|
NUP98
Nuclear pore complex protein Nup98-Nup96 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUP98'' gene. Function Signal-mediated nuclear import and export proceed through the nuclear pore complex (NPC), which is composed of approximately 30 unique proteins collectively known as nucleoporins. The 98 kD nucleoporin is generated through a biogenesis pathway that involves synthesis and proteolytic cleavage of a 186 kD precursor protein. This cleavage results in the 98 kD nucleoporin as well as a 96 kD nucleoporin, both of which are localized to the nucleoplasmic side of the NPC. Rat studies show that the 98 kD nucleoporin functions as one of several docking site nucleoporins of transport substrates. The human gene has been shown to fuse to several genes following chromosome translocations in acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) and T-cell acute lymphocytic leukemia (T-ALL). This gene is one of several genes located in the imprinted gene domain of 11p15.5, an important tumor-suppressor g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
RAE1
mRNA export factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAE1'' gene. Mutations in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Rae1 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae Gle2 genes have been shown to result in accumulation of poly(A)-containing mRNA in the nucleus, suggesting that the encoded proteins are involved in RNA export. The protein encoded by this gene is a homolog of yeast Rae1. It contains four WD40 motifs, and has been shown to localize to distinct foci in the nucleoplasm, to the nuclear rim, and to meshwork-like structures throughout the cytoplasm. This gene is thought to be involved in nucleocytoplasmic transport, and in directly or indirectly attaching cytoplasmic mRNPs to the cytoskeleton. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. Interactions RAE1 has been shown to interact with NUP98 Nuclear pore complex protein Nup98-Nup96 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUP98'' gene. Function Signal-mediated nuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
NUP88
Nucleoporin 88 (Nup88) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUP88'' gene. Function The nuclear pore complex is a massive structure that extends across the nuclear envelope, forming a gateway that regulates the flow of macromolecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Nucleoporins, a family of 50 to 100 proteins, are the main components of the nuclear pore complex in eukaryotic cells. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the nucleoporin family and is associated with the oncogenic nucleoporin CAN/Nup214 in a dynamic subcomplex. This protein is also overexpressed in a large number of malignant neoplasms and precancerous dysplasias. Interactions NUP88 has been shown to interact with NUP98 Nuclear pore complex protein Nup98-Nup96 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NUP98'' gene. Function Signal-mediated nuclear import and export proceed through the nuclear pore complex (NPC), which is composed of approximately 30 un .... References F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
KPNB1
Importin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KPNB1'' gene. Function Nucleocytoplasmic transport, a signal- and energy-dependent process, takes place through nuclear pore complexes embedded in the nuclear envelope. The import of proteins containing a classical nuclear localization signal (NLS) requires the NLS import receptor, a heterodimer of importin alpha and beta subunits. Each of these subunits are part of the karyopherin family of proteins. Importin alpha binds the NLS-containing cargo in the cytoplasm and importin beta docks the complex at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex. In the presence of nucleoside triphosphates and the small GTP binding protein Ran, the complex moves into the nuclear pore complex and the importin subunits dissociate. Importin alpha enters the nucleoplasm with its passenger protein and importin beta remains at the pore. Interactions between importin beta and the FG repeats of nucleoporins are essent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
TNPO2
Transportin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNPO2'' gene. Interactions TNPO2 has been shown to interact with NXF1, NUP98 and Ran (biology) Ran (RAs-related Nuclear protein) also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase .... References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid resid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
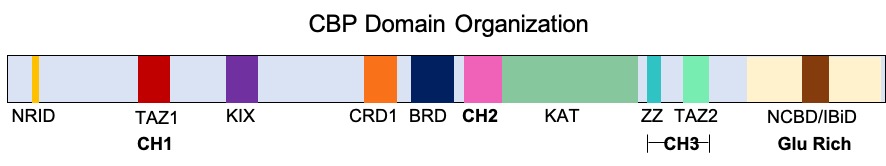 |
CREB-binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |