|
KPNB1
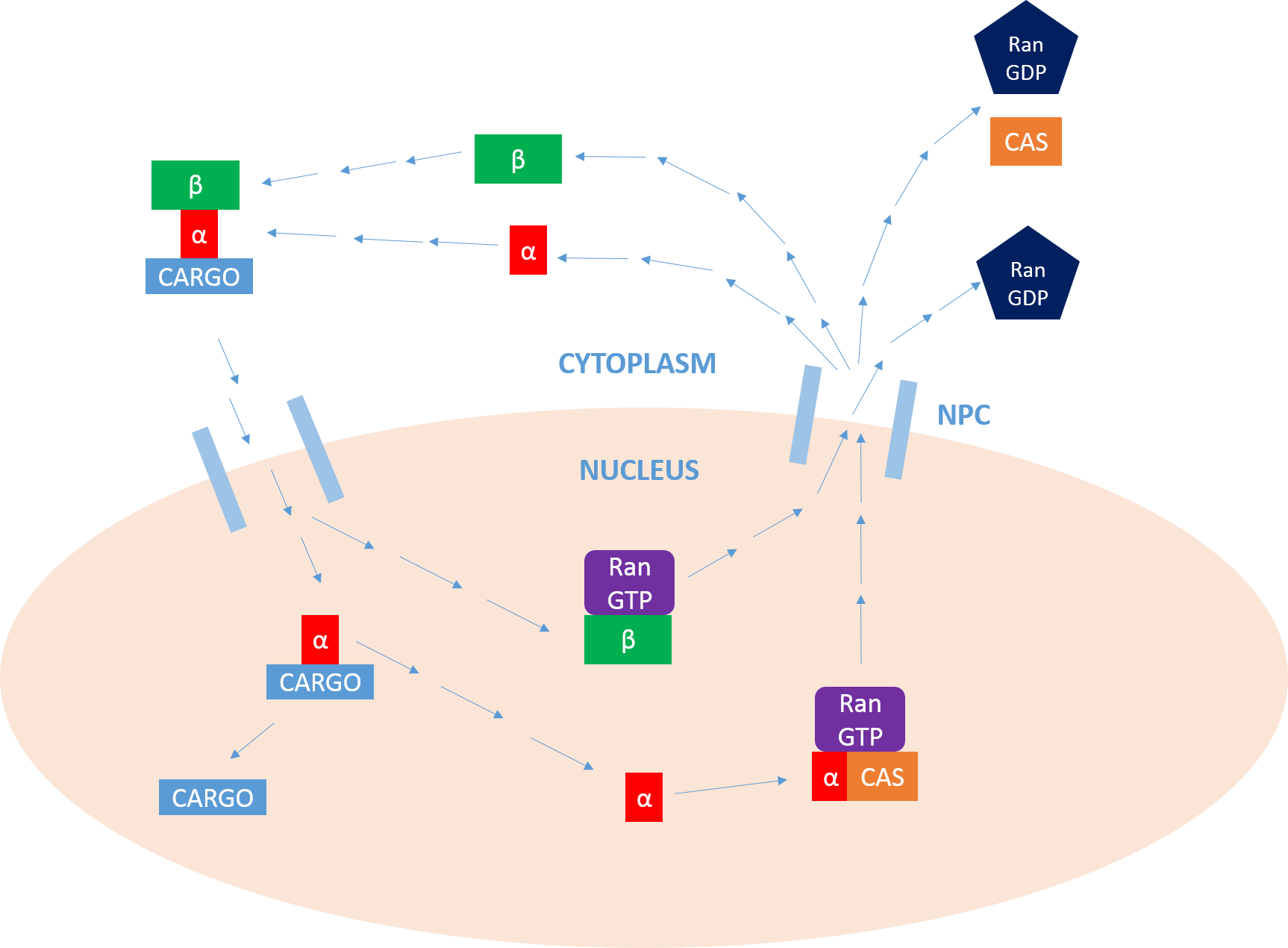
Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNB1'' gene. Function Nucleocytoplasmic transport, a signal- and energy-dependent process, takes place through nuclear pore complexes embedded in the nuclear envelope. The import of proteins containing a classical nuclear localization signal (NLS) requires the NLS import receptor, a heterodimer of importin alpha and beta subunits. Each of these subunits are part of the karyopherin family of proteins. Importin alpha binds the NLS-containing cargo in the cytoplasm and importin beta docks the complex at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex. In the presence of nucleoside triphosphates and the small GTP binding protein Ran, the complex moves into the nuclear pore complex and the importin subunits dissociate. Importin alpha enters the nucleoplasm with its passenger protein and importin beta remains at the pore. Interactions between importin beta and the FG repeats of nucleoporins are essential in tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Importin
Importin is a type of karyopherin that transports protein molecules from the cell's cytoplasm to the nucleus. It does so by binding to specific recognition sequences, called nuclear localization sequences (NLS). Importin has two subunits, importin α and importin β. Members of the importin-β family can bind and transport cargo by themselves, or can form heterodimers with importin-α. As part of a heterodimer, importin-β mediates interactions with the pore complex, while importin-α acts as an adaptor protein to bind the nuclear localization signal (NLS) on the cargo. The NLS-Importin α-Importin β trimer dissociates after binding to Ran GTP inside the nucleus, with the two importin proteins being recycled to the cytoplasm for further use. Discovery Importin can exist as either a heterodimer of importin-α/β or as a monomer of Importin-β. Importin-α was first isolated in 1994 by a group includinEnno Hartmann based at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine. The p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ran (biology)
Ran (RAs-related Nuclear protein) also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase and also involved in mitosis. It is a member of the Ras superfamily. Ran is a small G protein that is essential for the translocation of RNA and proteins through the nuclear pore complex. The Ran protein has also been implicated in the control of DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression, as mutations in Ran have been found to disrupt DNA synthesis. Function Ran cycle Ran exists in the cell in two nucleotide-bound forms: GDP-bound and GTP-bound. RanGDP is converted into RanGTP through the action of RCC1, the nucleotide exchange factor for Ran. RCC1 is also known as RanGEF (Ran Guanine nucleotide Exchange Factor). Ran's intrinsic GTPase-activity is activated through interaction with Ran GTPase activating protein (RanGAP), facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyopherin Alpha 1
Importin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA1'' gene. Interactions Importin subunit alpha-5 has been shown to interact with KPNB1 and UBR5 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''UBR5'' gene. Function This gene encodes a progestin-induced protein, which belongs to the HECT (homology to E6-AP carboxyl terminus) family. The HECT family protei .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Armadillo-repeat-containing proteins {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RANBP2
RAN binding protein 2 (RANBP2) is protein which in humans is encoded by the ''RANBP2'' gene. It is also known as nucleoporin 358 (Nup358) since it is a member nucleoporin family that makes up the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2 has a mass of 358 kDa. Function RAN is a small GTP-binding protein of the RAS superfamily. Ran GTPase is a master regulatory switch, which among other functions, controls the shuttling of proteins between the nuclear and cytoplasm compartments of the cell. Ran GTPase controls a variety of cellular functions through its interactions with other proteins. The ''RanBP2'' gene encodes a very large RAN-binding protein that localizes to cytoplasmic filaments emanating from the nuclear pore complex. RanBP2/Nup358 is a giant scaffold and mosaic cyclophilin-related nucleoporin implicated in controlling selective processes of the Ran-GTPase cycle. RanBP2 is composed of multiple domains. Each domain of RanBP2 selectively and directly interacts with distinct proteins suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RANBP1
