|
Judah Abravanel
Judah Leon Abravanel or Abrabanel () (c. 1460 Lisbon – c. 1530 ? Naples?), otherwise known by the pen name of Leo the Hebrew (in Latin: ''Leo Hebraeus''; in Portuguese: ''Leão Hebreu''; in Italian: ''Leone Ebreo''; in Spanish: ''León Hebreo''; in French: ''León l'Hebreu''), was a Portuguese–Jewish medieval philosopher, physician, and poet. His work ''Dialogues of Love'' was one of the most important philosophical works of his time. Biography The Abravanel (or Abrabanel) family was extraordinarily prominent among Jewish families in the Middle Ages, active in public service in the court of Castile. Judah (or Leon, as he is known in Spanish) was the son of Isaac ben Judah Abravanel (meaning Isaac “son of Judah” Abravanel) who, according to Soria was “the last great commentator of the Bible of Medieval Jewry” (12). Don Isaac was a statesman, financier, and a defender of the Jewish faith, who was also born in Lisbon in 1437 and spent most of his life in Portugal, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Encyclopedia Of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') combines an online encyclopedia of philosophy with peer-reviewed publication of original papers in philosophy, freely accessible to Internet users. It is maintained by Stanford University. Each entry is written and maintained by an expert in the field, including professors from many academic institutions worldwide. Authors contributing to the encyclopedia give Stanford University the permission to publish the articles, but retain the copyright to those articles. Approach and history As of August 5th, 2022, the ''SEP'' has 1,774 published entries. Apart from its online status, the encyclopedia uses the traditional academic approach of most encyclopedias and academic journals to achieve quality by means of specialist authors selected by an editor or an editorial committee that is competent (although not necessarily considered specialists) in the field covered by the encyclopedia and peer review. The encyclopedia was created in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Ben Judah Abrabanel
Isaac ben Judah Abarbanel ( he, יצחק בן יהודה אברבנאל; 1437–1508), commonly referred to as Abarbanel (), also spelled Abravanel, Avravanel, or Abrabanel, was a Portuguese Jewish statesman, philosopher, Bible commentator, and financier. Name Some debate exists over whether his last name should be pronounced ''Abarbanel'' or ''Abravanel''. The traditional pronunciation is ''Abarbanel''. Modern scholarly literature, since Graetz and Baer, has most commonly used ''Abravanel'', but his own son Judah insisted on ''Abarbanel'', and ''Sefer HaTishbi'' by Elijah Levita, who was a nearby contemporary, twice vowels the name as ''Abarbinel'' (אַבַּרְבִּינֵאל).Abarbanel and the Censor page 1, note 1 The name's etymology is uncertain. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Transfer
Population transfer or resettlement is a type of mass migration, often imposed by state policy or international authority and most frequently on the basis of ethnicity or religion but also due to economic development. Banishment or exile is a similar process, but is forcibly applied to individuals and groups. Population transfer differs more than simply technically from individually motivated migration, but at times of war, the act of fleeing from danger or famine often blurs the differences. If a state can preserve the fiction that migrations are the result of innumerable "personal" decisions, the state may be able to claim that it is not to blame for the displacement. Often the affected population is transferred by force to a distant region, perhaps not suited to their way of life, causing them substantial harm. In addition, the process implies the loss of immovable property and substantial amounts of movable property when rushed. This transfer may be motivated by the more p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forced Conversion
Forced conversion is the adoption of a different religion or the adoption of irreligion under duress. Someone who has been forced to convert to a different religion or irreligion may continue, covertly, to adhere to the beliefs and practices which were originally held, while outwardly behaving as a convert. Crypto-Jews, crypto-Christians, crypto-Muslims and crypto-Pagans are historical examples of the latter. Religion and power In general, anthropologists have shown that the relationship between religion and politics is complex, especially when viewed over the expanse of human history.Firth, Raymond (1981Spiritual Aroma: Religion and Politics ''American Anthropologist'', New Series, Vol. 83, No. 3, pp. 582–601 While religious leaders and the state generally have different aims, both are concerned with power and order; both use reason and emotion to motivate behavior. Throughout history, leaders of religious and political institutions have cooperated, opposed one another, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraham (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the main Islamic prophet. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices of Muhammad ('' sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (''hadith''). With an estimated population of almost 1.9 billion followers as of 2020 year estimation, Muslims comprise more than 24.9% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each continental landmass stands at: 45% of Africa, 25% of Asia and Oceania (collectively), 6% of Europe, and 1% of the Americas. Additionally, in subdivided geographical regions, the figure stands at: 91% of the Middle East–North Africa, 90% of Central Asia, 65% of the Caucasus, 42% of Southeast As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada (Spain), Sierra Nevada mountains, at the confluence of four rivers, the Darro (river), Darro, the Genil, the Monachil (river), Monachil and the Beiro. Ascribed to the Vega de Granada ''comarca'', the city sits at an average elevation of Above mean sea level, above sea level, yet is only one hour by car from the Mediterranean coast, the Costa Tropical. Nearby is the Sierra Nevada Ski Station, where the FIS Alpine World Ski Championships 1996 were held. In the 2021 national census, the population of the city of Granada proper was 227,383, and the population of the entire municipal area was estimated to be 231,775, ranking as the Ranked lists of Spanish municipalities, 20th-largest urban area of Spain. About 3.3% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
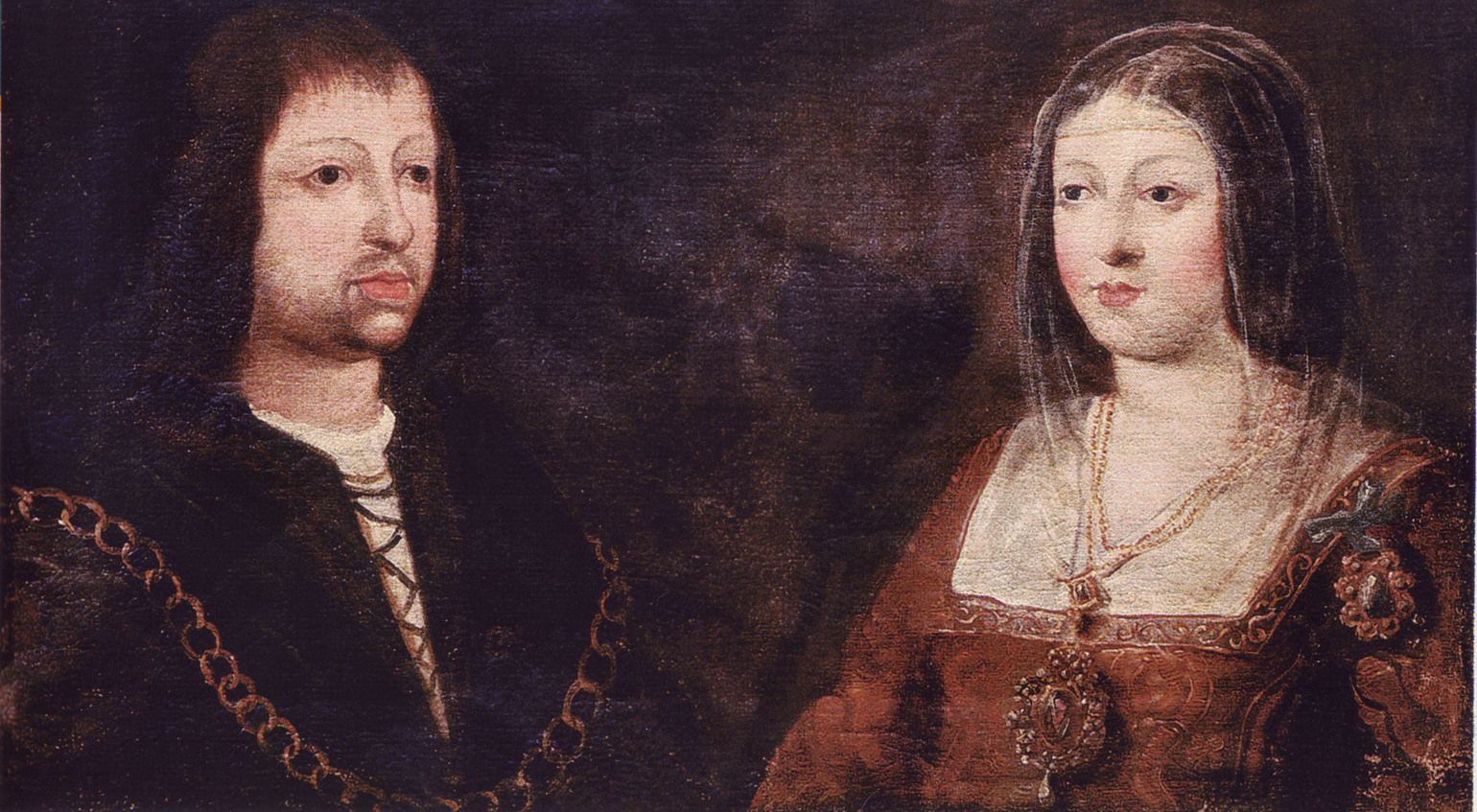
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; to remove the obstacle that this consanguinity would otherwise have posed to their marriage under canon law, they were given a papal dispensation by Sixtus IV. They married on October 19, 1469, in the city of Valladolid; Isabella was eighteen years old and Ferdinand a year younger. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the unification of Spain can essentially be traced back to the marriage of Ferdinand and Isabella. Spain was formed as a dynastic union of two crowns rather than a unitary state, as Castile and Aragon remained separate kingdoms until the Nueva Planta decrees of 1707–16. The court of Ferdinand and Isabella was constantly on the move, in order to bolster local support for the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand II Of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia from 1479, King of Sicily from 1468, King of Naples (as Ferdinand III) from 1504 and King of Navarre (as Ferdinand I) from 1512 until his death in 1516. He was also the nominal Duke of the ancient Duchies of Athens and Neopatria. He was King of Castile and León (as Ferdinand V) from 1475 to 1504, alongside his wife Queen Isabella I. From 1506 to 1516, he was the Regent of the Crown of Castile, making him the effective ruler of Castile. From 1511 to 1516, he styled himself as ''Imperator totius Africa'' (Emperor of All Africa) after having conquered Tlemcen and making the Zayyanid Sultan, Abu Abdallah V, his vassal. He was also the Grandmaster of the Spanish Military Orders of Santiago (1499-1516), Calatrava (1487-1516), Alcantara (1492- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabel De Castilla
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by virtue of her marriage to King Ferdinand II of Aragon. Reigning together over a dynastically unified Spain, Isabella and Ferdinand are known as the Catholic Monarchs. After a struggle to claim the throne, Isabella reorganized the governmental system, brought the crime rate to the lowest it had been in years, and unburdened the kingdom of the enormous debt her half-brother King Henry IV had left behind. Isabella's marriage to Ferdinand in 1469 created the basis of the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. Her reforms and those she made with her husband had an influence that extended well beyond the borders of their united kingdoms. Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon are known for being the first monarchs to be referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toledo, Spain
Toledo ( , ) is a city and municipality of Spain, capital of the province of Toledo and the ''de jure'' seat of the government and parliament of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castilla–La Mancha. Toledo was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1986 for its extensive monumental and cultural heritage. Located on the banks of the Tagus in central Iberian Peninsula, Iberia, Toledo is known as the "City of the Three Cultures" for the cultural influences of Christians, Muslims, and Jews throughout its history. It was the capital, from 542 to 725 CE, of the Visigothic kingdom, which followed the fall of the Roman Empire. Toledo was also the location of historic events such as the Councils of Toledo and was labelled the "Imperial City" due to the fact that it was the main venue of the court of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in Spain. The city, seat of a powerful archdiocese for much of its history, has a Gothic Cathedral, the ''Cathedral of Toledo, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seville
Seville (; es, Sevilla, ) is the capital and largest city of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia and the province of Seville. It is situated on the lower reaches of the River Guadalquivir, in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Seville has a municipal population of about 685,000 , and a metropolitan population of about 1.5 million, making it the largest city in Andalusia, the fourth-largest city in Spain and the 26th most populous municipality in the European Union. Its old town, with an area of , contains three UNESCO World Heritage Sites: the Alcázar palace complex, the Cathedral and the General Archive of the Indies. The Seville harbour, located about from the Atlantic Ocean, is the only river port in Spain. The capital of Andalusia features hot temperatures in the summer, with daily maximums routinely above in July and August. Seville was founded as the Roman city of . Known as ''Ishbiliyah'' after the Islamic conquest in 711, Seville became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
João II
John II ( pt, João II; ; 3 March 1455 – 25 October 1495), called the Perfect Prince ( pt, o Príncipe Perfeito, link=no), was King of Portugal from 1481 until his death in 1495, and also for a brief time in 1477. He is known for re-establishing the power of the Portuguese monarchy, reinvigorating the Portuguese economy, and renewing his country's exploration of Africa and Asia. Early life Born in Lisbon, the son of King Afonso V of Portugal by his wife, Isabella of Coimbra, John II succeeded his father as ruler of Portugal in 1477, when the king retired to a monastery, but only became king in 1481, after the death of his father and predecessor. As a prince, John II accompanied his father in the campaigns in northern Africa and was made a knight after the victory in the Conquest of Arzila in 1471. In 1473, he married Leonor of Viseu, an infanta of Portugal and his first cousin. Even at a young age, John was not popular among the peers of the kingdom since he was immune to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



.png)