|
John Reid (British Army Officer)
John Reid (13 February 1721 – 6 February 1807), previously known as John Robertson, was a British army general and founder of the chair of music at the University of Edinburgh. Strongly connected to Edinburgh, he gives his name to the Reid School of Music. Reid Concerts and Reid Orchestra. Early life Born John Robertson, he changed his name from Robertson to Reid (the name given to his paternal ancestor on account of the colour of his red hair) on inheriting the Straloch estate in Perthshire from his father. He was the son of Alexander Robertson of Straloch, whose forefathers had for three centuries been known as the Barons Ruadh, Roy or Red, though the family name had remained Robertson, a tradition not followed by the General. Reid's father, Alexander Robertson, took an active part and incurred heavy losses in resisting the Jacobite rising of 1745. He was of the same stock as the Robertsons of Struan, Matilda, the granddaughter of Duncan, third Baron of Struan, having ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General John Reid
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank scal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
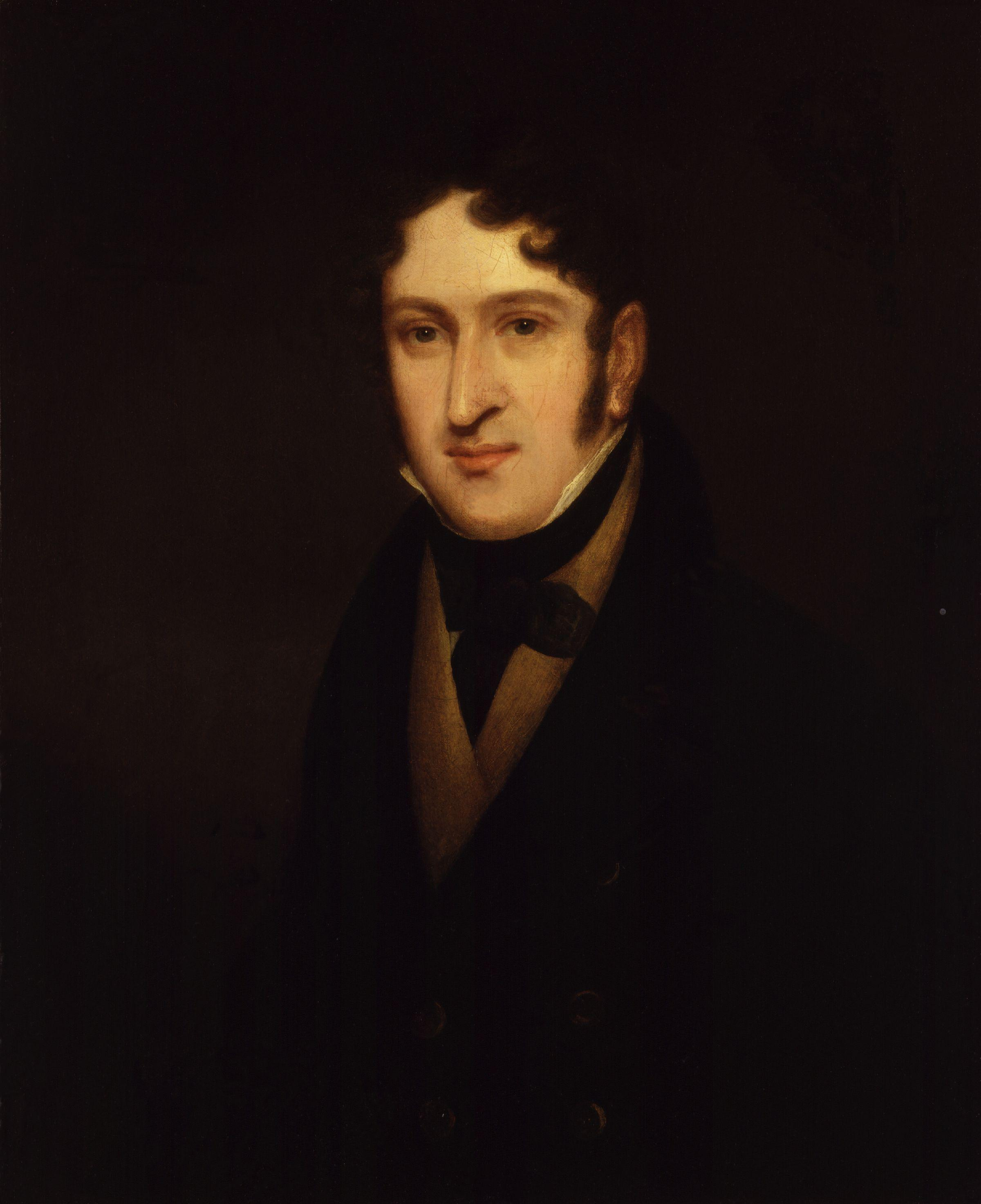
Robert Monckton
Lieutenant-General Robert Monckton (24 June 1726 – 21 May 1782) was an officer of the British Army and colonial administrator in British North America. He had a distinguished military and political career, being second in command to General James Wolfe at the battle of Quebec and later being named the Governor of the Province of New York. Monckton is also remembered for his role in a number of other important events in the French and Indian War (the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War), most notably the capture of Fort Beauséjour in Acadia, and the island of Martinique in the West Indies, as well as for his role in the deportation of the Acadians from British controlled Nova Scotia and also from French-controlled Acadia (present-day New Brunswick). The city of Moncton, New Brunswick, (about west of Fort Beauséjour) and Fort Monckton in Port Elgin, New Brunswick, are named for him. A second more important Fort Monckton in Portsmouth, England, is also named for him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scots Guards
The Scots Guards (SG) is one of the five Foot Guards regiments of the British Army. Its origins are as the personal bodyguard of King Charles I of England and Scotland. Its lineage can be traced back to 1642, although it was only placed on the English Establishment (thus becoming part of what is now the British Army) in 1686. History Formation; 17th century The regiment now known as the Scots Guards traces its origins to the Marquis of Argyll's Royal Regiment, a unit raised in 1642 by Archibald Campbell, 1st Marquess of Argyll in response to the 1641 Irish Rebellion. After the Restoration of Charles II, the Earl of Linlithgow received a commission dated 23 November 1660 to raise a regiment which was called The Scottish Regiment of Footguards. It served in the 1679 Covenanter rising of 1679, as well as Argyll's Rising in June 1685, after which it was expanded to two battalions. When the Nine Years War began in 1689, the first battalion was sent to Flanders; the second served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Henry Erskine, 5th Baronet
Sir Henry Erskine, 5th Baronet (23 Dec 1710 – 7 August 1765) was a Scottish soldier and politician. He was a younger son of Sir John Erskine, 3rd Baronet, M.P. of Alva, Clackmannanshire, and Catherine Sinclair, was probably educated at Eton College and entered Lincoln's Inn to study law in 1728. However, instead of a legal career he joined the Army and rose to the rank of Lieutenant-General in 1765. He succeeded to the baronetcy and family estate when his elder brother Charles was killed in action at the Battle of Lauffeld in 1747. Erskine then served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Ayr Burghs 1749–1754 and for Anstruther Easter Burghs 1754–1765. He died in 1765. He had married Janet, the daughter of Peter Wedderburn, Lord Chesterhall, and with her had two sons and a daughter. He was succeeded by his eldest son James, who later became the 2nd Earl of Rosslyn. References * * * 1710s births 1765 deaths Members of Lincoln's Inn Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Garb Of Old Gaul