Ran-specific binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RANBP1'' gene. Ran/TC4-binding protein, RanBP1, interacts specifically with GTP-charged RAN. RANBP1 encodes a 23-kD protein that binds to RAN complexed with GTP but not GDP. RANBP1 does not activate GTPase activity of RAN but does markedly increase GTP hydrolysis by the RanGTPase-activating protein (RANGAP1). The RANBP1 cDNA encodes a 201-amino acid protein that is 92% similar to its mouse homolog. In both mammalian cells and in yeast, RANBP1 acts as a negative regulator of RCC1 by inhibiting RCC1-stimulated guanine nucleotide release from RAN. Interactions RANBP1 has been shown to interact with XPO1, KPNB1 and Ran Ran, RaN and ran may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Ran'' (film), a 1985 film directed by Akira Kurosawa * "Ran" (song), a 2013 Japanese song by Luna Sea * '' Ran Online'', a 2004 MMORPG (massively multiplayer online role playing game) * .... References Further reading * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein
Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP) is a proteinaceous hormone and a member of the parathyroid hormone family secreted by mesenchymal stem cells. It is occasionally secreted by cancer cells (for example, breast cancer, certain types of lung cancer including squamous-cell lung carcinoma). However, it also has normal functions in bone, teeth, vascular tissues and other tissues. Function PTHrP acts as an endocrine, autocrine, paracrine, and intracrine hormone. It regulates endochondral bone development by maintaining the endochondral growth plate at a constant width. It also regulates epithelial–mesenchymal interactions during the formation of the mammary glands. PTHrP plays a major role in regulating calcium homeostasis in vertebrates, including sea bream, chick, and mammals. In 2005, Australian pathologist and researcher Thomas John Martin found that PTHrP produced by osteoblasts is a physiological regulator of bone formation. Martin and Miao ''et al.'' demonstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleoporin 62
Nuclear pore glycoprotein p62 is a protein complex associated with the nuclear envelope. The p62 protein remains associated with the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. p62 is synthesized as a soluble cytoplasmic precursor of 61 kDa followed by modification that involve addition of N-acetylglucosamine residues, followed by association with other complex proteins. In humans it is encoded by the ''NUP62'' gene. The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure that extends across the nuclear envelope, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nucleoporins are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the FG repeat containing nucleoporins and is localized to the nuclear pore central plug. This protein associates with the importin alpha/beta complex which is involved in the import of proteins containing nuclear localization signals. Multiple transcript va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NUP98
Nuclear pore complex protein Nup98-Nup96 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUP98'' gene. Function Signal-mediated nuclear import and export proceed through the nuclear pore complex (NPC), which is composed of approximately 30 unique proteins collectively known as nucleoporins. The 98 kD nucleoporin is generated through a biogenesis pathway that involves synthesis and proteolytic cleavage of a 186 kD precursor protein. This cleavage results in the 98 kD nucleoporin as well as a 96 kD nucleoporin, both of which are localized to the nucleoplasmic side of the NPC. Rat studies show that the 98 kD nucleoporin functions as one of several docking site nucleoporins of transport substrates. The human gene has been shown to fuse to several genes following chromosome translocations in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (T-ALL). This gene is one of several genes located in the imprinted gene domain of 11p15.5, an important tumor-suppressor gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NUP50
Nucleoporin 50 (Nup50) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUP50'' gene. The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure that extends across the nuclear envelope, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nucleoporins are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the FG-repeat containing nucleoporins that functions as a soluble cofactor in importin-alpha:beta-mediated nuclear protein import. Pseudogenes of this gene are found on chromosomes 5, 6, and 14. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Interactions NUP50 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with KPNB1 and CDKN1B. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * Nuclear pore complex {{gene-22-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NUP153
Nucleoporin 153 (Nup153) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NUP153'' gene. It is an essential component of the basket of nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) in vertebrates, and required for the anchoring of NPCs. It also acts as the docking site of an importing karyopherin. On the cytoplasmic side of the NPC, Nup358 fulfills an analogous role. Background Nuclear pore complexes are extremely elaborate structures that mediate the regulated movement of macromolecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. These complexes are composed of at least 100 different polypeptide subunits, many of which belong to the nucleoporin family. Nucleoporins are pore complex-specific glycoproteins characterized by cytoplasmically oriented O-linked N-acetylglucosamine residues and numerous repeats of the pentapeptide sequence XFXFG. Structure Nucleoporin 153 has a mass of 153 kDA (hence its name). It is filamentous and it contains three distinct domains: a N-terminal region within which a pore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyopherin Alpha 2
Importin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA2'' gene. The import of proteins into the nucleus is a process that involves at least 2 steps. The first is an energy-independent docking of the protein to the nuclear envelope and the second is an energy-dependent translocation through the nuclear pore complex. Imported proteins require a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) which generally consists of a short region of basic amino acids or 2 such regions spaced about 10 amino acids apart. Proteins involved in the first step of nuclear import are members of the alpha importin family of karyopherins such as importin subunit alpha-1. These include the ''Xenopus'' protein importin and its yeast homolog, SRP1 (a suppressor of certain temperature-sensitive mutations of RNA polymerase I in ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae''), which bind to the NLS. KPNA2 protein interacts with the NLSs of DNA helicase Q1 and SV40 T antigen and may be involved in the nuclear tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KPNA3
Importin subunit alpha-4 also known as karyopherin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNA3'' gene. The transport of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in eukaryotic cells is mediated by the nuclear pore complex (NPC) which consists of 60–100 proteins and is probably 120 million daltons in molecular size. Small molecules (up to 70 kD) can pass through the nuclear pore by nonselective diffusion; larger molecules are transported by an active process. Most nuclear proteins contain short basic amino acid sequences known as nuclear localization signals (NLSs). KPNA3, encodes a protein similar to certain nuclear transport proteins of Xenopus and human. The predicted amino acid sequence shows similarity to Xenopus importin, yeast SRP1, and human RCH1 (KPNA2), respectively. The similarities among these proteins suggests that karyopherin alpha-3 may be involved in the nuclear transport system. Interactions KPNA3 has been shown to interact with KP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |