|
Jōban Line (Local)
The is a railway line in Japan operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). The line officially begins at Nippori Station in Arakawa, Tokyo before the line officially ends at Iwanuma Station in Iwanuma, Miyagi. However, following the opening of the Ueno–Tokyo Line, Jōban Line train services originate at or ; likewise, Jōban Line trains continue past Iwanuma onto the Tōhoku Main Line tracks to . The line approximately parallels the Pacific coasts of Chiba, Ibaraki, and Fukushima Prefectures. The name "Jōban" is derived from the names of the former provinces of Hitachi ( ja, 常陸, links=no), and Iwaki ( ja, 磐城, links=no), which are connected by the line to reach Tokyo. The section of the Jōban Line between and , which extends through the exclusion zone surrounding the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear meltdown, closed in the wake of the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster. After some major repairs, the section reopened o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 million residents ; the city proper has a population of 13.99 million people. Located at the head of Tokyo Bay, the prefecture forms part of the Kantō region on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. Tokyo serves as Japan's economic center and is the seat of both the Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. Originally a fishing village named Edo, the city became politically prominent in 1603, when it became the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. By the mid-18th century, Edo was one of the most populous cities in the world with a population of over one million people. Following the Meiji Restoration of 1868, the imperial capital in Kyoto was moved to Edo, which was renamed "Tokyo" (). Tokyo was devastate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ueno–Tokyo Line
The Ueno–Tokyo Line ( ja, 上野東京ライン, ), formerly known as the Tōhoku Through Line ( ja, 東北縦貫線, links=no, ) is a railway line in Tokyo, Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East), linking the Ueno Station and the Tokyo Station, extending the services of the Utsunomiya Line, the Takasaki Line, and the Joban Line southward and onto the Tokaido Main LineJR East Annual Report 2010 retrieved 2013-12-09 and vice versa. The project began in May 2008. The line opened with the 14 March 2015 timetable revision, with the project costing about JPY 40 billion. Direct travel was expected to ease congestion on the |
E653 Series
The is an AC/ DC dual-voltage electric multiple unit (EMU) train type operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) in Japan on limited express services since 1997. Originally used on Joban Line ''Fresh Hitachi'' limited express services between in Tokyo and , they were reallocated to for use on '' Inaho'' limited express services from 2013 and on '' Shirayuki'' limited express services from 2015. Variants * E653-0 series: Original (eight 7-car and four 4-car) AC/DC sets built from 1997 for use on Joban Line ''Fresh Hitachi'' limited express services * E653-1000 series: 7-car sets modified from E653-0 series between 2013 and 2014 for use on '' Inaho'' limited express services from September 2013 * E653-1100 series: 4-car sets modified from E653-0 series between 2014 and 2015 for use on '' Shirayuki'' limited express services from March 2015 Operations 1997-2013 ''Fresh Hitachi'' From their introduction in 1997, the E653 series trains operated on ''Fresh Hitachi'' limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