''The Garb of Old Gaul'' (sometimes given as "Auld Gaul") is an 18th-century patriotic Scottish march and song about Highland soldiers during the Seven Years' War. Origins The music was written by General John Reid, who was a senior officer of the 42nd Regiment of Foot (The Black Watch) during the Seven Years' War. The words have traditionally been attributed to Sir Harry Erskine (1710 -1765). Robert Burns described it as "This excellent loyal Scottish song" and states that it first appeared in print in Herd's Collection of 1769. Alternative titles include ''The Highland Character'' and ''The Highland or 42nd Regiment's March''. The tune was originally a quick march but was later rearranged as a slow march. Lyrics The lyrics of the song are about the martial prowess of Highland soldiers and the perceived British tradition of freedom and fighting against the despotic French. The phrase "Garb of Old Gaul" refers to the traditional Highland dress, ancient Gaul being thought of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Bishop (composer)
Sir Henry Rowley Bishop (18 November 178730 April 1855) was an English composer from the early Romantic era. He is most famous for the songs "Home! Sweet Home!" and "Lo! Hear the Gentle Lark." He was the composer or arranger of some 120 dramatic works, including 80 operas, light operas, cantatas, and ballets. Bishop was Knighted in 1842. Bishop worked for all the major theatres of London in his era – including the Royal Opera House at Covent Garden, the Theatre Royal, Drury Lane, Vauxhall Gardens and the Haymarket Theatre, and was Professor of Music at the universities of Edinburgh and Oxford. His second wife was the noted soprano Anna Bishop, who scandalised British society by leaving him and conducting an open liaison with the harpist Nicolas-Charles Bochsa until the latter's death in Sydney. Life Bishop was born in London, where his father was a watchmaker and haberdasher. At the age of 13, Bishop left full-time education and worked as a music-publisher with his cousin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reid Concert Hall
The Reid Concert Hall is a small music venue in the city of Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located in the south-western corner of Bristo Square about south of the Royal Mile, and is part of the University of Edinburgh. Originally opened in 1859 as the Reid School of Music by the university's professor of music, John Donaldson (1789-1865), it was designed by the Scottish Architect David Cousin and is a Category A listed building. The hall is named after General John Reid, an army officer and musician who founded the Chair of Music (Reid Professor of Music) at the university. The Reid Concerts take place every 13 February. Performances The Reid Hall is hosts a number of classical chamber music concerts throughout the year, mostly performed by students and academics. The Reid Concerts are performed every year under the organisation of the Reid Professor. They are held on 13 February in remembrance of General John Reid and in line with the terms of his bequest that established the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick to the northeast and Quebec to the north. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east and southeast, and Long Island Sound is to the southwest. Boston is New England's largest city, as well as the capital of Massachusetts. Greater Boston is the largest metropolitan area, with nearly a third of New England's population; this area includes Worcester, Massachusetts (the second-largest city in New England), Manchester, New Hampshire (the largest city in New Hampshire), and Providence, Rhode Island (the capital of and largest city in Rhode Island). In 1620, the Pilgrims, Puritan Separatists from England, established Plymouth Colony, the second successful English settlement in America, following the Jamestown Settlement in Virginia foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the north. Admitted to the union in 1791 as the 14th state, it is the only state in New England not bordered by the Atlantic Ocean. According to the 2020 U.S. census, the state has a population of 643,503, ranking it the second least-populated in the U.S. after Wyoming. It is also the nation's sixth-smallest state in area. The state's capital Montpelier is the least-populous state capital in the U.S., while its most-populous city, Burlington, is the least-populous to be a state's largest. For some 12,000 years, indigenous peoples have inhabited this area. The competitive tribes of the Algonquian-speaking Abenaki and Iroquoian-speaking Mohawk were active in the area at the time of European encounter. During the 17th century, Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
88th Regiment Of Foot (Connaught Rangers)
The 88th Regiment of Foot (Connaught Rangers) was an infantry Regiment of the British Army, raised in 1793. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 94th Regiment of Foot to form the Connaught Rangers in 1881. History Formation The regiment was raised in Connaught by John Thomas de Burgh, 13th Earl of Clanricard as the 88th Regiment of Foot (Connaught Rangers), in response to the threat posed by the French Revolution, on 25 September 1793. The regiment was sent to join the Duke of York's army in the Netherlands in summer 1794 as part of the unsuccessful defence of that country against the Republican French during the Flanders Campaign. The regiment embarked for the West Indies in autumn 1795 and, after a difficult voyage, two companies took part in the capture of Grenada and the siege of Saint Lucia before returning to England in summer 1796.Cannon, p. 4 The regiment then embarked for India in January 1799 and arrived in Bombay in June 1800. The regiment sailed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
95th Regiment Of Foot (Reid's)
95 or 95th may refer to: * 95 (number) * one of the years 95 BC, AD 95, 1995, 2095, etc. * 95th Division (other) * 95th Regiment ** 95th Regiment of Foot (other) * 95th Squadron (other) * Atomic number 95: americium *Microsoft Office 95 * Saab 95 * Windows 95 See also * 9 to 5 (other) 9 to 5, or working time, is the standard period of working hours for some employees. 9 to 5 or Nine to Five may also refer to: Film and television * 9 to 5 (film), ''9 to 5'' (film), a 1980 American comedy film ** 9 to 5 (soundtrack), ''9 to 5'' ... * * List of highways numbered {{Numberdis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
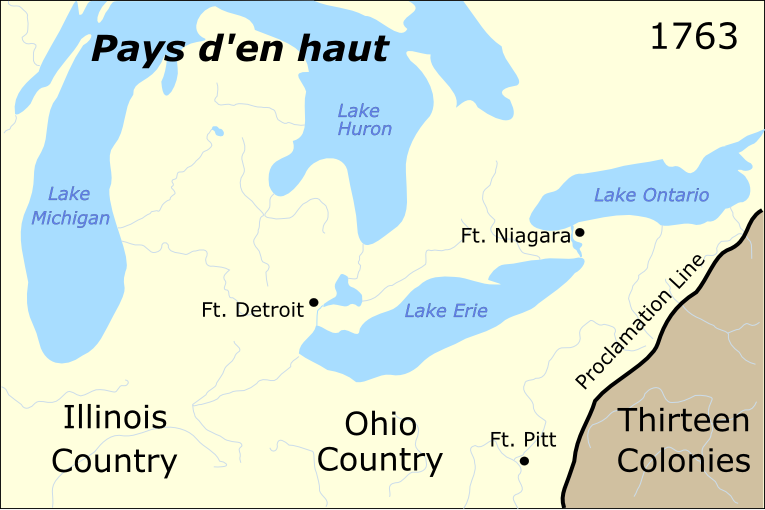
Pontiac's Rebellion
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–1763). Warriors from numerous nations joined in an effort to drive British soldiers and settlers out of the region. The war is named after Odawa leader Pontiac, the most prominent of many indigenous leaders in the conflict. The war began in May 1763 when Native Americans, alarmed by policies imposed by British General Jeffrey Amherst, attacked a number of British forts and settlements. Eight forts were destroyed, and hundreds of colonists were killed or captured, with many more fleeing the region. Hostilities came to an end after British Army expeditions in 1764 led to peace negotiations over the next two years. The Natives were unable to drive away the British, but the uprising prompted the British government to modify the policies that ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |