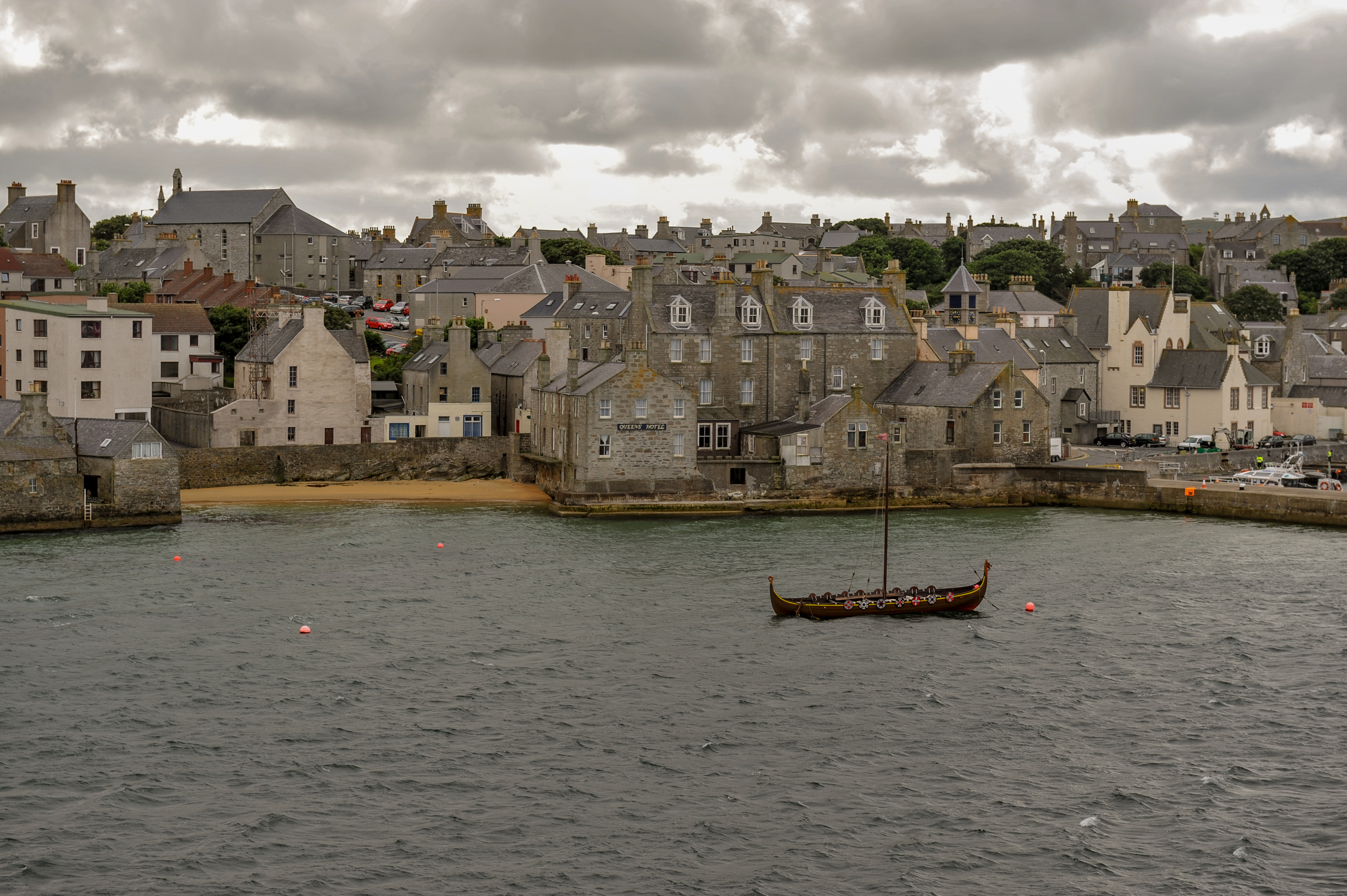|
James Barron (harbour Engineer)
James Barron MICE JP (1842–1929) was a 19th/20th century Scottish engineer who specialised in harbour design in the north-east of Scotland. Life He was born in Peterhead the son of Archibald Barron, a trainee mason, and his first wife, Elizabeth. The family moved to Aberdeen and James appears there in 1861 noted as a "carpenter". In 1871 he appears as an "estate factor" working in Larbert and by 1881 is a "factor and engineer". His first known employment as a harbour engineer is as assistant to William Dyce Cay building the Cluny Harbour at Buckie in 1873. In the early 1880s he and his family were living in Rathven. Due to projects moving from town to town he frequently relocated. In 1891 he is living in Wick, Caithness. In 1893 he was living in Aberdeen and had an office at 166 Union Street in the city centre and was living at 46 Carden Place. He became a member of the Aberdeen Philosophical Society. In Aberdeen he was also a Justice of the Peace and town councillor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
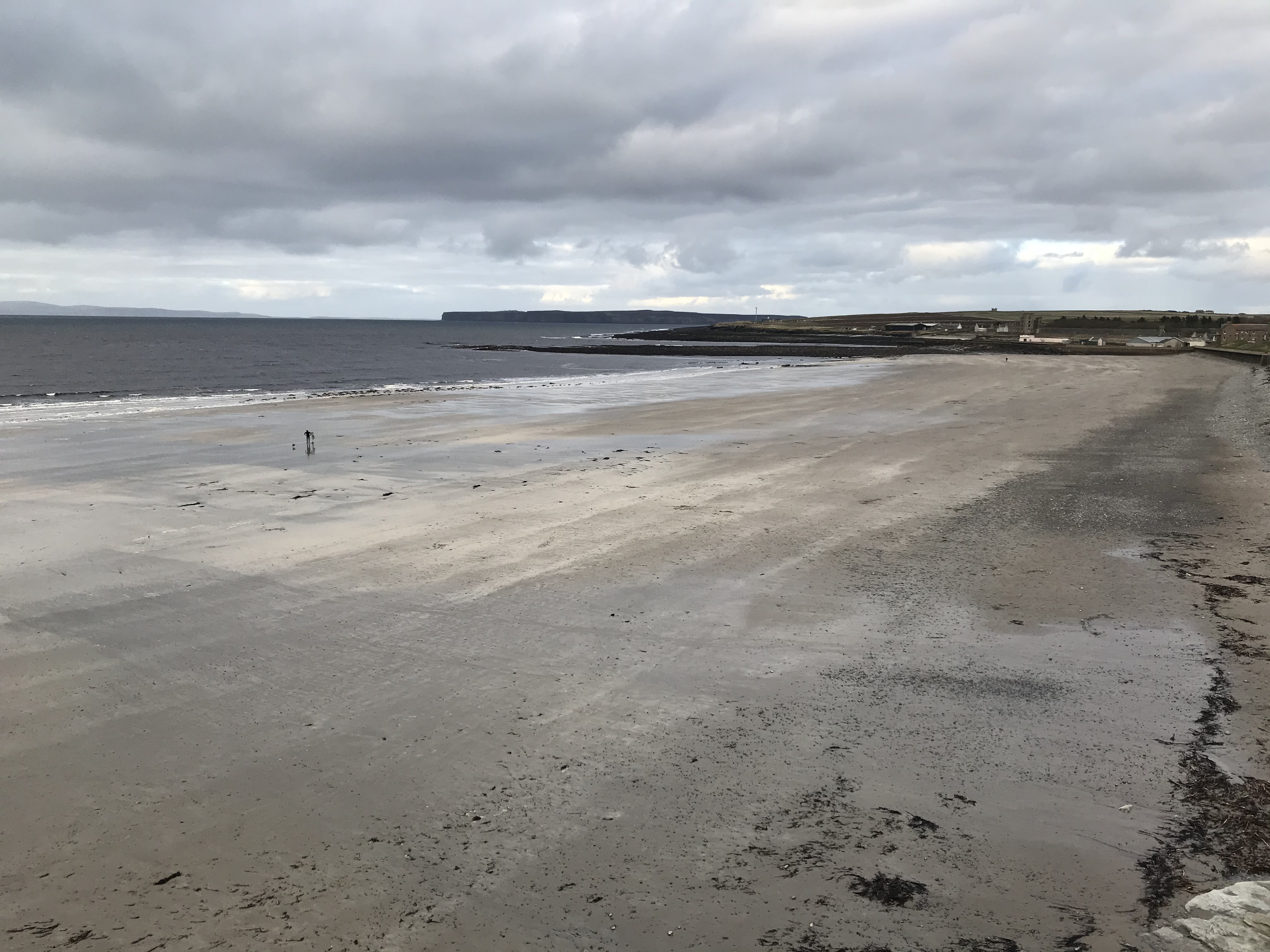
Thurso
Thurso (pronounced ; sco, Thursa, gd, Inbhir Theòrsa ) is a town and former burgh on the north coast of the Highland council area of Scotland. Situated in the historical County of Caithness, it is the northernmost town on the island of Great Britain. From a latitudal standpoint, Thurso is located further north than the southernmost point of Norway and in addition lies more than north of London. It lies at the junction of the north–south A9 road and the west–east A836 road, connected to Bridge of Forss in the west and Castletown in the east. The River Thurso flows through the town and into Thurso Bay and the Pentland Firth. The river estuary serves as a small harbour. At the 2011 Census, Thurso had a population of 7,933. The larger Thurso civil parish including the town and the surrounding countryside had a population of 9,112. Thurso functioned as an important Norse port, and later traded with ports throughout northern Europe until the 19th century. A thriving fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lerwick
