|
Ichniotherium
''Ichniotherium'' (meaning "marking creature") is an ichnogenus of tetrapod footprints from between the Late Carboniferous period to the Early Permian period attributed to diadectomorph track-makers.Buchwitz M & Voigt S. (2018On the morphological variability of Ichniotherium tracks and evolution of locomotion in the sistergroup of amniotes PeerJ 6:e4346 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4346 These footprints are commonly found in Europe, and have also been identified in North America and Morocco. Three ichnospecies of ''Ichniotherium'' have been proposed as valid: ''I. cotta'', ''I. sphaerodactylum'', and ''I. praesidentis.'' In a 2007 study, the diadectid species ''Diadectes absitus'' was determined to be the track-maker associated with ''I. cotta'' tracks, and the related diadectid species ''Orobates pabsti'' was linked to ''I. praesidentis'' based on analysis of Lower Permian trackways and fossils skeletons in Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
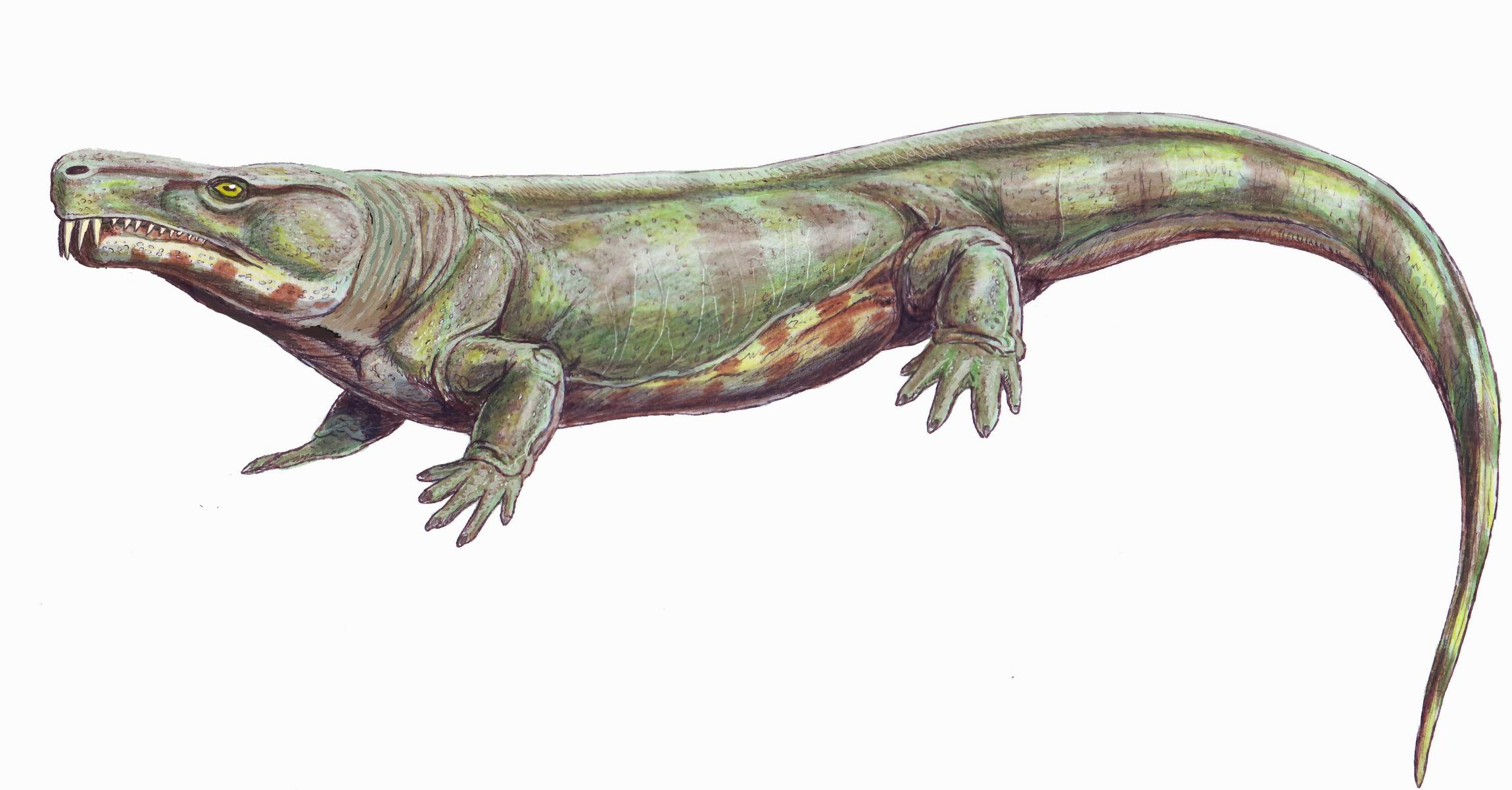
Orobates
''Orobates'' is an extinct genus of diadectid reptiliomorphs that lived during the Early Permian. Its fossilised remains were found in Germany. A combination of primitive and derived traits (i.e. autapomorphic and plesiomorphic) distinguish it from all other well-known members of Diadectidae, a family of herbivorous reptiliomorphs. It weighed about 4 kg and appears to have been part of an upland fauna, browsing on high fibre plants. Locomotion The trace fossil species ''Ichniotherium sphaerodactylum'', from Bromacker in Germany, has been attributed to ''Orobates''. A study in 2015 found that the genus was characterized by a long body and tail, with fairly short legs and a short skull compared to the more derived ''Diadectes''. This indicates ''Orobates'' was less specialised for long treks compared to ''Diadectes''. A three-dimensional digital reconstruction of the holotype specimen allowed further analysis of the postcranium. An analysis of the mobility of the hip joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Footprint
A fossil track or ichnite (Greek "''ιχνιον''" (''ichnion'') – a track, trace or footstep) is a fossilized footprint. This is a type of trace fossil. A fossil trackway is a sequence of fossil tracks left by a single organism. Over the years, many ichnites have been found, around the world, giving important clues about the behaviour (and foot structure and stride) of the animals that made them. For instance, multiple ichnites of a single species, close together, suggest 'herd' or 'pack' behaviour of that species. Combinations of footprints of different species provide clues about the interactions of those species. Even a set of footprints of a single animal gives important clues, as to whether it was bipedal or quadrupedal. In this way, it has been suggested that some pterosaurs, when on the ground, used their forelimbs in an unexpected quadrupedal action. Special conditions are required, in order to preserve a footprint made in soft ground (such as an alluvial plain or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichnogenus
An ichnotaxon (plural ichnotaxa) is "a taxon based on the fossilized work of an organism", i.e. the non-human equivalent of an artifact. ''Ichnotaxa'' comes from the Greek ίχνος, ''ichnos'' meaning ''track'' and ταξις, ''taxis'' meaning ''ordering''.Definition o'ichno'at dictionary.com. Ichnotaxa are names used to identify and distinguish morphologically distinctive ichnofossils, more commonly known as trace fossils. They are assigned genus and species ranks by ichnologists, much like organisms in Linnaean taxonomy. These are known as ichnogenera and ichnospecies, respectively. "Ichnogenus" and "ichnospecies" are commonly abbreviated as "igen." and "isp.". The binomial names of ichnospecies and their genera are to be written in italics. Most researchers classify trace fossils only as far as the ichnogenus rank, based upon trace fossils that resemble each other in morphology but have subtle differences. Some authors have constructed detailed hierarchies up to ichnosupe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carboniferous'' means "coal-bearing", from the Latin '' carbō'' ("coal") and '' ferō'' ("bear, carry"), and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time. The first of the modern 'system' names, it was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822, based on a study of the British rock succession. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian. Terrestrial animal life was well established by the Carboniferous Period. Tetrapods (four limbed vertebrates), which had originated from lobe-finned fish during the preceding Devonian, became pentadactylous in and diversified during the Carboniferous, including early amphibian line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectomorpha
Diadectomorpha is a clade of large tetrapods that lived in Euramerica during the Carboniferous and Early Permian periods and in Asia during Late Permian (Wuchiapingian), They have typically been classified as advanced reptiliomorphs (transitional between "amphibians" ''sensu lato'' and amniotes) positioned close to, but outside of the clade Amniota, though some recent research has recovered them as the sister group to the traditional Synapsida within Amniota, based on inner ear anatomy and cladistic analyses. They include both large (up to 2 meters long) carnivorous and even larger (to 3 meters) herbivorous forms, some semi-aquatic and others fully terrestrial. The diadectomorphs seem to have originated during late Mississippian times, although they only became common after the Carboniferous rainforest collapse and flourished during the Late Pennsylvanian and Early Permian periods. Anatomy Diadectomorphs possessed both amphibian-like and amniote-like characteristics. Originall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents of Earth#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the west and south by the Pacific Ocean. Because it is on the North American Plate, North American Tectonic Plate, Greenland is included as a part of North America geographically. North America covers an area of about , about 16.5% of Earth's land area and about 4.8% of its total surface. North America is the third-largest continent by area, following Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. In 2013, its population was estimated at nearly 579 million people in List of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's population. In Americas (terminology)#Human ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to the south. Mauritania lies to the south of Western Sahara. Morocco also claims the Spanish exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It spans an area of or , with a population of roughly 37 million. Its official and predominant religion is Islam, and the official languages are Arabic and Berber; the Moroccan dialect of Arabic and French are also widely spoken. Moroccan identity and culture is a mix of Arab, Berber, and European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. In a region inhabited since the Paleolithic Era over 300,000 years ago, the first Moroccan s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadectes
''Diadectes'' (meaning ''crosswise-biter'') is an extinct genus of large reptiliomorphs or synapsids that lived during the early Permian period (Artinskian-Kungurian stages of the Cisuralian epoch, between 290 and 272 million years ago). ''Diadectes'' was one of the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also one of the first fully terrestrial vertebrates to attain large size. Description ''Diadectes'' was a heavily built animal, up to long, with a thick-boned skull, heavy vertebrae and ribs, massive limb girdles, and short, robust limbs. The nature of the limbs and vertebrae clearly indicates a terrestrial animal. The rib cage was assumed to be barrel-shaped, but new fossils show the ribs were actually sticking out to the sides. Paleobiology It possesses some characteristics of reptilians and amphibians, combining a reptile-like skeleton with a more primitive, seymouriamorph-like skull. ''Diadectes'' has been classified as belonging to the sister group of the amniotes. Among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