651 Series
The is an AC/ DC dual-voltage electric multiple unit (EMU) type operated by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) in Japan since March 1989. Trains originally operated as 7+4-car formations on ''Super Hitachi'' limited express services between in Tokyo and via the Jōban Line, but were withdrawn from regular scheduled services from the start of the revised timetable on 16 March 2013. The majority of the fleet was subsequently modified to become the 651-1000 series, and re-employed on '' Akagi'' and '' Kusatsu'' limited express services from March 2014. Variants * 651-0 series: Original (nine 7-car and nine 4-car) AC/DC sets built from 1989 * 651-1000 series: 7-car and 4-car DC-only sets modified from 651-0 series between 2013 and 2014 * ''Izu Craile'': Rebuilt 4-car resort trainset entering service in July 2016 Operations , a four-car 651-0 series set operates as a local service on a segment of Jōban Line between Iwaki and Tomioka, making 2 round trips a day. The 651-100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
203 Series
The is an electric multiple unit (EMU) train type operated in Japan between 1982 and 2011 by Japanese National Railways (JNR) and later by East Japan Railway Company (JR East), and currently operated by KAI Commuter and Philippine National Railways. Formation The sets were formed as follows. Cars 3, 6, and 9 were each fitted with one PS21 pantograph. Interior File:JNR203-interior.JPG, Interior view in September 2007 File:203 priority seating Yoyogi-Uehara 20101106.JPG, Priority seating in November 2010 History and operations The 203 series sets were made to replace the 103-1000 series EMUs in 1982. The 203 series EMUs were on through services between the Joban Line and Tokyo Metro Chiyoda Line. Withdrawal The trains were gradually replaced by new E233-2000 series EMUs, and the last set ran in revenue service on 26 September 2011. Overseas operations Indonesia Five former 203 series ten-car sets (Set numbers 51, 52, 66, 68, 69) were shipped to KAI Commuter in Jakarta, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Metro Chiyoda Line
The is a subway line owned and operated by Tokyo Metro in Tokyo, Japan. On average, the line carries 1,447,730 passengers daily (2017), the second highest of the Tokyo Metro network, behind the Tozai Line (1,642,378).Tokyo Metro station ridership in 2010 ''Train Media (sourced from Tokyo Metro)'' Retrieved July 23, 2018. The line was named after the Chiyoda ward, under which it passes. On maps, diagrams and signboards, the line is shown using the color green (), and its stations are given numbers using the letter "C". Overview The 24.0 km line serves the wards of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hitachi (Japanese Train)