Lerwick (; non, Leirvik; nrn, Larvik) is the main town and port of the Shetland archipelago, Scotland. Shetland's only burgh, Lerwick had a population of about 7,000 residents in 2010. Centred off the north coast of the Scottish mainland and on the east coast of the Shetland Mainland, Lerwick lies north-by-northeast of Aberdeen; west of the similarly sheltered port of Bergen in Norway; and south east of Tórshavn in the Faroe Islands. One of the UK's coastal weather stations is situated there, with the local climate having small seasonal variation due to the maritime influence. Being located further north than Saint Petersburg and the three mainland Nordic capitals, Lerwick's nights in the middle of summer only get dark twilight and winters have below six hours of complete daylight. History Lerwick is a name with roots in Old Norse and its local descendant, Norn, which was spoken in Shetland until the mid-19th century. The name "Lerwick" means ''bay of clay''. The c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennan
Pennan ( sco, Peenan) is a small village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, consisting of a small harbour and a single row of homes, including a hotel. It is on the north-facing coast and is about one hour's drive from Aberdeen. It was formerly known as St Magnus Haven or Auchmedden. Etymology The name ''Pennan'' was recorded in 1587 as ''Pennand''. It is possibly derived from the Brittonic element ''*pen'' meaning "head, end, promontory" ( Welsh ''pen''). Area history Pennan seems to have come into existence as a fishing village in the 18th century. The people of Pennan were dependent on the sea. Most families had small boats for their own personal use. Where the men would catch the fish, it was usually down to the women and children to try to sell it to clients in the country. Until the 1930s, the population of the village seems to have come under three main surnames - Watt, Gatt and West. In the last 50 years, most of the native families have moved out and most of the houses have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalloway
Scalloway ( non, Skálavágr, "bay with the large house(s)") is the largest settlement on the west coast of the Mainland, the largest island of the Shetland Islands, Scotland. The village had a population of roughly 900, at the 2011 census. Now a fishing port, until 1708 it was the capital of the Shetland Islands (now Lerwick, on the east coast of the Shetland Mainland). It contains one of the two castles built in Shetland; this one was constructed in 1600. Scalloway is the location of the North Atlantic Fisheries College (part of the University of the Highlands and Islands), which offers courses and supports research programmes in fisheries sciences, aquaculture, marine engineering and coastal management. It is also home to the Centre for Nordic Studies. NAFC Marine Centre at Ness of Westshore offers courses in "nautical studies, marine science and technology, and seafood quality". Nearby are the Scalloway Islands, which derive their name from the village. The village has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huntly, Aberdeenshire
