|
John (Mauro-Roman King)
John ( gr, Ἰωάννης, Iōannēs), referred to as John the Tyrant and sometimes given the nickname Stotzas the Younger (Latin: ''Stutias Iunior'') after his predecessor, Stotzas, was a Berber military leader and briefly King of the Mauro-Roman Kingdom following the death of his predecessor. Given his name, ''Ioannes'', John was probably, like Stotzas, of Eastern Roman descent and only briefly commanded his army against the Eastern Roman Empire. After the defeat of Stotzas, John was chosen by the combined Berber-Eastern Roman rebel army and he supported the Vandal restoration attempt of ''dux Numidiae'' Guntarith, who seized the province of Africa proconsularis in spring 546 and killed the imperial governor Aerobindus in Carthage. When Guntarith began to consolidate his regime with purges and mass executions, the ''strategos'' Artabanes managed to have Guntarith assassinated just five weeks after the rebellion began. John, who had taken refuge in a church, was arrested by Art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis (Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
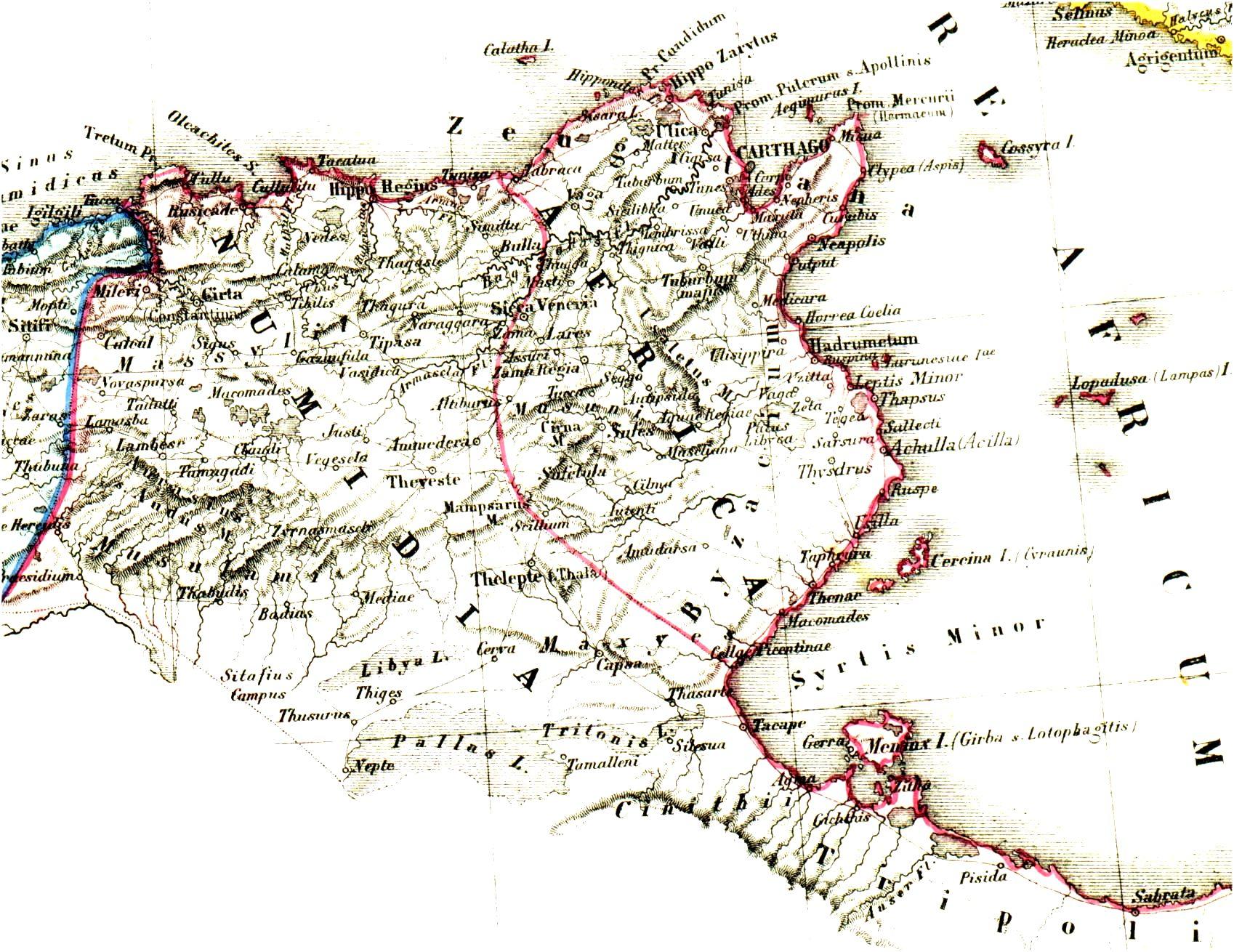
Africa Proconsularis
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century Byzantine People
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
546 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 546 ( DXLVI) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 546 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * December 17 – Sack of Rome: After almost a year's siege, the capture of a grain fleet sent by the exiled Pope Vigilius near the mouth of the Tiber, and failure of troops of the Byzantine Empire under Belisarius to relieve the city, the Ostrogoths under King Totila plunder Rome and destroy its fortifications. He then withdraws to Apulia (Southern Italy). * Winter – Pope Vigilius arrives in Constantinople, to meet with Emperor Justinian I. The future Pope Pelagius is sent by Totila to negotiate with Justinian. Europe * Audoin murders and succeeds Walthari as king of the Lombards. * Audoin receives subsidies from Justinian I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Of The Moors And Romans
The Mauro-Roman Kingdom (Latin: ''Regnum Maurorum et Romanorum'') was an independent Christian Berber kingdom centred in the capital city of Altava (present-day Algeria) which controlled much of the ancient Roman province of Mauretania Caesariensis. The kingdom was first formed in the fifth century as Roman control over the province weakened and Imperial resources had to be concentrated elsewhere, notably in defending the Italian Peninsula itself from invading Germanic tribes. The rulers of the Mauro-Roman Kingdom repeatedly came into conflict with the Vandals of the neighbouring Vandalic Kingdom, which had been established following the Vandalic conquest of the Roman province of Africa. King Masuna of the Moors and Romans allied with the armies of the Eastern Roman Empire during their reconquest of Northern Africa in the Vandalic War. Following the Eastern Roman victory over the Vandals, the Mauro-Roman Kingdom maintained its alliance with the Eastern Roman Empire, assisting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Prosopography Of The Later Roman Empire
''Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire'' (abbreviated as ''PLRE'') is a work of Roman prosopography published in a set of three volumes collectively describing many of the people attested to have lived in the Roman Empire from AD 260, the date of the beginning of Gallienus' sole rule, to 641, the date of the death of Heraclius. Sources cited include histories, literary texts, inscriptions, and miscellaneous written sources. Individuals who are known only from dubious sources (e.g., the '' Historia Augusta''), as well as identifiable people whose names have been lost, are included with signs indicating the reliability. A project of the British Academy, the work set out with the goal of doing The volumes were published by Cambridge University Press, and involved many authors and contributors. Arnold Hugh Martin Jones, John Robert Martindale, and John Morris were the principal editors. *Volume 1, published on March 2, 1971, comes to 1,176 pages and covers the years from 260 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artabanes
Artabanes ( el, , Armenian: ''Artawan'', from Parthian ''Artawân'', ''fl.'' 538–554) was an East Roman (Byzantine) general of Armenian origin who served under Justinian I (r. 527–565). Initially a rebel against Byzantine authority, he fled to the Sassanid Persians but soon returned to Byzantine allegiance. He served in Africa, where he won great fame by killing the rebel general Guntharic and restoring the province to imperial allegiance. He became engaged to Justinian's niece Praejecta, but did not marry her due to the opposition of the Empress Theodora. Recalled to Constantinople, he became involved in a failed conspiracy against Justinian in 548/549, but wasn't punished severely after its revelation. He was soon pardoned and sent to Italy to fight in the Gothic War, where he participated in the decisive Byzantine victory at Casilinum. Early life Artabanes was a descendant of the royal Armenian Arsacid line, a branch of which at the time was recognized as autonomous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. The city developed from a Canaanite Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. According to accounts by Timaeus of Tauromenium, she purchased from a local tribe the amount of land that could be covered by an oxhide. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule the colonies. The ancient city was destroyed in the nearly-three year siege of Carthage by the Roman Republic during the Third Punic War in 146 BC and then re-developed as R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guntarith
Guntarith ( Vandalic: ''Gontharis''; died 546), sometimes referred to as Guntharic, was an Eastern Roman military officer and rebel of Vandalic descent. Life After the conquest of the Vandal Kingdom by Belisarius in 533/534, the Eastern Roman Empire was faced with numerous Moorish and Vandalic revolts. Only after the defeat of Stotzas's rebellion (545), would Guntarith, the dux of Numidia, play a leading role. With Moorish and Numidian support, he seized the province of Africa proconsularis and killed the imperial governor Areobindus in Carthage. The wife of Areobindus, Praejecta, niece of emperor Justinian I, was however spared. The goal of the rebels was probably the secession of the African provinces from the rule of Constantinople la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
İstanbul
) , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = 34000 to 34990 , area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side) , registration_plate = 34 , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .ist, .istanbul , website = , blank_name = GDP (Nominal) , blank_info = 2021 , blank1_name = - Total , blank1_info = US$ 248 billion , blank2_name = - Per capita , blank2_info = US$ 15,666 , blank3_name = HDI (2019) , blank3_info = 0.846 () · 1st , timezone = TRT , utc_offset = +3 , module = , name = , government_type = Mayor–council government , governing_body = Municipal Council of Istanbul , image_shield = , established_date = 11 May 330 AD , image_m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |