History
 The earliest known inhabitants of New England were Native American who spoke a variety of the Eastern Algonquian languages. Prominent tribes included the Abenakis, Mi'kmaq, Penobscot, Pequots, Mohegans, Narragansetts, Pocumtucks, and Wampanoag. Prior to the arrival of European colonists, the Western Abenakis inhabited what is modern New Hampshire, New York and Vermont, as well as parts of Quebec and western Maine. Their principal town was Norridgewock in present-day Maine.
The Penobscot lived along the
The earliest known inhabitants of New England were Native American who spoke a variety of the Eastern Algonquian languages. Prominent tribes included the Abenakis, Mi'kmaq, Penobscot, Pequots, Mohegans, Narragansetts, Pocumtucks, and Wampanoag. Prior to the arrival of European colonists, the Western Abenakis inhabited what is modern New Hampshire, New York and Vermont, as well as parts of Quebec and western Maine. Their principal town was Norridgewock in present-day Maine.
The Penobscot lived along the Colonial period
On April 10, 1606, King James I of England issued a charter for the Virginia Company, which comprised theFrench and Indian Wars

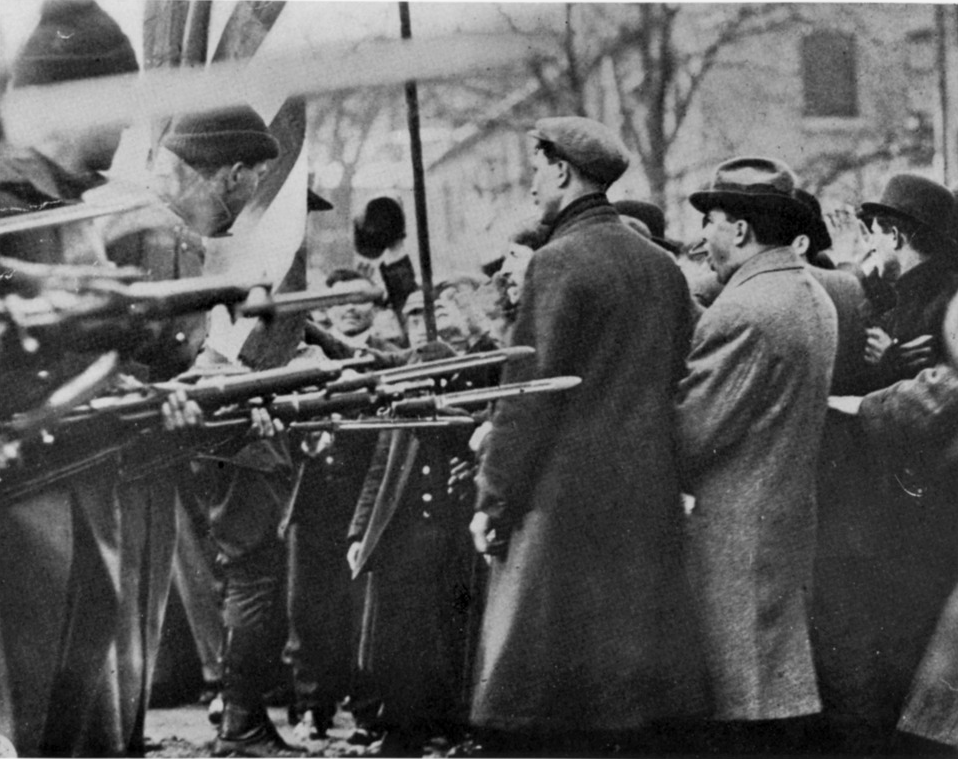
 Relationships between colonists and local Indian tribes alternated between peace and armed skirmishes, the bloodiest of which was the
Relationships between colonists and local Indian tribes alternated between peace and armed skirmishes, the bloodiest of which was the Dominion of New England
New England in the new nation
After the dissolution of the Dominion of New England, the colonies of New England ceased to function as a unified political unit but remained a defined cultural region. There were often disputes over territorial jurisdiction, leading to land exchanges such as those regarding the Equivalent Lands and New Hampshire Grants. By 1784, all of the states in the region had taken steps towards the abolition of slavery, with Vermont and Massachusetts introducing total abolition in 1777 and 1783, respectively. The nickname "Yankeeland" was sometimes used to denote the New England area, especially among Southerners and the British. Vermont was admitted to statehood in 1791 after settling a dispute with New York. The territory of Maine had been a part of Massachusetts, but it was granted statehood on March 15, 1820, as part of the Missouri Compromise. Today, New England is defined as the six states of Maine, Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut. New England's economic growth relied heavily on trade with theIndustrial Revolution
 New England was key to the industrial revolution in the United States."New England", Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006. The Blackstone Valley running through Massachusetts and Rhode Island has been called the birthplace of America's industrial revolution. In 1787, the first cotton mill in America was founded in the
New England was key to the industrial revolution in the United States."New England", Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2006. The Blackstone Valley running through Massachusetts and Rhode Island has been called the birthplace of America's industrial revolution. In 1787, the first cotton mill in America was founded in the 20th century and beyond
 The flow of immigrants continued at a steady pace from the 1840s until cut off by World War I. The largest numbers came from Ireland and Britain before 1890, and after that from Quebec, Italy, and Southern Europe. The immigrants filled the ranks of factory workers, craftsmen, and unskilled laborers. The Irish assumed a larger and larger role in the Democratic Party in the cities and statewide, while the rural areas remained Republican. Yankees left the farms, which never were highly productive; many headed west, while others became professionals and businessmen in the New England cities.
The Great Depression in the United States of the 1930s hit the region hard, with high unemployment in the industrial cities. The Boston Stock Exchange rivaled the New York Stock Exchange in 1930. In the beginning of 1930 John C. Hull (politician), John C. Hull, first Securities Director of Massachusetts (1930–1936), helped to mitigate the consequences of the Wall Street Crash of 1929 and the Great Depression. He was helpful in the passing of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 with his war on "unlisted securities". Hull gave testimony to the US Senate (Sen. Duncan Upshaw Fletcher) for work on the Pecora Commission, which revealed that neither Albert H. Wiggin (born in Medfield, MA) nor J. P. Morgan Jr. had paid any income taxes in 1931 and 1932; a public outcry ensued.
On the subject of securities laws in the early 1930s in response to the Great Depression,
The flow of immigrants continued at a steady pace from the 1840s until cut off by World War I. The largest numbers came from Ireland and Britain before 1890, and after that from Quebec, Italy, and Southern Europe. The immigrants filled the ranks of factory workers, craftsmen, and unskilled laborers. The Irish assumed a larger and larger role in the Democratic Party in the cities and statewide, while the rural areas remained Republican. Yankees left the farms, which never were highly productive; many headed west, while others became professionals and businessmen in the New England cities.
The Great Depression in the United States of the 1930s hit the region hard, with high unemployment in the industrial cities. The Boston Stock Exchange rivaled the New York Stock Exchange in 1930. In the beginning of 1930 John C. Hull (politician), John C. Hull, first Securities Director of Massachusetts (1930–1936), helped to mitigate the consequences of the Wall Street Crash of 1929 and the Great Depression. He was helpful in the passing of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 with his war on "unlisted securities". Hull gave testimony to the US Senate (Sen. Duncan Upshaw Fletcher) for work on the Pecora Commission, which revealed that neither Albert H. Wiggin (born in Medfield, MA) nor J. P. Morgan Jr. had paid any income taxes in 1931 and 1932; a public outcry ensued.
On the subject of securities laws in the early 1930s in response to the Great Depression,  What remains is very high technology manufacturing, such as jet engines, nuclear submarines, pharmaceuticals, robotics, scientific instruments, and medical devices. MIT (the Massachusetts Institute of Technology) invented the format for university-industry relations in high tech fields and spawned many software and hardware firms, some of which grew rapidly. By the 21st century, the region had become famous for its leadership roles in the fields of education, medicine, medical research, high-technology, finance, and tourism.
Some industrial areas were slow in adjusting to the new service economy. In 2000, New England had two of the ten poorest cities in the U.S. (by percentage living below the poverty line): the state capitals of Providence, Rhode Island and Hartford, Connecticut. They were no longer in the bottom ten by 2010; Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire remain among the ten wealthiest states in the United States in terms of median household income and per capita income.
What remains is very high technology manufacturing, such as jet engines, nuclear submarines, pharmaceuticals, robotics, scientific instruments, and medical devices. MIT (the Massachusetts Institute of Technology) invented the format for university-industry relations in high tech fields and spawned many software and hardware firms, some of which grew rapidly. By the 21st century, the region had become famous for its leadership roles in the fields of education, medicine, medical research, high-technology, finance, and tourism.
Some industrial areas were slow in adjusting to the new service economy. In 2000, New England had two of the ten poorest cities in the U.S. (by percentage living below the poverty line): the state capitals of Providence, Rhode Island and Hartford, Connecticut. They were no longer in the bottom ten by 2010; Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire remain among the ten wealthiest states in the United States in terms of median household income and per capita income.
Geography
 The states of New England have a combined area, including water surfaces, of , making the region slightly larger than the Washington (state), state of Washington and slightly smaller than Great Britain. Maine alone constitutes nearly one-half of the total area of New England, yet is only the 39th-largest state, slightly smaller than Indiana. The remaining states are among the smallest in the U.S., including the List of U.S. states and territories by area, smallest state—Rhode Island.
The areas of the states (including water area) are:
* Maine,
*
The states of New England have a combined area, including water surfaces, of , making the region slightly larger than the Washington (state), state of Washington and slightly smaller than Great Britain. Maine alone constitutes nearly one-half of the total area of New England, yet is only the 39th-largest state, slightly smaller than Indiana. The remaining states are among the smallest in the U.S., including the List of U.S. states and territories by area, smallest state—Rhode Island.
The areas of the states (including water area) are:
* Maine,
*Geology
New England's long rolling hills, mountains, and jagged coastline are glacial landforms resulting from the retreat of ice sheets approximately 18,000 years ago, during the last glacial period. New England is geologically a part of the New England province, an terrane, exotic terrane region consisting of the Appalachian Mountains, the New England highlands and the seaboard lowlands. The Appalachian Mountains roughly follow the border between New England and New York. The Berkshires in Massachusetts and Connecticut, and the Green Mountains in Vermont, as well as the Taconic Mountains, form a spine of Precambrian rock. The Appalachians extend northwards into New Hampshire as the White Mountains (New Hampshire), White Mountains, and then into Maine and Canada. Mount Washington in New Hampshire is the highest peak in the Northeast, although it is not among the ten highest peaks in the eastern United States. It is the site of the second Wind speed#Highest speed, highest recorded wind speed on Earth, and has the reputation of having the world's most severe weather. The coast of the region, extending from southwestern Connecticut to northeastern Maine, is dotted with lakes, hills, marshes and wetlands, and sandy beaches. Important valleys in the region include the Champlain Valley, the Connecticut River Valley and the Merrimack Valley. The longest river is theClimate

Regions

Largest cities
The most populous cities as of the 2020 U.S. Census were (metropolitan areas in parentheses): # Boston, Boston, Massachusetts: 675,647 (4,941,632) # Worcester, Massachusetts: 206,518 (923,672) # Providence, Rhode Island: 190,934 (1,604,291) # Springfield, Massachusetts: 155,929 (699,162) # Bridgeport, Connecticut: 148,654 (939,904) # Stamford, Connecticut: 135,470 (part of Bridgeport's MSA) # New Haven, Connecticut: 134,023 (862,477) # Hartford, Connecticut: 121,054 (1,214,295) # Cambridge, Massachusetts: 118,403 (part of Greater Boston) # Manchester, New Hampshire: 115,644 (406,678) During the 20th century, urban expansion in regions surrounding New York City has become an important economic influence on neighboring Connecticut, parts of which belong to the New York metropolitan area. The U.S. Census Bureau groups Fairfield County, Connecticut, Fairfield, New Haven County, Connecticut, New Haven and Litchfield County, Connecticut, Litchfield counties in western Connecticut together with New York City and other parts of New York and New Jersey as a combined statistical area.Metropolitan areas and capitals
Metropolitan areas
The following are metropolitan statistical areas as defined by the United States Census Bureau. * Penobscot County, Maine, Bangor, ME MSA * Barnstable County, Massachusetts, Barnstable Town, MA MSA ( Greater Boston) * Greater Boston, Boston-Cambridge-Newton, MA-NH MSA ( Greater Boston) * Greater Bridgeport, Bridgeport-Stamford-Norwalk-Danbury, CT MSA (New York metropolitan area, New York-Newark CSA) * Burlington, Vermont metropolitan area, Burlington-South Burlington, VT MSA * Greater Hartford, Hartford-East Hartford-Middletown, CT MSA * Androscoggin County, Maine, Lewiston-Auburn, ME MSA * Hillsborough County, New Hampshire, Manchester-Nashua, NH MSA * Greater New Haven, New Haven-Milford, CT MSA (New York metropolitan area, New York-Newark CSA) * Southeastern Connecticut, Norwich-New London, CT MSA * Berkshire County, Massachusetts, Pittsfield, MA MSA * Portland metropolitan area, Maine, Portland-South Portland, ME MSA * Springfield metropolitan area, Massachusetts, Springfield, MA MSA * Providence metropolitan area, Providence-Warwick, RI-MA MSA ( Greater Boston) * Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester, MA-CT MSA ( Greater Boston)State capitals
 * Hartford, Connecticut
* Augusta, Maine
* Boston, Boston, Massachusetts
* Concord, New Hampshire
* Providence, Rhode Island
* Montpelier, Vermont
* Hartford, Connecticut
* Augusta, Maine
* Boston, Boston, Massachusetts
* Concord, New Hampshire
* Providence, Rhode Island
* Montpelier, Vermont
Demographics
 In 2020, New England had a population of 15,116,205, a growth of 4.6% from 2010. Massachusetts is the most populous state with 7,029,917 residents, while Vermont is the least populous state with 643,077 residents. Boston is by far the region's most populous city and metropolitan area.
Although a great disparity exists between New England's northern and southern portions, the region's average population density is 234.93 inhabitants/sq mi (90.7/km2). New England has a significantly higher population density than that of the U.S. as a whole (79.56/sq mi), or even just the contiguous 48 states (94.48/sq mi). Three-quarters of the population of New England, and most of the major cities, are in the states of Connecticut, Massachusetts and Rhode Island. The combined population density of these states is 786.83/sq mi, compared to northern New England's 63.56/sq mi (2000 census).
According to the 2006–08 American Community Survey, 48.7% of New Englanders were male and 51.3% were female. Approximately 22.4% of the population were under 18 years of age; 13.5% were over 65 years of age. The six states of New England have the lowest birth rate in the U.S.
White Americans make up the majority of New England's population at 73.4% of the total population, Hispanic and Latino Americans are New England's largest minority, and they are the second-largest group in the region behind non-Hispanic European Americans. As of 2014, Hispanics and Latinos of any race made up 10.2% of New England's population. Connecticut had the highest proportion at 13.9%, while Vermont had the lowest at 1.3%. There were nearly 1.5 million Hispanic and Latino individuals reported in New England in 2014.
Stateside Puerto Ricans, Puerto Ricans were the most numerous of the Hispanic and Latino subgroups. Over 660,000 Puerto Ricans lived in New England in 2014, forming 4.5% of the population. The Dominican Americans, Dominican population is over 200,000, and the Mexican Americans, Mexican and Guatemalan Americans, Guatemalan populations are each over 100,000. Cuban Americans, Americans of Cuban descent are scant in number; there were roughly 26,000 Cuban Americans in the region in 2014. People of all other Hispanic and Latino ancestries, including Salvadoran Americans, Salvadoran, Colombian Americans, Colombian and Bolivian Americans, Bolivian, formed 2.5% of New England's population and numbered over 361,000 combined.
According to the 2014 American Community Survey, the top ten largest reported European ancestries were the following: Irish Americans, Irish: 19.2% (2.8 million), English Americans, English (includes "American ancestry, American" ancestry): 16.7% (2.4 million), Italian Americans, Italian: 13.6% (2.0 million), French Americans, French and French Canadian: 13.1% (1.9 million), German Americans, German: 7.4% (1.1 million), Polish Americans, Polish: 4.9% (roughly 715,000), Portuguese Americans, Portuguese: 3.2% (467,000), Scottish Americans, Scottish: 2.5% (370,000), Russian Americans, Russian: 1.4% (206,000), and Greek Americans, Greek: 1.0% (152,000).
English is, by far, the most common language spoken at home. Approximately 81.3% of all residents (11.3 million people) over the age of five spoke only English at home. Roughly 1,085,000 people (7.8% of the population) spoke Spanish at home, and roughly 970,000 people (7.0% of the population) spoke other Indo-European languages at home. Over 403,000 people (2.9% of the population) spoke an Languages of Asia, Asian or Pacific Island language at home. Slightly fewer (about 1%) spoke French at home, although this figure is above 20% in northern New England, which borders francophone Québec. Roughly 99,000 people (0.7% of the population) spoke languages other than these at home.
As of 2014, approximately 87% of New England's inhabitants were born in the U.S., while over 12% were foreign-born. 35.8% of foreign-born residents were born in Latin America, 28.6% were born in Asia, 22.9% were born in Europe, and 8.5% were born in Africa.
Southern New England forms an integral part of the Northeast megalopolis, BosWash megalopolis (city type), megalopolis, a conglomeration of urban centers that spans from Boston to Washington, D.C. The region includes three of the four List of U.S. states by population density, most densely populated states in the U.S.; only New Jersey has a higher population density than the states of Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and Connecticut.
Greater Boston, which includes parts of southern New Hampshire, has a total population of approximately 4.8 million, while over half the population of New England falls inside Boston's Combined Statistical Area of over 8.2 million.
In 2020, New England had a population of 15,116,205, a growth of 4.6% from 2010. Massachusetts is the most populous state with 7,029,917 residents, while Vermont is the least populous state with 643,077 residents. Boston is by far the region's most populous city and metropolitan area.
Although a great disparity exists between New England's northern and southern portions, the region's average population density is 234.93 inhabitants/sq mi (90.7/km2). New England has a significantly higher population density than that of the U.S. as a whole (79.56/sq mi), or even just the contiguous 48 states (94.48/sq mi). Three-quarters of the population of New England, and most of the major cities, are in the states of Connecticut, Massachusetts and Rhode Island. The combined population density of these states is 786.83/sq mi, compared to northern New England's 63.56/sq mi (2000 census).
According to the 2006–08 American Community Survey, 48.7% of New Englanders were male and 51.3% were female. Approximately 22.4% of the population were under 18 years of age; 13.5% were over 65 years of age. The six states of New England have the lowest birth rate in the U.S.
White Americans make up the majority of New England's population at 73.4% of the total population, Hispanic and Latino Americans are New England's largest minority, and they are the second-largest group in the region behind non-Hispanic European Americans. As of 2014, Hispanics and Latinos of any race made up 10.2% of New England's population. Connecticut had the highest proportion at 13.9%, while Vermont had the lowest at 1.3%. There were nearly 1.5 million Hispanic and Latino individuals reported in New England in 2014.
Stateside Puerto Ricans, Puerto Ricans were the most numerous of the Hispanic and Latino subgroups. Over 660,000 Puerto Ricans lived in New England in 2014, forming 4.5% of the population. The Dominican Americans, Dominican population is over 200,000, and the Mexican Americans, Mexican and Guatemalan Americans, Guatemalan populations are each over 100,000. Cuban Americans, Americans of Cuban descent are scant in number; there were roughly 26,000 Cuban Americans in the region in 2014. People of all other Hispanic and Latino ancestries, including Salvadoran Americans, Salvadoran, Colombian Americans, Colombian and Bolivian Americans, Bolivian, formed 2.5% of New England's population and numbered over 361,000 combined.
According to the 2014 American Community Survey, the top ten largest reported European ancestries were the following: Irish Americans, Irish: 19.2% (2.8 million), English Americans, English (includes "American ancestry, American" ancestry): 16.7% (2.4 million), Italian Americans, Italian: 13.6% (2.0 million), French Americans, French and French Canadian: 13.1% (1.9 million), German Americans, German: 7.4% (1.1 million), Polish Americans, Polish: 4.9% (roughly 715,000), Portuguese Americans, Portuguese: 3.2% (467,000), Scottish Americans, Scottish: 2.5% (370,000), Russian Americans, Russian: 1.4% (206,000), and Greek Americans, Greek: 1.0% (152,000).
English is, by far, the most common language spoken at home. Approximately 81.3% of all residents (11.3 million people) over the age of five spoke only English at home. Roughly 1,085,000 people (7.8% of the population) spoke Spanish at home, and roughly 970,000 people (7.0% of the population) spoke other Indo-European languages at home. Over 403,000 people (2.9% of the population) spoke an Languages of Asia, Asian or Pacific Island language at home. Slightly fewer (about 1%) spoke French at home, although this figure is above 20% in northern New England, which borders francophone Québec. Roughly 99,000 people (0.7% of the population) spoke languages other than these at home.
As of 2014, approximately 87% of New England's inhabitants were born in the U.S., while over 12% were foreign-born. 35.8% of foreign-born residents were born in Latin America, 28.6% were born in Asia, 22.9% were born in Europe, and 8.5% were born in Africa.
Southern New England forms an integral part of the Northeast megalopolis, BosWash megalopolis (city type), megalopolis, a conglomeration of urban centers that spans from Boston to Washington, D.C. The region includes three of the four List of U.S. states by population density, most densely populated states in the U.S.; only New Jersey has a higher population density than the states of Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and Connecticut.
Greater Boston, which includes parts of southern New Hampshire, has a total population of approximately 4.8 million, while over half the population of New England falls inside Boston's Combined Statistical Area of over 8.2 million.
Economy
 Several factors combine to make the New England economy unique. The region is distant from the geographic center of the country, and it is a relatively small region but densely populated. It historically has been an important center of industry and manufacturing and a supplier of natural resource products, such as granite, lobster, and codfish. The service industry is important, including tourism, education, financial and insurance services, and architectural, building and construction services. The U.S. Department of Commerce has called the New England economy a microcosm for the entire U.S. economy.
The region underwent a long period of deindustrialization in the first half of the 20th century, as traditional manufacturing companies relocated to the Midwest, with textile and furniture manufacturing migrating to the South. In the late-20th century, an increasing portion of the regional economy included high technology, military defense industry, finance and insurance services, and education and health services. As of 2018, the GDP of New England was $1.1 trillion.
New England exports food products ranging from fish to lobster, cranberries, potatoes, and maple syrup. About half of the region's exports consist of industrial and commercial machinery, such as computers and electronic and electrical equipment. Granite is quarried at Barre (town), Vermont, Barre, Vermont, guns made at Springfield, Massachusetts, and Saco, Maine, submarines at Groton, Connecticut, surface naval vessels at Bath, Maine, and hand tools at Turners Falls, Massachusetts.
Several factors combine to make the New England economy unique. The region is distant from the geographic center of the country, and it is a relatively small region but densely populated. It historically has been an important center of industry and manufacturing and a supplier of natural resource products, such as granite, lobster, and codfish. The service industry is important, including tourism, education, financial and insurance services, and architectural, building and construction services. The U.S. Department of Commerce has called the New England economy a microcosm for the entire U.S. economy.
The region underwent a long period of deindustrialization in the first half of the 20th century, as traditional manufacturing companies relocated to the Midwest, with textile and furniture manufacturing migrating to the South. In the late-20th century, an increasing portion of the regional economy included high technology, military defense industry, finance and insurance services, and education and health services. As of 2018, the GDP of New England was $1.1 trillion.
New England exports food products ranging from fish to lobster, cranberries, potatoes, and maple syrup. About half of the region's exports consist of industrial and commercial machinery, such as computers and electronic and electrical equipment. Granite is quarried at Barre (town), Vermont, Barre, Vermont, guns made at Springfield, Massachusetts, and Saco, Maine, submarines at Groton, Connecticut, surface naval vessels at Bath, Maine, and hand tools at Turners Falls, Massachusetts.
Urban centers
 In 2017, Boston was ranked as having the ninth-most competitive financial center in the world and the fourth-most competitive in the United States. Boston-based Fidelity Investments helped popularize the mutual fund in the 1980s and has made Boston one of the top financial centers in the United States. The city is home to the headquarters of Santander Bank and a center for venture capital firms. State Street Corporation specializes in asset management and custody services and is based in the city.
Boston is also a printing and publishing center. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt is headquartered there, along with Bedford-St. Martin's and Beacon Press. The city is also home to the Hynes Convention Center in the Back Bay and the Seaport Hotel and Seaport World Trade Center and Boston Convention and Exhibition Center on the South Boston waterfront.
The General Electric Corporation announced its decision to move the company's global headquarters to the Boston Seaport District from Fairfield, Connecticut, in 2016, citing factors including Boston's preeminence in the realm of higher education. The city also holds the headquarters to several major athletic and footwear companies, including Converse (shoe company), Converse, New Balance and Reebok. Rockport (company), Rockport, Puma (brand), Puma and Wolverine World Wide have headquarters or regional offices just outside the city.
Hartford is the historic international center of the insurance industry, with companies such as Aetna, Conning & Company, The Hartford, Harvard Pilgrim Health Care, The Phoenix Companies and Hartford Steam Boiler Inspection and Insurance Company, Hartford Steam Boiler based in the city, and The Travelers Companies and Lincoln National Corporation have major operations in the city. It is also home to the corporate headquarters of U.S. Fire Arms Mfg. Co., United Technologies, and Virtus Investment Partners.
Fairfield County, Connecticut, has a large concentration of investment management firms in the area, most notably Bridgewater Associates (one of the world's largest hedge fund companies), Aladdin Capital Management and Point72 Asset Management. Moreover, many international banks have their North American headquarters in Fairfield County, such as NatWest Group and UBS.
In 2017, Boston was ranked as having the ninth-most competitive financial center in the world and the fourth-most competitive in the United States. Boston-based Fidelity Investments helped popularize the mutual fund in the 1980s and has made Boston one of the top financial centers in the United States. The city is home to the headquarters of Santander Bank and a center for venture capital firms. State Street Corporation specializes in asset management and custody services and is based in the city.
Boston is also a printing and publishing center. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt is headquartered there, along with Bedford-St. Martin's and Beacon Press. The city is also home to the Hynes Convention Center in the Back Bay and the Seaport Hotel and Seaport World Trade Center and Boston Convention and Exhibition Center on the South Boston waterfront.
The General Electric Corporation announced its decision to move the company's global headquarters to the Boston Seaport District from Fairfield, Connecticut, in 2016, citing factors including Boston's preeminence in the realm of higher education. The city also holds the headquarters to several major athletic and footwear companies, including Converse (shoe company), Converse, New Balance and Reebok. Rockport (company), Rockport, Puma (brand), Puma and Wolverine World Wide have headquarters or regional offices just outside the city.
Hartford is the historic international center of the insurance industry, with companies such as Aetna, Conning & Company, The Hartford, Harvard Pilgrim Health Care, The Phoenix Companies and Hartford Steam Boiler Inspection and Insurance Company, Hartford Steam Boiler based in the city, and The Travelers Companies and Lincoln National Corporation have major operations in the city. It is also home to the corporate headquarters of U.S. Fire Arms Mfg. Co., United Technologies, and Virtus Investment Partners.
Fairfield County, Connecticut, has a large concentration of investment management firms in the area, most notably Bridgewater Associates (one of the world's largest hedge fund companies), Aladdin Capital Management and Point72 Asset Management. Moreover, many international banks have their North American headquarters in Fairfield County, such as NatWest Group and UBS.
Agriculture
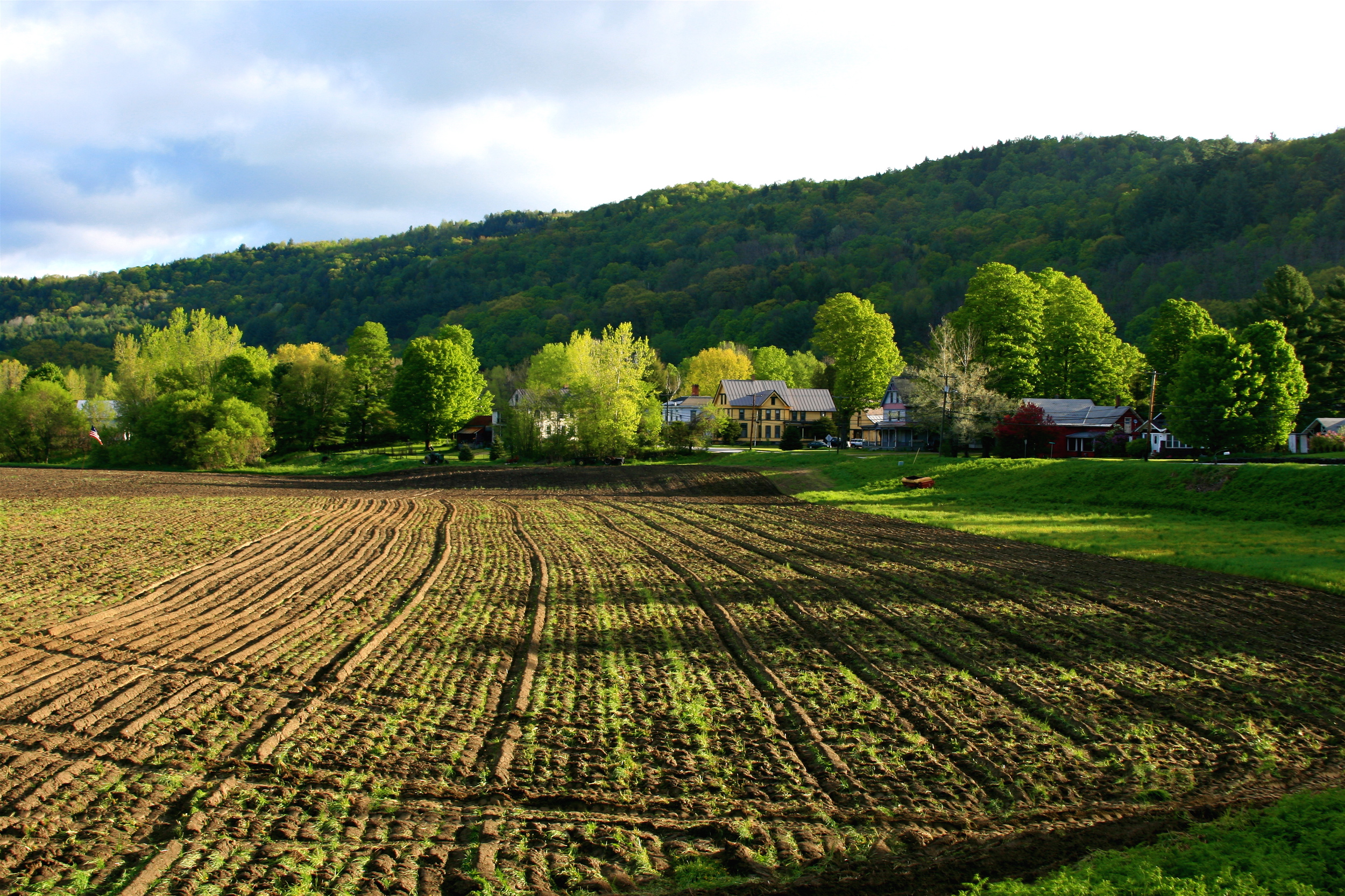 Agriculture is limited by the area's rocky soil, cool climate, and small area. Some New England states, however, are ranked highly among U.S. states for particular areas of production. Maine is ranked ninth for aquaculture, and has abundant potato fields in its northeast part. Vermont is fifteenth for dairy products, and Connecticut and Massachusetts seventh and eleventh for tobacco, respectively. Cranberries are grown in Massachusetts' Cape Cod-Plymouth-South Shore area, and blueberries in Maine.
Agriculture is limited by the area's rocky soil, cool climate, and small area. Some New England states, however, are ranked highly among U.S. states for particular areas of production. Maine is ranked ninth for aquaculture, and has abundant potato fields in its northeast part. Vermont is fifteenth for dairy products, and Connecticut and Massachusetts seventh and eleventh for tobacco, respectively. Cranberries are grown in Massachusetts' Cape Cod-Plymouth-South Shore area, and blueberries in Maine.
Energy
 The region is mostly energy-efficient compared to the U.S. at large, with every state but Maine ranking within the ten most energy-efficient states; every state in New England also ranks within the ten most expensive states for electricity prices. Wind power, mainly from offshore sources, is expected to gain market share in the 2020s.
The region is mostly energy-efficient compared to the U.S. at large, with every state but Maine ranking within the ten most energy-efficient states; every state in New England also ranks within the ten most expensive states for electricity prices. Wind power, mainly from offshore sources, is expected to gain market share in the 2020s.
Employment
As of January 2017, employment is stronger in New England than in the rest of the United States. During the Great Recession, unemployment rates ballooned across New England as elsewhere; however, in the years that followed, these rates declined steadily, with New Hampshire and Massachusetts having the lowest unemployment rates in the country, respectively. The most extreme swing was in Rhode Island, which had an unemployment rate above 10% following the recession, but which saw this rate decline by over 6% in six years. As of December 2016, the metropolitan statistical area (MSA) with the lowest unemployment rate, 2.1%, was Burlington, Vermont, Burlington-South Burlington, Vermont; the MSA with the highest rate, 4.9%, was Waterbury, Connecticut.Overall tax burden
In 2018, four of the six New England states were among the top ten states in the country in terms of taxes paid per taxpayer. The rankings included #3 Maine (11.02%), #4 Vermont (10.94%), #6 Connecticut (10.19%) and #7 Rhode Island (10.14%). Additionally New Hampshire, Vermont, Maine and Rhode Island took four of the top five spots for "Highest Property Tax as a Percentage of Personal Income".Government
Town meetings
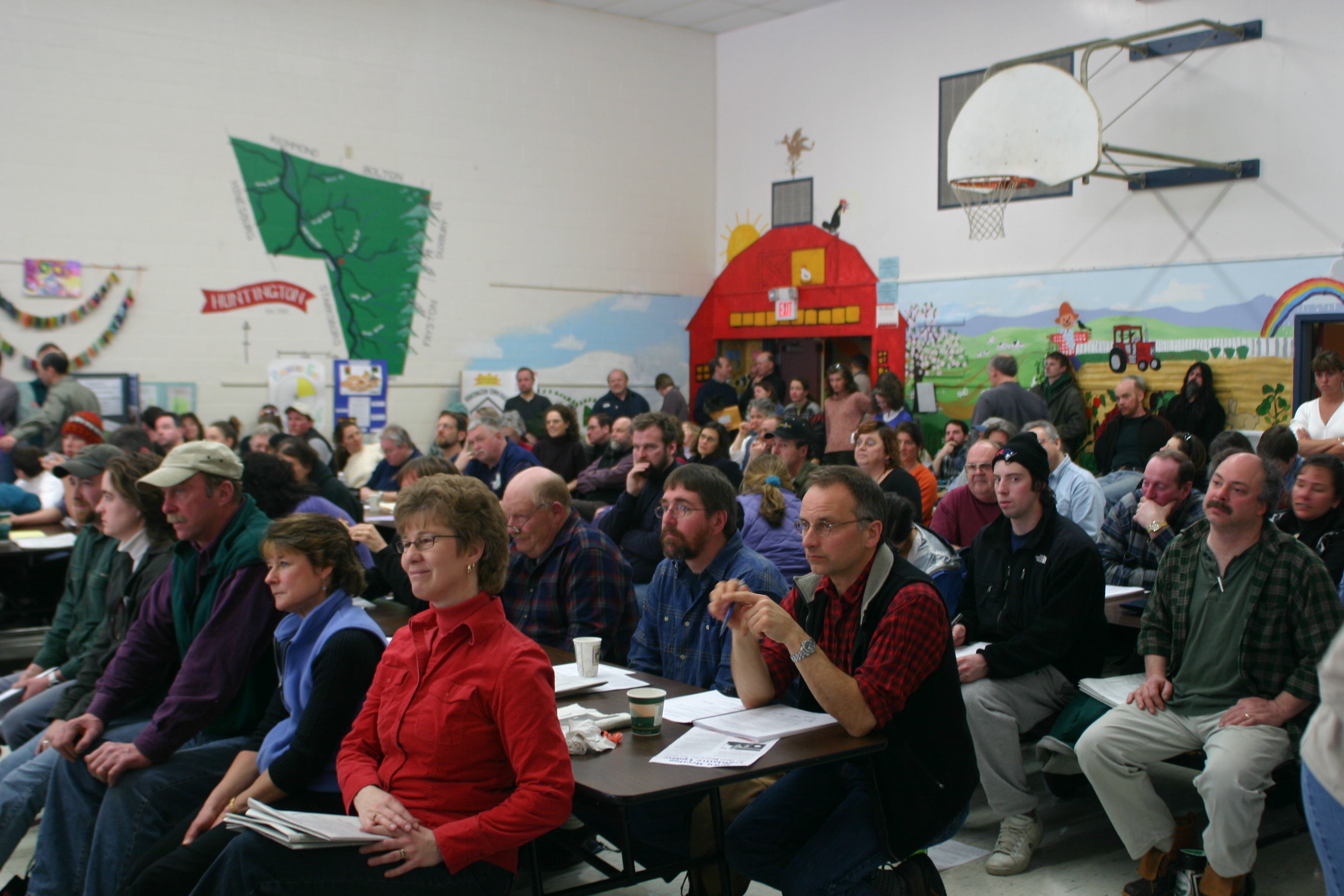 New England town meetings were derived from meetings held by church elders, and are still an integral part of government in many New England towns. At such meetings, any citizen of the town may discuss issues with other members of the community and vote on them. This is the strongest example of direct democracy in the U.S. today, and the strong democratic tradition was even apparent in the early 19th century, when Alexis de Tocqueville wrote in ''Democracy in America'':
By contrast, James Madison wrote in ''Federalist Papers, Federalist No. 55'' that, regardless of the assembly, "passion never fails to wrest the scepter from reason. Had every Athenian citizen been a Socrates, every Athenian assembly would still have been a mob." The use and effectiveness of town meetings is still discussed by scholars, as well as the possible application of the format to other regions and countries.
New England town meetings were derived from meetings held by church elders, and are still an integral part of government in many New England towns. At such meetings, any citizen of the town may discuss issues with other members of the community and vote on them. This is the strongest example of direct democracy in the U.S. today, and the strong democratic tradition was even apparent in the early 19th century, when Alexis de Tocqueville wrote in ''Democracy in America'':
By contrast, James Madison wrote in ''Federalist Papers, Federalist No. 55'' that, regardless of the assembly, "passion never fails to wrest the scepter from reason. Had every Athenian citizen been a Socrates, every Athenian assembly would still have been a mob." The use and effectiveness of town meetings is still discussed by scholars, as well as the possible application of the format to other regions and countries.
Politics
Elections
State and national elected officials in New England recently have been elected mainly from the Democratic Party. The region is generally considered to be the most liberal in the United States, with more New Englanders identifying as liberals than Americans elsewhere. In 2010, four of six of the New England states were polled as the most liberal in the United States.Political party strength
Judging purely by party registration rather than voting patterns, New England today is one of the most Democratic regions in the U.S. According to Gallup (company), Gallup,New Hampshire primary
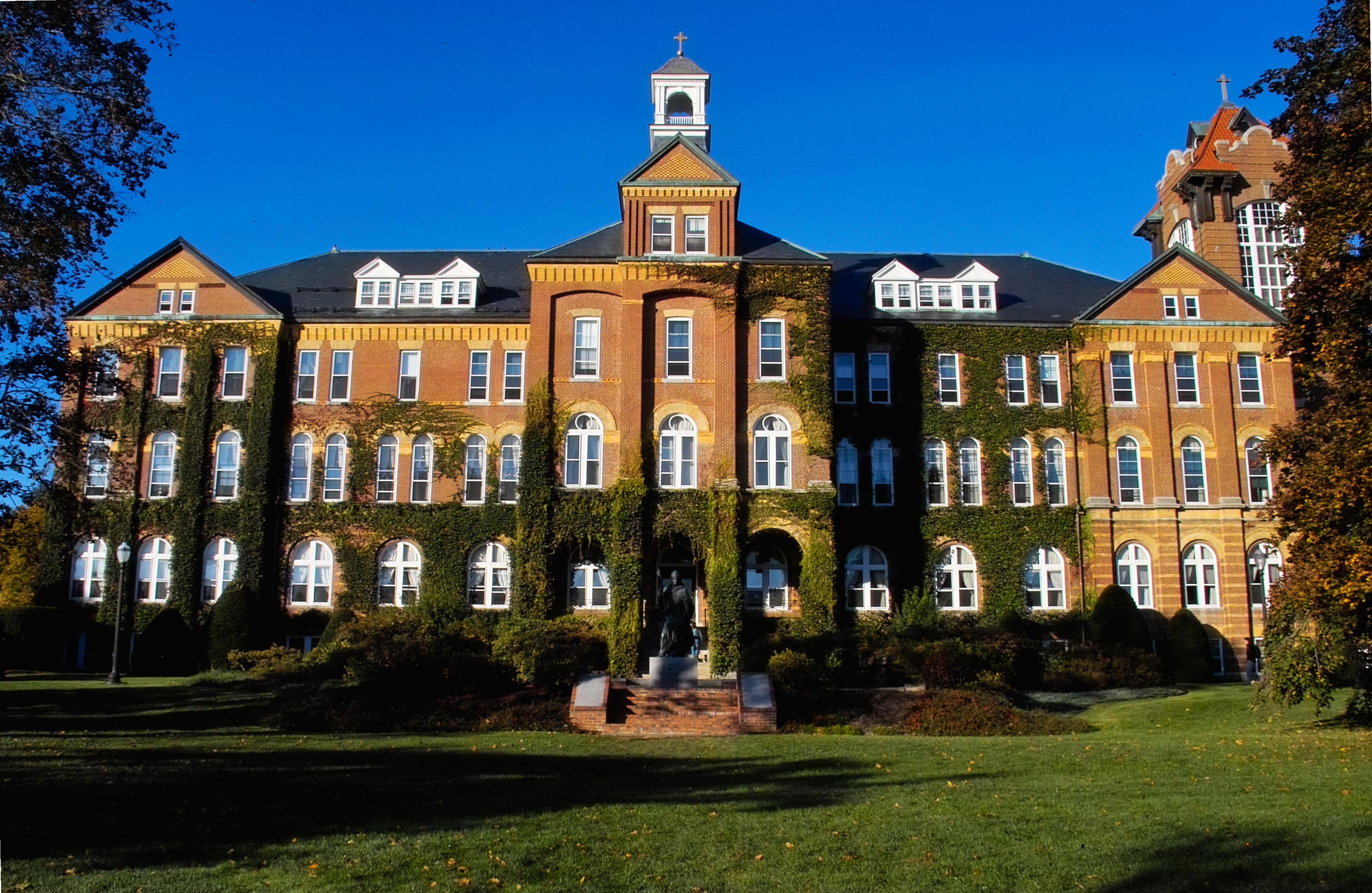 Historically, the New Hampshire primary has been the first in a series of nationwide political party primary elections held in the United States every four years. Held in the state of New Hampshire, it usually marks the beginning of the United States presidential election, U.S. presidential election process. Even though few delegates are chosen from New Hampshire, the primary has always been pivotal to both New England and American politics. One college in particular, Saint Anselm College, has been home to numerous national presidential debates and visits by candidates to its campus.
Historically, the New Hampshire primary has been the first in a series of nationwide political party primary elections held in the United States every four years. Held in the state of New Hampshire, it usually marks the beginning of the United States presidential election, U.S. presidential election process. Even though few delegates are chosen from New Hampshire, the primary has always been pivotal to both New England and American politics. One college in particular, Saint Anselm College, has been home to numerous national presidential debates and visits by candidates to its campus.
Education
Colleges and universities
Private and independent secondary schools
 At the pre-college level, New England is home to a number of American independent schools (also known as private schools). The concept of the elite "New England university-preparatory school, prep school" (preparatory school) and the "preppy" lifestyle is an iconic part of the region's image.
:See the list of private schools for each state:
At the pre-college level, New England is home to a number of American independent schools (also known as private schools). The concept of the elite "New England university-preparatory school, prep school" (preparatory school) and the "preppy" lifestyle is an iconic part of the region's image.
:See the list of private schools for each state::Private schools in Connecticut, Connecticut, :Private schools in Massachusetts, Massachusetts, :Private schools in Maine, Maine, :Private schools in New Hampshire, New Hampshire, :Private schools in Rhode Island, Rhode Island, :Private schools in Vermont, Vermont.
Public education
New England is home to some of the oldest public schools in the nation and was the first region in the United States to implement universal compulsory schooling. Boston Latin School is the oldest public school in America and was attended by several signatories of the Declaration of Independence. Hartford Public High School is the second oldest operating high school in the U.S. As of 2005, the National Education Association ranked Connecticut as having the highest-paid teachers in the country. Massachusetts and Rhode Island ranked eighth and ninth, respectively. New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont have cooperated in developing a New England Common Assessment Program test under the No Child Left Behind guidelines. These states can compare the resultant scores with each other.Academic journals and press
There are several academic journals and publishing companies in the region, including ''The New England Journal of Medicine'', Harvard University Press and Yale University Press. Some of its institutions lead the Open access (publishing), open access alternative to conventional academic publication, including MIT, the University of Connecticut, and the University of Maine. The Federal Reserve Bank of Boston publishes the ''New England Economic Review''.Culture
 New England has a shared heritage and culture primarily shaped by waves of immigration from Europe. In contrast to other American regions, many of New England's earliest Puritan settlers came from eastern England, contributing to New England's distinctive accents, foods, customs, and social structures. Within modern New England a cultural divide exists between urban New Englanders living along the densely populated coastline, and rural New Englanders in western Massachusetts, northwestern and northeastern Connecticut, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine, where population density is low. There is also a substantial divide between Connecticut and the other states of the region, owing to the former's close cultural and economic ties with the New York metropolitan area.
New England has a shared heritage and culture primarily shaped by waves of immigration from Europe. In contrast to other American regions, many of New England's earliest Puritan settlers came from eastern England, contributing to New England's distinctive accents, foods, customs, and social structures. Within modern New England a cultural divide exists between urban New Englanders living along the densely populated coastline, and rural New Englanders in western Massachusetts, northwestern and northeastern Connecticut, Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine, where population density is low. There is also a substantial divide between Connecticut and the other states of the region, owing to the former's close cultural and economic ties with the New York metropolitan area.
Religion
 Today, New England is the least religious region of the U.S. In 2009, less than half of those polled in Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont claimed that religion was an important part of their daily lives. Connecticut and Rhode Island are among the ten least religious states, where 55% and 53% of those polled (respectively) claimed that it was important. According to the American Religious Identification Survey, 34% of Vermonters claimed to have no religion; nearly one out of every four New Englanders identifies as having no religion, more than in any other part of the U.S. New England had one of the highest percentages of Catholics in the U.S. This number declined from 50% in 1990 to 36% in 2008.
Today, New England is the least religious region of the U.S. In 2009, less than half of those polled in Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and Vermont claimed that religion was an important part of their daily lives. Connecticut and Rhode Island are among the ten least religious states, where 55% and 53% of those polled (respectively) claimed that it was important. According to the American Religious Identification Survey, 34% of Vermonters claimed to have no religion; nearly one out of every four New Englanders identifies as having no religion, more than in any other part of the U.S. New England had one of the highest percentages of Catholics in the U.S. This number declined from 50% in 1990 to 36% in 2008.
Cultural roots
Many of the first European colonists of New England had a Sea, maritime orientation toward whaling (first noted about 1650) and fishing, in addition to farming. New England has developed a distinct New England cuisine, cuisine, Eastern New England English, dialect, Connected farm, architecture, and government. New England cuisine has a reputation for its emphasis on seafood and dairy; clam chowder, lobster, and other products of the sea are among some of the region's most popular foods. New England has largely preserved its regional character, especially in its historic places. The region has become more Ethnic diversity, ethnically diverse, having seen waves of immigration from Ireland, Quebec, Italy, Portugal, Germany, Poland, Scandinavia, Asia, Latin America, Africa, other parts of the U.S., and elsewhere. The enduring European influence can be seen in the region in the use of traffic roundabout, rotaries; the bilingual French and English towns of northern Vermont, Maine, and New Hampshire; the unique, often non-Rhotic and non-rhotic accents, rhotic traditional coastal dialect akin to the southeastern half of England; and the region's heavy prevalence of English town- and county-names. These repeat from state to state, primarily due to settlers throughout the region having named their new towns after their old ones. For example, the town of North Yarmouth, Maine, was named by settlers from Yarmouth, Massachusetts, which was in turn named for Great Yarmouth (still locally called Yarmouth) in England. Every New England state has a town named Warren (a French-English noble family of wealthy settlers), and each except Rhode Island has a city/town named Franklin and Washington (constitutional founding fathers), Andover, Bridgewater, Chester, Manchester, Plymouth, and Windsor (these six were towns in England). Every state except Connecticut has a Lincoln and has a Richmond. Massachusetts, Vermont, and Maine each contain a Franklin County (disambiguation)#in the United States, Franklin County.Cuisine
New England maintains a distinct cuisine and food culture. Early foods in the region were influenced by Native American and English cuisines. The early colonists often adapted their original cuisine to fit with the available foods of the region. New England staples reflect the convergence of American Indian and Pilgrim cuisine, such as johnnycakes, succotash, cornbread and various seafood recipes. The Wabanaki Confederacy, Wabanaki tribal nations made Plant milk, nut milk. New England also has a distinct food language. A few of the unique regional terms include "grinders" for submarine sandwiches and "frappes" for thick milkshakes, referred to as "Cabinets" in Rhode Island. Other foods native to the region include steak tips (marinated sirloin steak), bulkie rolls, maple syrup, cranberry recipes and clam chowder. A type of India pale ale known as New England India Pale Ale (NEIPA) was developed in Vermont in the 2010s. Other regional beverages include Moxie, one of the first mass-produced soft drinks in the United States, introduced in Lowell, Massachusetts, in 1876; it remains popular in New England, particularly in Maine. Coffee milk is associated with Rhode Island as the official state drink. Portuguese cuisine is an important element in the annual Feast of the Blessed Sacrament in New Bedford, Massachusetts, the largest ethnic heritage festival in New England.Accents and dialects
There are several American English dialects spoken in the region, most famously the Boston accent, which is native to the northeastern coastal regions of New England. The most identifiable features of the Boston accent are believed to have originated from England's Received Pronunciation, which shares features such as the broad A and rhoticity in English, dropping the final R. Another source was 17th century speech in East Anglia and Lincolnshire, where many of the Puritan immigrants had originated. The East Anglian "whine" developed into the Yankee "twang". Boston accents were most strongly associated at one point with the so-called "The Establishment, Eastern Establishment" and Boston Brahmin, Boston's upper class, although today the accent is predominantly associated with blue-collar natives, as exemplified by movies such as ''Good Will Hunting'' and ''The Departed''. The Boston accent and those accents closely related to it cover eastern Massachusetts, New Hampshire and Maine. Some Rhode Islanders speak with a rhoticity in English, non-rhotic accent that many compare to a "Brooklyn" accent or a cross between a New York and Boston accent, where "water" becomes "wata". Many Rhode Islanders distinguish the ''aw'' sound , as one might hear in New Jersey; e.g., the word "coffee" is pronounced . This type of accent was brought to the region by early settlers from eastern England in the Puritan migration in the mid-seventeenth century.Social activities and music
Acadian and French-speaking Quebecer, Québécois culture are included in music and dance in much of rural New England, particularly Maine. Contra dancing and country square dancing are popular throughout New England, usually backed by live Irish, Acadian or other folk music. Fife and drum corps are common, especially in southern New England and more specifically New England was an important center of American classical music for some time. The Yankee tunesmiths, First New England School of composers was active between 1770 and 1820, and the Second New England School about a century later. Prominent modernist composers also come from the region, including Charles Ives and John Adams (composer), John Adams. Boston is the site of the New England Conservatory, Boston Conservatory at Berklee, and the Boston Symphony Orchestra.
In popular music, the region has produced Donna Summer, JoJo (singer), JoJo, New Edition, Bobby Brown, Bel Biv Devoe, Passion Pit, MGMT, Meghan Trainor, New Kids on the Block, Rachel Platten and John Mayer. In rock music, the region has produced Rob Zombie, Aerosmith, The Modern Lovers, Phish, the Pixies (band), Pixies, The Cars, The J. Geils Band, The Mighty Mighty Bosstones, Grace Potter, GG Allin, The Dresden Dolls, Dinosaur Jr., the Dropkick Murphys and Boston (band), Boston. Quincy, Massachusetts native Dick Dale helped popularize surf rock. Hip hop acts hailing from New England include Gang Starr.
New England was an important center of American classical music for some time. The Yankee tunesmiths, First New England School of composers was active between 1770 and 1820, and the Second New England School about a century later. Prominent modernist composers also come from the region, including Charles Ives and John Adams (composer), John Adams. Boston is the site of the New England Conservatory, Boston Conservatory at Berklee, and the Boston Symphony Orchestra.
In popular music, the region has produced Donna Summer, JoJo (singer), JoJo, New Edition, Bobby Brown, Bel Biv Devoe, Passion Pit, MGMT, Meghan Trainor, New Kids on the Block, Rachel Platten and John Mayer. In rock music, the region has produced Rob Zombie, Aerosmith, The Modern Lovers, Phish, the Pixies (band), Pixies, The Cars, The J. Geils Band, The Mighty Mighty Bosstones, Grace Potter, GG Allin, The Dresden Dolls, Dinosaur Jr., the Dropkick Murphys and Boston (band), Boston. Quincy, Massachusetts native Dick Dale helped popularize surf rock. Hip hop acts hailing from New England include Gang Starr.
Media
The leading U.S. cable TV sports broadcaster ESPN is headquartered in Bristol, Connecticut. New England has several regional cable networks, including New England Cable News (NECN) and the New England Sports Network (NESN). New England Cable News is the largest regional 24-hour news cycle, 24-hour United States cable news, cable news network in the U.S., broadcasting to more than 3.2 million homes in all of the New England states. Its studios are located in Newton, Massachusetts, outside of Boston, and it maintains bureaus in Manchester, New Hampshire; Hartford, Connecticut; Worcester, Massachusetts; Portland, Maine; and Burlington, Vermont. In Connecticut, Litchfield, Fairfield, and New Haven counties it also broadcasts New York based news programs—this is due in part to the immense influence New York has on this region's economy and culture, and also to give Connecticut broadcasters the ability to compete with overlapping media coverage from New York-area broadcasters. NESN broadcasts the Boston Red Sox baseball and Boston Bruins hockey throughout the region, save for Fairfield County, Connecticut. Connecticut also receives the YES Network, which broadcasts the games of the New York Yankees and Brooklyn Nets as well as SportsNet New York (SNY), which broadcasts New York Mets games. NBC Sports Boston broadcasts the games of the Boston Celtics, New England Revolution and Boston Cannons to all of New England except Fairfield County. While most New England cities have daily newspapers, ''The Boston Globe'' and ''The New York Times'' are distributed widely throughout the region. Major newspapers also include ''The Providence Journal'', ''Portland Press Herald'', and ''Hartford Courant'', the oldest continuously published newspaper in the U.S.Comedy
New Englanders are well represented in American comedy. Writers for ''The Simpsons'' and late-night television programs often come by way of the Harvard Lampoon. A number of ''Saturday Night Live'' (SNL) cast members have roots in New England, from Adam Sandler to Amy Poehler, who also starred in the NBC television series ''Parks and Recreation''. Former ''The Daily Show, Daily Show'' correspondents John Hodgman, Rob Corddry and Steve Carell are from Massachusetts. Carell was also involved in film and The Office (U.S. TV series), the American adaptation of ''The Office'' (alongside fellow Massachusetts natives Mindy Kaling, B. J. Novak, and John Krasinski), which features Dunder-Mifflin branches set in Stamford, Connecticut and Nashua, New Hampshire. Late-night television hosts Jay Leno and Conan O'Brien have roots in the Boston area. Notable stand-up comedians are also from the region, including Bill Burr, Steve Sweeney (comedian), Steve Sweeney, Steven Wright, Sarah Silverman, Lisa Lampanelli, Denis Leary, Lenny Clarke, Patrice O'Neal and Louis CK. ''SNL'' cast member Seth Meyers once attributed the region's imprint on American humor to its "sort of wry New England sense of pointing out anyone who's trying to make a big deal of himself", with the ''Boston Globe'' suggesting that irony and sarcasm are its trademarks, as well as Irish influences.Literature
 New Englanders have made significant contributions to literature. The first printing press in America was set up in Cambridge, Massachusetts, by Stephen Daye in the 17th century. Writers in New England produced many works on religious subjects, particularly on Puritan theology and poetry during colonial times and on Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment ideas during the American Revolution. The literature of New England has had an enduring influence on American literature in general, with themes that are emblematic of the larger concerns of American letters, such as religion, race, the individual versus society, social repression and nature.
19th century New England was a center for progressive ideals, and many abolitionist and transcendentalist tracts were produced. Leading transcendentalists were from New England, such as
New Englanders have made significant contributions to literature. The first printing press in America was set up in Cambridge, Massachusetts, by Stephen Daye in the 17th century. Writers in New England produced many works on religious subjects, particularly on Puritan theology and poetry during colonial times and on Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment ideas during the American Revolution. The literature of New England has had an enduring influence on American literature in general, with themes that are emblematic of the larger concerns of American letters, such as religion, race, the individual versus society, social repression and nature.
19th century New England was a center for progressive ideals, and many abolitionist and transcendentalist tracts were produced. Leading transcendentalists were from New England, such as Film, television, and acting
New England has a rich history in filmmaking dating back to the dawn of the motion picture era at the turn of the 20th century, sometimes dubbed Hollywood East by film critics. A theater at 547 Washington Street in Boston was the second location to debut a picture projected by the Vitascope, and shortly thereafter several novels were being adapted for the screen and set in New England, including ''The Scarlet Letter'' and ''The House of Seven Gables''. The New England region continued to churn out films at a pace above the national average for the duration of the 20th century, including blockbuster hits such as ''Jaws (film), Jaws'', ''Good Will Hunting'' and ''The Departed'', all of which won Academy Awards. The New England area became known for a number of themes that recurred in films made during this era, including the development of yankee characters, smalltown life contrasted with city values, seafaring tales, family secrets and haunted New England. These themes are rooted in centuries of New England culture and are complemented by the region's diverse natural landscape and architecture, from the Atlantic Ocean and brilliant fall foliage to church steeples and skyscrapers. Since the turn of the millennium, Boston and the greater New England region have been home to the production of numerous films and television series, thanks in part to tax incentive programs put in place by local governments to attract filmmakers to the region. Notable actors and actresses that have come from the New England area include Ben Affleck, Matt Damon, Chris Evans (actor), Chris Evans, Ryan O’Neal, Amy Poehler, Elizabeth Banks, Steve Carell, Ruth Gordon, John Krasinski, Edward Norton, Mark Wahlberg and Matthew Perry. Many films and television series have been List of films set in New England, produced in and set in New England.
Notable actors and actresses that have come from the New England area include Ben Affleck, Matt Damon, Chris Evans (actor), Chris Evans, Ryan O’Neal, Amy Poehler, Elizabeth Banks, Steve Carell, Ruth Gordon, John Krasinski, Edward Norton, Mark Wahlberg and Matthew Perry. Many films and television series have been List of films set in New England, produced in and set in New England.
Museums, historical societies, and libraries
 There are many museums located throughout New England, especially in the Greater Boston area. These museums include privately held collections as well as public institutions. Most notable of these museums are the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, Museum of Fine Arts, the Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum, Worcester Art Museum, and the Peabody Essex Museum. The oldest public museum in continuous operation in the United States is the Pilgrim Hall Museum in Plymouth, Massachusetts, which opened in 1824.
The Boston Public Library is the largest public library in the region with over 8 million materials in its collection. The largest academic research library in the world is the Harvard Library in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The W. E. B. Du Bois Library of the University of Massachusetts Amherst is the tallest academic library in the world.
There are also many historical societies in the region. Historic New England operates museums and historic sites in the name of historical preservation. Many properties belonging to HNE include preserved Historic house museum, house museums of prominent figures in New England and American history. Other societies include the Massachusetts Historical Society, the Essex Institute, the American Antiquarian Society, and The Bostonian Society. The Massachusetts Historical Society, founded in 1791, is the oldest operating in the United States. Many cities and towns across New England operate their own historical societies focused on historical preservation of local sites and the recording of local history.
There are many museums located throughout New England, especially in the Greater Boston area. These museums include privately held collections as well as public institutions. Most notable of these museums are the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, Museum of Fine Arts, the Institute of Contemporary Art, Boston, the Isabella Stewart Gardner Museum, Worcester Art Museum, and the Peabody Essex Museum. The oldest public museum in continuous operation in the United States is the Pilgrim Hall Museum in Plymouth, Massachusetts, which opened in 1824.
The Boston Public Library is the largest public library in the region with over 8 million materials in its collection. The largest academic research library in the world is the Harvard Library in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The W. E. B. Du Bois Library of the University of Massachusetts Amherst is the tallest academic library in the world.
There are also many historical societies in the region. Historic New England operates museums and historic sites in the name of historical preservation. Many properties belonging to HNE include preserved Historic house museum, house museums of prominent figures in New England and American history. Other societies include the Massachusetts Historical Society, the Essex Institute, the American Antiquarian Society, and The Bostonian Society. The Massachusetts Historical Society, founded in 1791, is the oldest operating in the United States. Many cities and towns across New England operate their own historical societies focused on historical preservation of local sites and the recording of local history.
Sports
New England has a strong heritage of athletics, and many internationally popular sports were invented and codified in the region, including basketball, volleyball, and American football. Football is the most popular sport in the region and was developed by Walter Camp in New Haven, Connecticut, in the 1870s and 1880s. The New England Patriots are based in Foxborough, Massachusetts, and are the most popular professional sports team in New England. The Patriots have won six Super Bowl championships and are one of the most winning teams in the National Football League. There are also high-profile collegiate and high school football rivalries in New England. These games are most often played on Thanksgiving Day and are some of the oldest sports rivalries in the United States. The high school rivalry between Wellesley High School and Needham High School in Massachusetts is considered to be the nation's oldest football rivalry, having started in 1882. Before the advent of modern rules of baseball, a different form was played called the Massachusetts Game. This version of baseball was an early rival of the Knickerbocker Rules of New York and was played throughout New England. In 1869, there were 59 teams throughout the region which played according to the Massachusetts rules. The New York rules gradually became more popular throughout the United States, and professional and semi-professional clubs began to appear. Early teams included the Providence Grays, the Worcester Worcesters and the Hartford Dark Blues; these did not last long, but other teams grew to renown, such as the History of the Boston Braves, Boston Braves and the Boston Red Sox. Fenway Park was built in 1912 and is the oldest ballpark still in use in Major League Baseball. Other professional baseball teams in the region include the Hartford Yard Goats, New Hampshire Fisher Cats, Vermont Lake Monsters, Portland Sea Dogs, Bridgeport Bluefish, New Britain Bees and the Worcester Red Sox. Basketball was developed in Springfield, Massachusetts, by James Naismith in 1891. Naismith was attempting to create a game which could be played indoors so that athletes could keep fit during New England winters. The Boston Celtics were founded in 1946 and are one of the most successful National Basketball Association, NBA teams, winning 17 titles. The NBA G League team the Maine Red Claws is based in Portland, Maine. The Women's National Basketball Association's Connecticut Sun is based in Uncasville, Connecticut. The UConn Huskies women's basketball team is the most successful women's collegiate team in the nation, winning 11 NCAA Division I titles. The Basketball Hall of Fame is located in Springfield, Massachusetts. Winter sports are extremely popular and have a long history in the region, including alpine skiing, snowboarding, and Nordic skiing. Ice hockey is also a popular sport. The Boston Bruins were founded in 1924 as an Original Six team, and they have a historic rivalry with the Montreal Canadiens. The Bruins play in the TD Garden, a venue that they share with the Boston Celtics. College hockey is also a popular spectator sport, with Boston's annual Beanpot (ice hockey), Beanpot tournament between Northeastern University, Boston University, Harvard University and Boston College. Other hockey teams include the Maine Mariners (ECHL), Maine Mariners, Providence Bruins, Springfield Thunderbirds, Worcester Railers, Bridgeport Sound Tigers and the Hartford Wolf Pack. The Connecticut Whale (PHF), Connecticut Whale hockey team and the Boston Pride are two of the six teams of the Premier Hockey Federation. The region's largest ice hockey and skating facility is the New England Sports Center in Marlborough, Massachusetts, home to the Skating Club of Boston, one of the oldest ice skating clubs in the United States. Volleyball was invented in Holyoke, Massachusetts, in 1895 by William G. Morgan. Morgan was an instructor at a YMCA and wanted to create an indoor game for his athletes. The game was based on badminton and was spread as a sport through YMCA facilities. The international Volleyball Hall of Fame is located in Holyoke. Rowing, sailing, and yacht racing are also popular events in New England. The Head of the Charles race is held on the Charles River in October every year and attracts over 10,000 athletes and over 200,000 spectators each year. Sailing regattas include the Newport Bermuda Race, the Marblehead to Halifax Ocean Race, and the Single-Handed Trans-Atlantic Race. The ''New York Times'' considers the Newport and Marblehead races to be among the most prestigious in the world. The Boston Marathon is run on Patriots' Day every year and was first run in 1897. It is a World Marathon Major and is operated by the Boston Athletic Association. The race route goes from Hopkinton, Massachusetts through Greater Boston, finishing at Copley Square in Boston. The race offers far less prize money than many other marathons, but its difficulty and long history make it one of the world's most prestigious marathons. It is New England's largest sporting event with nearly 500,000 spectators each year. New England is represented in professional soccer by the New England Revolution, an inaugural team of the Major League Soccer founded in 1994 and playing in Gillette Stadium which it shares with the New England Patriots. The Revolution have won a U.S. Open Cup and a 2008 North American SuperLiga, SuperLiga Championship, and they have appeared in five MLS finals.Transportation

See also
* Atlantic Northeast * Autumn in New England * Brother Jonathan * Extreme points of New England * Fieldstone * Historic New England * List of beaches in New England * List of birds of New England * List of mammals of New England * Greenwich#Manor of East Greenwich, Manor of East Greenwich * New Albion * New Albion (colony) * New England–Acadian forests * New England Confederation * New England (medieval) * New England Planters * New England Summer Nationals * Northeastern coastal forests * Offshore wind power * Southeastern New England AVA wine region * Swamp YankeeReferences
Citations
General sources
* ''New York: Atlas of Historical County Boundaries'', John H. Long, Editor; Compiled by Kathryn Ford Thorne; A Project of the Dr. William M. Scholl Center for Family and Community History, The new Berry Library, Simon & Schuster, 1993. *Further reading
* Bartlett, Ray et al. ''New England Trips''. * Berman, Eleanor. ''Eyewitness Travel Guides New England''. * Chenoweth, James. ''Oddity Odyssey: A Journey Through New England's Colorful Past''. Holt, 1996. Humorous travel guide. * Hall, Donald, Burt Feintuch, and David H. Watters, eds. ''Encyclopedia of New England'' (Yale U.P. 2005), 1596 pp; the major scholarly resource to the geography, history and culture of the region. * Koistinen, David. ''Confronting Decline: The Political Economy of Deindustrialization in Twentieth-Century New England'' (2013) * Muse, Vance. ''The Smithsonian Guide to Historic America: Northern New England''. Stewart, Tabori & Chang, 1998. A photographic guide to historic sites in New England. * Riess, Jana. ''The Spiritual Traveler Boston and New England: A Guide to Sacred Sites and Peaceful Places'', HiddenSpring * Sletcher, Michael. ''New England: The Greenwood Encyclopedia of American Regional Cultures'' (2004) * Wiencek, Henry. ''The Smithsonian Guide to Historic America: Southern New England''. Stewart, Tabori & Chang, 1998. A photographic guide to historic sites in New England.External links
PoliticalNew England Governors Conference
Historical
Historic New England
- American Revolution battle site Maps
Map of New England
From the 1871 Atlas of Massachusetts by Walling and Gray. Culture
{{DEFAULTSORT:New England New England, Census regions of the United States English colonization of the Americas History of New England Military history of New England Regions of the United States Maritime culture