is a limited express train service operated in Japan by East Japan Railway Company (JR East) on the Jōban Line between Shinagawa Station / Ueno Station in Tokyo and Sendai Station in Miyagi Prefecture. The ''Tokiwa'' service follows the same route but makes additional stops. History The name was taken from the former Hitachi Province (常陸), which is now part of the Ibaraki Prefecture. The service was first introduced on 1 October 1963 for a semi-express service which operated daily between Ueno and Taira (present-day Iwaki) using 451 series EMU stock, will all cars reserved. This service operated until 30 September 1967. The name was subsequently reintroduced on 1 October 1969 for a once-daily seasonal limited-express service operating between Ueno and Iwaki using 7-car KiHa 81 series diesel multiple units. This became a regular daily service the following year. 485 series EMUs were phased in from 2 October 1972, and were used until services were discontinued in Decem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatsukari
The and were limited express train services in Japan operated by Japanese National Railways (JNR) and later East Japan Railway Company (JR East) from 1958 until 2002. History The ''Hatsukari'' was first introduced on 1 October 1958 as a long-distance steam-hauled limited express service operating between in Tokyo and via the Jōban Line. From 1960, new KiHa 81 series diesel multiple units were introduced on the service, reducing the journey time to 10 hours 25 minutes. From 1 October 1968, the train was routed via the more direct Tōhoku Main Line using 583 series electric multiple units. From 15 November 1982, with the opening of the Tōhoku Shinkansen to , the ''Hatsukari'' service was truncated to operate between Morioka and Aomori. This was extended to operate to in Hokkaido from 13 March 1988, following the opening of the undersea Seikan Tunnel. The maximum speed was raised to through the Seikan Tunnel from 16 March 1991. New E751 series electric multiple units were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimoyama Incident
The was the disappearance and death of Sadanori Shimoyama, the first president of Japanese National Railways, in Tokyo on 5 July 1949. Shimoyama disappeared on his way to work and his body was discovered on the Jōban Line in Adachi the next day. The media offered conflicting explanations involving suicide and murder, while the police did not publicly report the results of their investigation, which was then ended. The Shimoyama incident, the Mitaka incident, and the Matsukawa derailment occurred within two months of one another, and together are known as JNR's Three Big Mysteries. Background was a bureaucrat of the Ministry of Transport, the successor to the Ministry of Railways which had operated Japan's railway network. Shimoyama was appointed the first president of Japanese National Railways (JNR) when it was established on 1 June 1949. Under the Dodge Line policy of the Japanese government, Shimoyama was responsible for drastic personnel cutbacks of JNR, as a part of whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