Huntly ( gd, Srath Bhalgaidh or ''Hunndaidh'') is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, formerly known as Milton of Strathbogie or simply Strathbogie. It had a population of 4,460 in 2004 and is the site of Huntly Castle. Its neighbouring settlements include Keith and Rothiemay. Both Huntly and the surrounding district of Gordon are named for a town and family that originated in the Border country. Huntly is the historic home of the Gordon Highlanders regiment which traditionally recruited throughout the North-East of Scotland. Huntly has a primary school (Gordon Primary) and a secondary school (The Gordon Schools) beside Huntly Castle. It is the home of the Deans bakers, which produce shortbread biscuits. In November 2007, Deans of Huntly opened their new visitor centre. Four of the owls from the local falconry centre starred in the Harry Potter films. History Settlement around the confluence of the Bogie and Deveron rivers dates back to the Neolithic period. Settlement remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
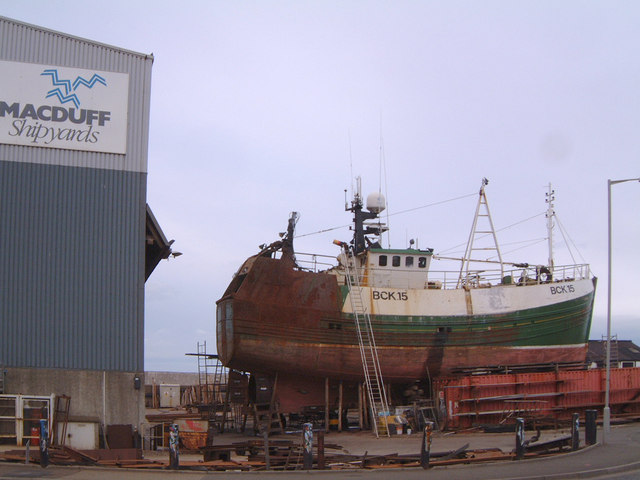
Macduff, Aberdeenshire
Macduff ( gd, An Dùn) is a town in the Banff and Buchan area of Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is situated on Banff Bay and faces the town of Banff across the estuary of the River Deveron. Macduff is a former burgh and was the last place in the United Kingdom where deep-water wooden fishing boats were built. History The settlement of Doune (from the Scottish Gaelic , "hill fort") was purchased in 1733 by William Duff, who became the first Earl Fife. In 1760, James Duff, the second earl, built a harbour there and in 1783 succeeded in raising Doune to the status of a burgh of barony, renaming it " Macduff" after his supposed ancestor. The 2nd Earl Fife appointed his factor, William Rose, as the first Provost of Macduff in 1783. The town celebrated its bicentenary in 1983, and the signs erected in that year still stand on the main approaches to the town (most visibly, a large sign next to the Banff Bridge on the Macduff side). Banff and Macduff are separated by the valley of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryculter
Maryculter () or Kirkton of Maryculter is a village in the Lower Deeside area of Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The River Dee separates it from the town of Peterculter, and the B979 road runs through Maryculter. Maryculter House Hotel lies slightly north of the village along the south bank of the River Dee and to the west of Templars Park. The Old Mill Inn, a former coaching inn dating back to the 18th century lay at the mouth of the Crynoch Burn from 1797 until its demolition in February 2021 after being damaged by an extensive fire. At the edge of the village of Maryculter is a public forest land, known as the Oldman Wood, through which flows the Crynoch Burn. Also the children's theme park, StoryBook Glen, which also consists of a shop and restaurant is located near the old church which is still in use today as a Church of Scotland. Other notable vicinity buildings include the former Lairhillock Inn which closed in March 2020 and Muchalls Castle. Maryculter also has an animal sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golspie
Golspie ( , gd, Goillspidh) is a village and parish in Sutherland, Highland, Scotland, which lies on the North Sea coast in the shadow of Ben Bhraggie. It has a population of around 1,350. History The name derives from the Norse for "gully village". Planned village During a series of visits from the Right Honourable Elizabeth Countess of Sutherland plans were drawn up for the regulations that were written in to future leases, imposing restrictions on the 'tacksmen' with regard to sub-setting and overstocking, and requiring them to adopt improving farming techniques. Consideration was also given to possible development of fishing villages on the east coast, the absence of any safe harbour being the greatest hindrance. Local fishermen used only small, light boats which could be drawn up onto the beach when not in use and this confined them to line fishing close to the shore. The herring fishing in the North Sea (at that time known as the German Ocean) was in the hands of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stromness
Stromness (, non, Straumnes; nrn, Stromnes) is the second-most populous town in Orkney, Scotland. It is in the southwestern part of Mainland Orkney. It is a burgh with a parish around the outside with the town of Stromness as its capital. Etymology The name "Stromness" comes from the Norse ''Straumnes''. ''Straumr'' refers to the strong tides that rip past the Point of Ness through Hoy Sound to the south of the town. ''Nes'' means "headland". Stromness thus means "headland protruding into the tidal stream". In Viking times the anchorage where Stromness now stands was called Hamnavoe. Town A long-established seaport, Stromness has a population of approximately 2,190 residents. The old town is clustered along the characterful and winding main street, flanked by houses and shops built from local stone, with narrow lanes and alleys branching off it. There is a ferry link from Stromness to Scrabster on the north coast of mainland Scotland. First recorded as the site of an inn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collieston
Collieston is a small former fishing village on the North Sea coast in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The village lies just north of the Sands of Forvie Special Protection Area, between Cruden Bay and Newburgh. History The earliest recorded history of Collieston is of the arrival of St Ternan, a Columban monk on a mission to convert the local picts to Christianity. There is, however, evidence that people lived here during much earlier times. Collieston was established as a fishing village by the 16th century, and it provides the first safe harbour in over fifteen miles of beaches and dunes stretching north from Aberdeen. Fishing for herring, haddock, whiting and cod flourished in the 17th century and 18th century and was the foundation of Collieston's economy. The village became known for 'Collieston Speldings', salted and sun-dried haddock and whiting, a popular delicacy throughout Britain. As drift netting developed during the mid 19th century, the fishing began to decline and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmsdale
Helmsdale ( sco, Helmsdal, gd, Bun Ilidh) is a village on the east coast of Sutherland, in the Highland (council area), Highland council area of Scotland. The modern village was planned in 1814 to resettle communities that had been removed from the surrounding straths as part of the highland clearances, Highland Clearances. Toponymy The River Helmsdale (Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic ''Ilidh'') was noted by Geographia, Ptolemy as ''Ila'', which remains an obscure name. The Gaelic name for the village, ''Bun Ilidh'', means ''Ilie-foot''. Norsemen, Norse settlers called the strath ''Hjalmundal'', meaning ''Dale of the Helmet'', from which the modern village name ''Helmsdale'' is derived. History The remains of Helmsdale Castle were demolished in the 1970s in order to build the new A9 road (Scotland), A9 road bridge. The castle was the location of the murder of John Gordon, 11th Earl of Sutherland and his Countess, Marion Seton, in 1567. They were poisoned by Isobel Sinclair, the wife o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |