noted composers such as Franz Liszt made Weimar a music centre. Later, artists and architects such as Henry van de Velde, Wassily Kandinsky, Paul Klee, Lyonel Feininger, and Walter Gropius came to the city and founded the Bauhaus movement, the most important German de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Regener
Erich Rudolf Alexander Regener (12 November 1881 – 27 February 1955) was a German physicist known primarily for the design and construction of instruments to measure cosmic ray intensity at various altitudes. He is also known for predicting a cosmic background radiation, for the invention of the scintillation counter which contributed to the discovery of the structure of the atom, for his calculation of the charge of an electron and for his early work on atmospheric ozone. He is also credited with the first use of rockets for scientific research. Regener was born in Schleusenau (Wilczak) near Bromberg (Bydgoszcz), West Prussia. He studied physics from 1900 to 1905 at the University of Berlin under Emil Warburg and from 1909 worked with Heinrich Rubens. In 1911 he became professor of experimental physics and meteorology at the Agricultural University of Berlin. In 1920 he became the professor in experimental physics at the University of Stuttgart working alongside the theo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schauinsland
The Schauinsland (literally "look-into-the-country"; near Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany) is a mountain in the Black Forest with an elevation of 1,284 m (4,213 ft) above sea level. It is a popular destination for day trips. Due to the high amount of silver mining, it was previously known as "Erzkasten" (literally "ore box"); the name "Schouwesland" first appeared in 1347. The mountain is located roughly ten kilometres (6 miles) south-east of Freiburg’s city centre. Geography The summit of the Schauinsland is located in the district of Freiburg. The mountain is surrounded by towns such as Oberried, Munstertal, Bollschweil, and Horben (clockwise). The closest village to the summit is Hofsgrund. In Autumn especially, during a temperature inversion, there is a clear view of the Vosges mountains from the top of the Schauinsland. Under appropriate weather conditions there is a view of a large portion of the Swiss Alps. Since 2003, the Holzschlägermatte on the Scha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Telescopes
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verlag Harri Deutsch
The (VHD, HD) with headquarters in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, as well as in Zürich and Thun, Switzerland, was a German publishing house founded in 1961 and closed in 2013. Overview The ' with headquarters in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, was a German publishing house founded by Harri Deutsch in 1961 as a spin-off of the scientific bookstore Fachbuchhandlung Harri Deutsch (FHD), which had existed for about a decade earlier. Both were situated near Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main. Between 1963 and about 1979 the publisher also had an office in Zürich. Around 1974 another branch was opened in Thun. The company's activities focussed mostly on textbooks and encyclopedic works in the areas of mathematics, physics, chemistry and other sciences and technologies, in the first three decades in particular titles licensed from publishers of the former Eastern Bloc including the East-German publishers Edition Leipzig, , Akademie Verlag, VEB Bibliographisches Institut, VEB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syracuse, Sicily
Syracuse ( ; it, Siracusa ; scn, Sarausa ), ; grc-att, Συράκουσαι, Syrákousai, ; grc-dor, Συράκοσαι, Syrā́kosai, ; grc-x-medieval, Συρακοῦσαι, Syrakoûsai, ; el, label=Modern Greek, Συρακούσες, Syrakoúses, . is a historic city on the Italian island of Sicily, the capital of the Italian province of Syracuse. The city is notable for its rich Greek and Roman history, culture, amphitheatres, architecture, and as the birthplace of the pre-eminent mathematician and engineer Archimedes. This 2,700-year-old city played a key role in ancient times, when it was one of the major powers of the Mediterranean world. Syracuse is located in the southeast corner of the island of Sicily, next to the Gulf of Syracuse beside the Ionian Sea. It is situated in a drastic rise of land with depths being close to the city offshore although the city itself is generally not so hilly in comparison. The city was founded by Ancient Greek Corinthians and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the sea co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø. Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the 21st largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. With a population of 77,544, Tromsø is the 12th most populous municipality in Norway. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 12.2% over the previous 10-year period. It is the largest urban area in Northern Norway and the third largest north of the Arctic Circle anywhere in the world (following Murmansk and Norilsk). The city center of Tromsø is located on the island of Tromsøya, but the urban area also encompasses part of the nearby mainland and part of the island Kvaløya. Tromsø is north of the Arctic Circle. Tromsøya is connected to the mainland by the Tromsø Bridge and the Tromsøysund Tunnel, and to the island of Kvaløya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, Fashion capital, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called Caput Mundi#Paris, the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a population of 2.4 million. The peninsula is almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Sivash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. Crimea (called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period) has historically been at the boundary between the classical world and the steppe. Greeks colonized its southern fringe and were absorbed by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeiz Observatory
Simeiz Observatory (also spelled Simeis or Simeïs) was an astronomy research observatory until the mid-1950s. It is located on Mount Koshka, Crimea, , by the town of Simeiz. Part of the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory, it is currently used for laser based studies of the orbits of satellites. The Minor Planet Center (MPC) credits Simeiz Observatory as the location where a total of 150 minor planets were discovered by astronomers Grigory Neujmin, Sergey Belyavsky, Vladimir Albitsky, Grigory Shajn, Nikolaj Ivanov, Pelageya Shajn, Praskov'ja Parchomenko, Alexander Deutsch and Evgenij Skvorcov. As of 2017, the discovery of the minor planet is directly credited to Simeiz Observatory by the MPC. History The Simeiz Observatory was founded by Russian amateur astronomer Nikolai Maltsov, who later became a honored member of the Russian Academy of Sciences and after whom asteroid 749 Malzovia was named. In 1900, he built a tower for refractor at his land plot near Sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using shortwave (SW) radio frequencies. There is no official definition of the band, but the range always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (100 to 10 metres); above the medium frequency band (MF), to the bottom of the VHF band. Radio waves in the shortwave band can be reflected or refracted from a layer of electrically charged atoms in the atmosphere called the ionosphere. Therefore, short waves directed at an angle into the sky can be reflected back to Earth at great distances, beyond the horizon. This is called skywave or "skip" propagation. Thus shortwave radio can be used for communication over very long distances, in contrast to radio waves of higher frequency, which travel in straight lines (line-of-sight propagation) and are limited by the visual horizon, about 64 km (40 miles). Shortwave broadcasts of radio programs played an important role in the early days of radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |