|
Japa
''Japa'' ( sa, जप) is the meditative repetition of a mantra or a divine name. It is a practice found in Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism, and Buddhism, with parallels found in other religions. ''Japa'' may be performed while sitting in a meditation posture, while performing other activities, or as part of formal worship in group settings. The mantra or name may be spoken softly, loud enough for the practitioner to hear it, or it may be recited silently within the practitioner's mind. Etymology The Sanskrit word ''japa'' is derived from the root ''jap-'', meaning "to utter in a low voice, repeat internally, mutter". It can be further defined as ''ja'' to destroy birth, death, and reincarnation and ''pa'' meaning to destroy ones sins. Monier-Williams states that the term appears in Vedic literature such as in the Aitareya Brahmana ( Rigveda) and the Shatapatha Brahmana ( Yajurveda). The term means muttering, whispering or murmuring passages from the scripture, or charm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japamala
A japamala, , or simply mala ( sa, माला; , meaning ' garland') is a loop of prayer beads commonly used in Indian religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism, and Buddhism for counting recitations when performing '' japa'' (reciting a mantra or other sacred sound) or for counting some other '' sadhana'' (spiritual practice) such as prostrating before a holy icon. They are similar to other forms of prayer beads used in various world religions and are sometimes referred to in Christianity as a " rosary". The main body of a mala is usually 108 beads of roughly the same size and material as each other though smaller versions, often factors of 108 such as 54 or 27, exist. A distinctive 109th "guru bead", not used for counting, is very common. Mala beads have traditionally been made of a variety of materials such as wood, stone, seeds, bone and precious metals—with various religions often favouring certain materials—and strung with natural fibres such as cotton, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japa Mala (prayer Beads) Of Tulasi Wood With 108 Beads - 20040101-02
A japamala, , or simply mala ( sa, माला; , meaning 'garland') is a loop of prayer beads commonly used in Indian religions such as Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism, and Buddhism for counting recitations when performing ''japa'' (reciting a mantra or other sacred sound) or for counting some other '' sadhana'' (spiritual practice) such as prostrating before a holy icon. They are similar to other forms of prayer beads used in various world religions and are sometimes referred to in Christianity as a "rosary". The main body of a mala is usually 108 beads of roughly the same size and material as each other though smaller versions, often factors of 108 such as 54 or 27, exist. A distinctive 109th "guru bead", not used for counting, is very common. Mala beads have traditionally been made of a variety of materials such as wood, stone, seeds, bone and precious metals—with various religions often favouring certain materials—and strung with natural fibres such as cotton, silk, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
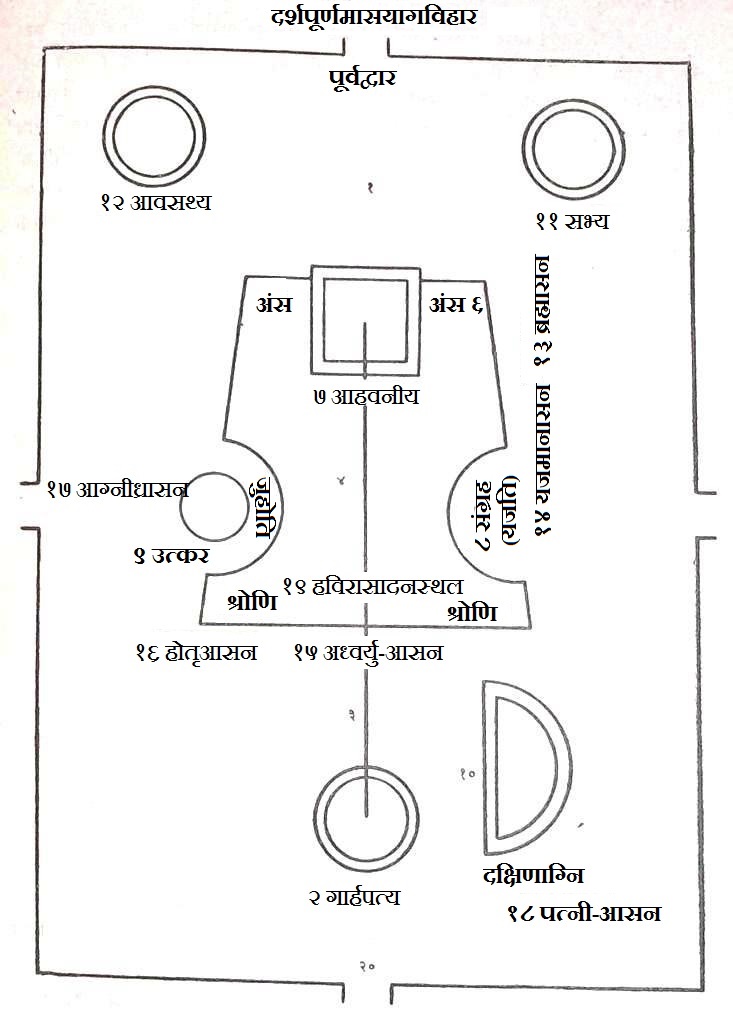
Shatapatha Brahmana
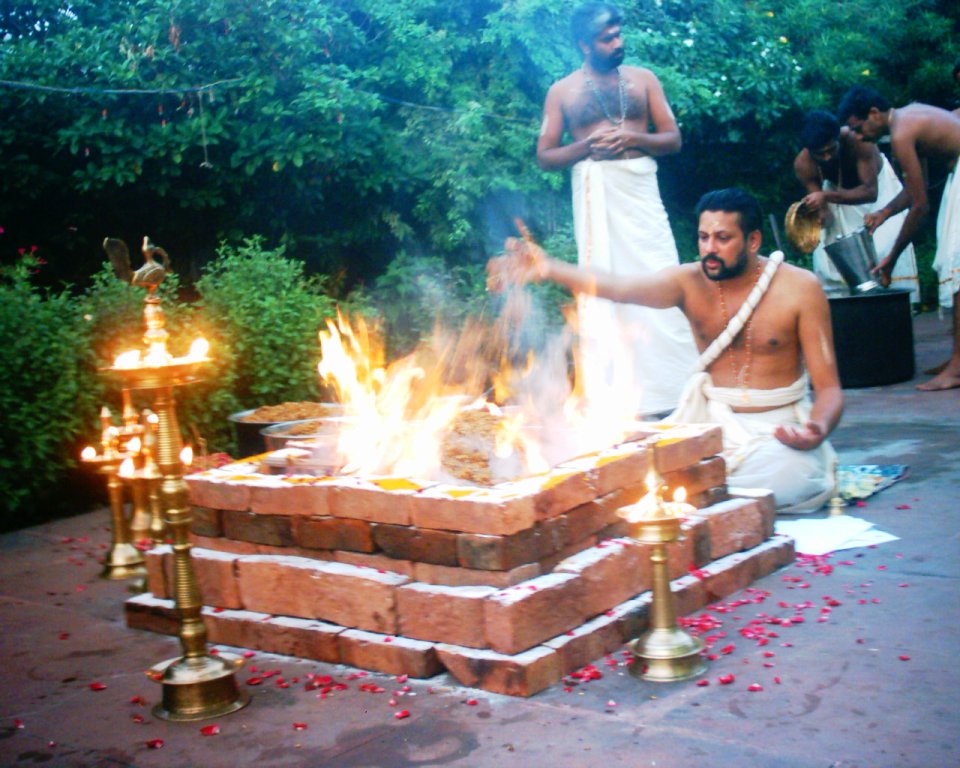
The Shatapatha Brahmana ( sa, शतपथब्राह्मणम् , Śatapatha Brāhmaṇam, meaning 'Brāhmaṇa of one hundred paths', abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Śukla (white) Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the Vedas), it contains detailed explanations of Vedic sacrificial rituals, symbolism, and mythology. Particularly in its description of sacrificial rituals (including construction of complex fire-altars), the Shatapatha Brahmana (SB) provides scientific knowledge of geometry (e.g. calculations of pi and the root of the Pythagorean theorem) and observational astronomy (e.g. planetary distances and the assertion that the Earth is circular) from the Vedic period. The Shatapatha Brahmana is also considered to be significant in the development of Vaishnavism as the origin of several Puranic legends and avatars of the RigVedic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantra
A mantra ( Pali: ''manta'') or mantram (मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words in Sanskrit, Pali and other languages believed by practitioners to have religious, magical or spiritual powers. Feuerstein, Georg (2003), ''The Deeper Dimension of Yoga''. Shambala Publications, Boston, MA Some mantras have a syntactic structure and literal meaning, while others do not. The earliest mantras were composed in Vedic Sanskrit in India. At its simplest, the word ॐ (Aum, Om) serves as a mantra, it is believed to be the first sound which was originated on earth. Aum sound when produced creates a reverberation in the body which helps the body and mind to be calm. In more sophisticated forms, mantras are melodic phrases with spiritual interpretations such as a human longing for truth, reality, light, immortality, peace, love, knowledge, and action. Some mantras without literal meaning are musically uplifting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, transcendental, and spiritual elements; however, there is no scholarly consensus over what precisely constitutes a religion. Different religions may or may not contain various elements ranging from the divine, sacred things, faith,Tillich, P. (1957) ''Dynamics of faith''. Harper Perennial; (p. 1). a supernatural being or supernatural beings or "some sort of ultimacy and transcendence that will provide norms and power for the rest of life". Religious practices may include rituals, sermons, commemoration or veneration (of deities or saints), sacrifices, festivals, feasts, trances, initiations, funerary services, matrimonial services, meditation, prayer, music, art, dance, public service, or other aspects of human culture. Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and ''aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''satya'' (truth), ''asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and ''aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). These pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm and stable state. Meditation is practiced in numerous religious traditions. The earliest records of meditation (''Dhyana in Hinduism, dhyana'') are found in the Upanishads, and meditation plays a salient role in the contemplative repertoire of Jainism, Buddhism and Hinduism. Since the 19th century, Asian meditative techniques have spread to other cultures where they have also found application in non-spiritual contexts, such as business and health. Meditation may significantly reduce Stress (biology), stress, anxiety, Depression (mood), depression, and pain, and enhance peace, perception, self-concept, and well-being. Research is ongoing to better understand the effects of meditation on health (psychology, psychological, neurology, neuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or ''dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other topi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nembutsu
Nianfo (, Japanese: , , vi, niệm Phật) is a term commonly seen in Pure Land Buddhism. In the context of Pure Land practice, it generally refers to the repetition of the name of Amitābha. It is a translation of Sanskrit '' '' (or, "recollection of the Buddha"). Indian Sanskrit Nianfo The Sanskrit phrase used in India is not mentioned originally in the bodies of the two main Pure Land sutras. It appears in the opening of the extant Sanskrit Infinite Life Sutra, as well as the Contemplation Sutra, although it is a reverse rendering from Chinese, as the following: :''namo'mitābhāya buddhāya'' The apostrophe and omission of the first "A" in "Amitābha" comes from normal Sanskrit sandhi transformation, and implies that the first "A" is omitted. A more accessible rendering might be: :''Namo Amitābhāya Buddhāya'' A literal English translation would be "Bow for the sake of Amitābha Buddha". The Sanskrit word-by-word pronunciation is the following; : While almost un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yajurveda
The ''Yajurveda'' ( sa, यजुर्वेद, ', from ' meaning "worship", and ''veda'' meaning "knowledge") is the Veda primarily of prose mantras for worship rituals.Michael Witzel (2003), "Vedas and Upaniṣads", in ''The Blackwell Companion to Hinduism'' (Editor: Gavin Flood), Blackwell, , pages 76-77 An ancient Vedic Sanskrit text, it is a compilation of ritual-offering formulas that were said by a priest while an individual performed ritual actions such as those before the yajna fire. Yajurveda is one of the four Vedas, and one of the scriptures of Hinduism. The exact century of Yajurveda's composition is unknown, and estimated by Witzel to be between 1200 and 800 BCE, contemporaneous with Samaveda and Atharvaveda. The Yajurveda is broadly grouped into two – the "black" or "dark" (''Krishna'') Yajurveda and the "white" or "bright" (''Shukla'') Yajurveda. The term "black" implies "the un-arranged, unclear, motley collection" of verses in Yajurveda, in contrast to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent. The term ''"Hindu"'' traces back to Old Persian which derived these names from the Sanskrit name ''Sindhu'' (सिन्धु ), referring to the river Indus. The Greek cognates of the same terms are "''Indus''" (for the river) and "''India''" (for the land of the river). The term "''Hindu''" also implied a geographic, ethnic or cultural identifier for people living in the Indian subcontinent around or beyond the Indus River, Sindhu (Indus) River. By the 16th century CE, the term began to refer to residents of the subcontinent who were not Turkic peoples, Turkic or Muslims. Hindoo is an archaic spelling variant, whose use today is considered derogatory. The historical development of Hindu self-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number 108
108 (one hundred ndeight) is the natural number following 107 and preceding 109. In mathematics 108 is: *an abundant number. *a semiperfect number. *a tetranacci number. *the hyperfactorial of 3 since it is of the form 1^1 \cdot 2^2 \cdot 3^3. *divisible by the value of its φ function, which is 36. *divisible by the total number of its divisors (12), hence it is a refactorable number. *the angle in degrees of the interior angles of a regular pentagon in Euclidean space. * palindromic in bases 11 (9911), 17 (6617), 26 (4426), 35 (3335) and 53 (2253) *a Harshad number in bases 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 and 16 *a self number. *an Achilles number because it is a powerful number but not a perfect power. *nine dozen There are 108 free polyominoes of order 7. The equation 2\sin\left(\frac\right) = \phi results in the golden ratio. This could be restated as saying that the "chord" of 108 degrees is \phi , the golden ratio. Religion and the arts The num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)
_of_Tulasi_wood_with_108_beads_-_20040101-02.jpg)