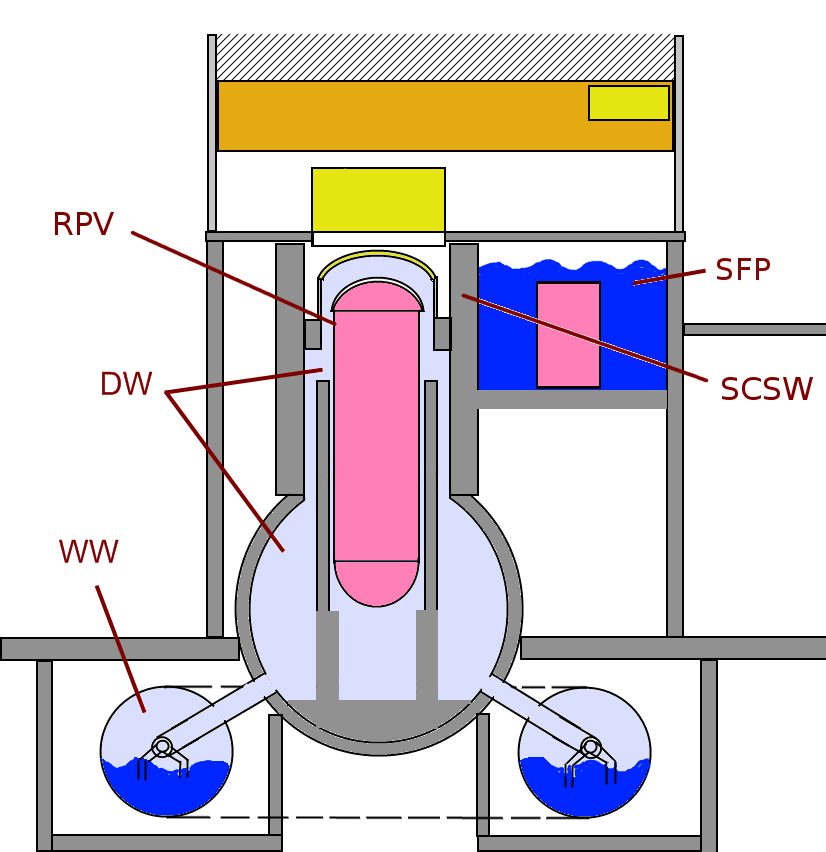
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 and remains the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan. The earthquake triggered a powerful tsunami, with 13–14-meter-high waves damaging the nuclear power plant's emergency diesel generators, leading to a loss of electric power. The result was the most severe nuclear accident since the Chernobyl disaster in 1986, classified as level seven on the International Nuclear Event Scale (INES) after initially being classified as level five, and thus joining Chernobyl as the only other accident to receive such classification. While the 1957 explosion at the Mayak facility was the second worst by radioactivity released, the INES ranks incidents by impact on population, so Chernobyl (335,000 people evacuated) and Fukushima (154,000 evacuate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
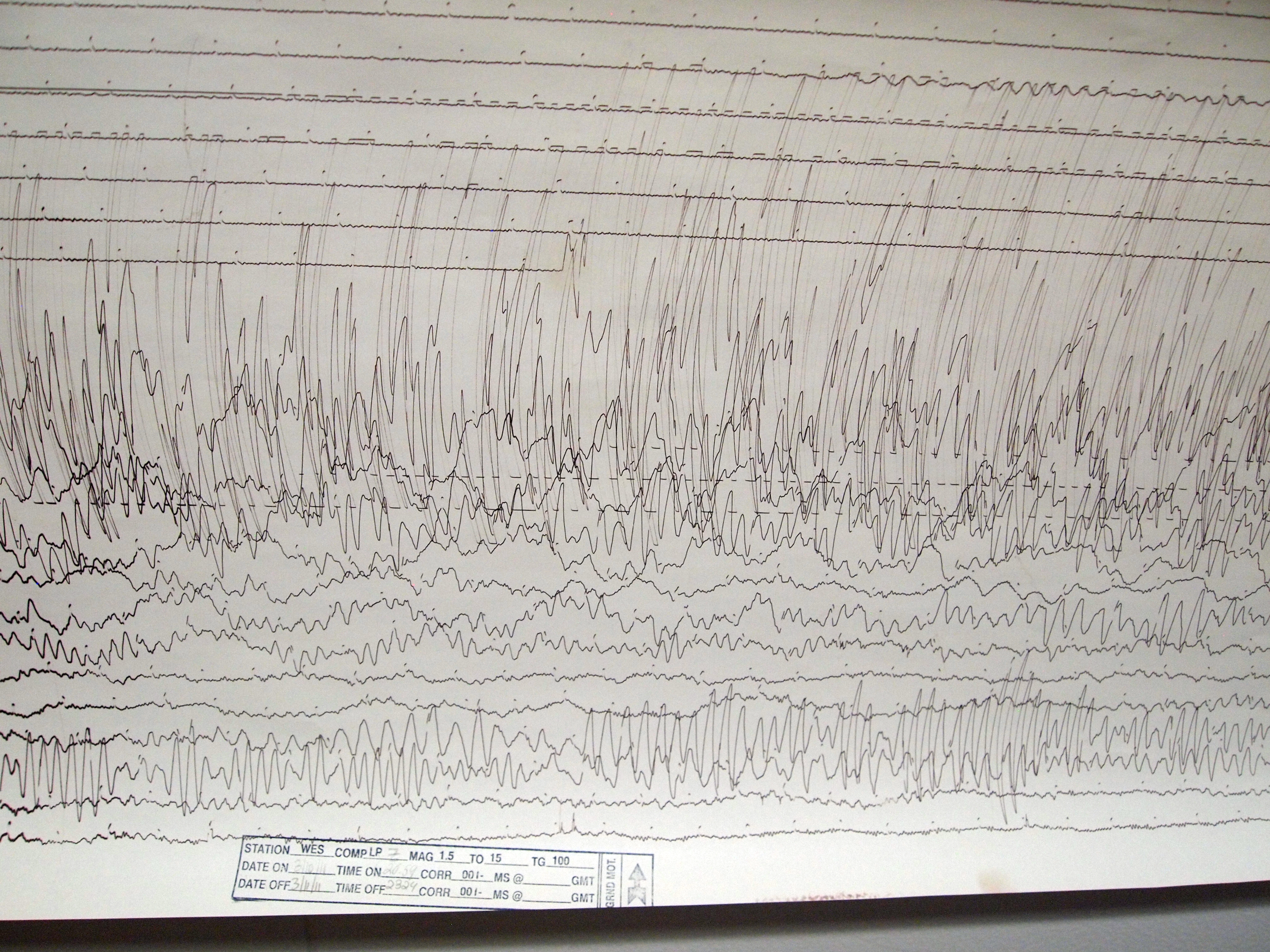
2011 Tōhoku Earthquake And Tsunami
The occurred at 14:46 JST (05:46 UTC) on 11 March. The magnitude 9.0–9.1 (M) undersea megathrust earthquake had an epicenter in the Pacific Ocean, east of the Oshika Peninsula of the Tōhoku region, and lasted approximately six minutes, causing a tsunami. It is sometimes known in Japan as the , among other names. The disaster is often referred to in both Japanese and English as simply 3.11 (read in Japanese). It was the most powerful earthquake ever recorded in Japan, and the fourth most powerful earthquake in the world since modern record-keeping began in 1900. The earthquake triggered powerful tsunami waves that may have reached heights of up to in Miyako in Tōhoku's Iwate Prefecture,Yomiuri Shimbun evening edition 2-11-04-15 page 15, nearby Aneyoshi fishery port (姉吉漁港)(Google map E39 31 57.8, N 142 3 7.6) 2011-04-15大震災の津波、宮古で38.9 m…明治三陸上回るby okayasu Akio (岡安 章夫) and which, in the Sendai area, traveled at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwaki Province (1868)
Map of the former Japanese provinces with Iwaki highlighted was an old province in the area that is today Fukushima Prefecture. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Iwaki''" in . It was sometimes called . History * This iteration of Iwaki Province was established in Meiji Era. It was cut out of Mutsu Province and corresponded to the eastern part of modern Fukushima Prefecture on December 17 of 1868 of Japanese calendar, which is January 19, 1869 of Gregorian calendar. Its population in 1872 was 348,608. Historical districts * Miyagi Prefecture ** Igu District (伊具郡) ** Katta District (刈田郡) ** Watari District (亘理郡) * Fukushima Prefecture ** Nakadōri Region, Fukushima *** Ishikawa District (石川郡) *** Shirakawa District (白川郡, a.k.a. Higashishirakawa or East Shirakawa) *** Shirakawa District (白河郡, a.k.a. Nishishirakwa or West Shirakawa) *** Tamura District (田村郡) ** Hamadōri Region, Fukushima *** Iwaki District (磐城郡) - absorbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |