|
István Gyöngy
István Gyöngy (born 1951) is a Hungarian mathematician working in the fields of stochastic differential equations, stochastic partial differential equations and their applications to nonlinear filtering and stochastic control. Recently, he has focused his attention on numerical analysis and especially accelerated numerical methods, making use of Richardson extrapolation . He obtained his Candidate degree at Moscow State University in 1981 under the supervision of Nicolai V. Krylov. Formerly at the Department of Probability Theory and Statistics of the Eötvös Loránd University of Budapest, he is currently a professor at the University of Edinburgh The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under th ..., where he is head of the Probability and Stochastic Analysis research group. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budapest
Budapest is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns of Hungary, most populous city of Hungary. It is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, tenth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the List of cities and towns on the river Danube, second-largest city on the river Danube. The estimated population of the city in 2025 is 1,782,240. This includes the city's population and surrounding suburban areas, over a land area of about . Budapest, which is both a List of cities and towns of Hungary, city and Counties of Hungary, municipality, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of and a population of 3,019,479. It is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary. The history of Budapest began when an early Celts, Celtic settlement transformed into the Ancient Rome, Roman town of Aquincum, the capital of Pannonia Inferior, Lower Pannonia. The Hungarian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People's Republic Of Hungary
The Hungarian People's Republic (HPR) was a landlocked country in Central Europe from its formation on 20 August 1949 until the establishment of the current Republic of Hungary on 23 October 1989. It was a professed communist state, governed first by the Hungarian Working People's Party and after the Hungarian Revolution of 1956, the Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party. Both governments were closely tied to the Soviet Union as part of the Eastern Bloc.Rao, B. V. (2006), ''History of Modern Europe A.D. 1789–2002'', Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. The state considered itself the heir to the Hungarian Soviet Republic, which was formed in 1919 as one of the first communist states created after the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR). It was designated a " people's democratic republic" by the Soviet Union in the 1940s. Geographically, it bordered Romania and the Soviet Union (via the Ukrainian SSR) to the east; Yugoslavia (via SRs Croatia, Serbia, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
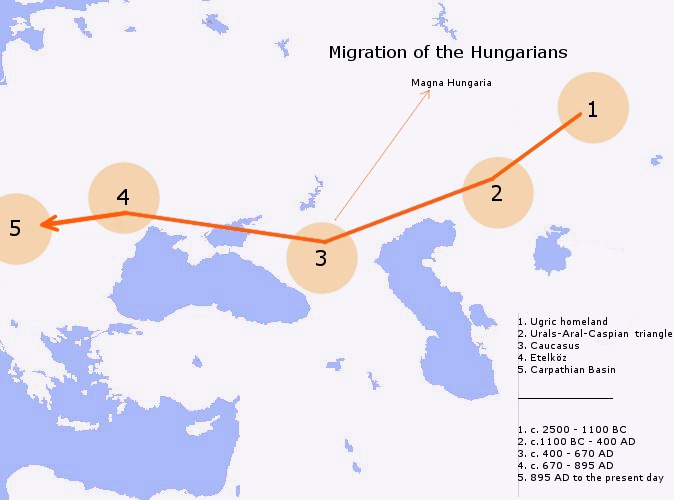
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under the authority of a royal charter from King James VI and I, James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's Ancient universities of Scotland, four ancient universities and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played a crucial role in Edinburgh becoming a leading intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the "Etymology of Edinburgh#Athens of the North, Athens of the North". The three main global university rankings (Academic Ranking of World Universities, ARWU, Times Higher Education World University Rankings, THE, and QS World University Rankings, QS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow State University
Moscow State University (MSU), officially M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,. is a public university, public research university in Moscow, Russia. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches. Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner were affiliated with the university. History Imperial Moscow University Ivan Shuvalov and Mikhail Lomonosov promoted the idea of a university in Moscow, and Elizabeth of Russia, Russian Empress Elizabeth decreed its establishment on . The first lectures were given on . Saint Petersburg State University and MSU each claim to be Russia's oldest university. Though Moscow State University was founded in 1755, St. Petersburg which has had a continuous existence as a "university" since 1819 sees itself as the successor of an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolai V
{{disambig ...
Nicolai may refer to: *Nicolai (given name) people with the forename ''Nicolai'' *Nicolai (surname) people with the surname ''Nicolai'' *Nicolai (crater), a crater on the Moon See also * Niccolai, a surname * Nicolae (other) * Nicolao * Nicolay (other) * Nikolai (other) * Nikolay (other) Nikolai or Nikolay is an East Slavic variant of the masculine name Nicholas. It may refer to: People Royalty * Nicholas I of Russia (1796–1855), or Nikolay I, Emperor of Russia from 1825 until 1855 * Nicholas II of Russia (1868–1918), or Niko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Differential Equation
A stochastic differential equation (SDE) is a differential equation in which one or more of the terms is a stochastic process, resulting in a solution which is also a stochastic process. SDEs have many applications throughout pure mathematics and are used to model various behaviours of stochastic models such as stock prices,Musiela, M., and Rutkowski, M. (2004), Martingale Methods in Financial Modelling, 2nd Edition, Springer Verlag, Berlin. random growth models or physical systems that are subjected to thermal fluctuations. SDEs have a random differential that is in the most basic case random white noise calculated as the distributional derivative of a Brownian motion or more generally a semimartingale. However, other types of random behaviour are possible, such as jump processes like Lévy processes or semimartingales with jumps. Stochastic differential equations are in general neither differential equations nor random differential equations. Random differential equation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Partial Differential Equation
Stochastic partial differential equations (SPDEs) generalize partial differential equations via random force terms and coefficients, in the same way ordinary stochastic differential equations generalize ordinary differential equations. They have relevance to quantum field theory, statistical mechanics, and spatial modeling. Examples One of the most studied SPDEs is the stochastic heat equation, which may formally be written as : \partial_t u = \Delta u + \xi\;, where \Delta is the Laplacian and \xi denotes space-time white noise. Other examples also include stochastic versions of famous linear equations, such as the wave equation and the Schrödinger equation. Discussion One difficulty is their lack of regularity. In one dimensional space, solutions to the stochastic heat equation are only almost 1/2-Hölder continuous in space and 1/4-Hölder continuous in time. For dimensions two and higher, solutions are not even function-valued, but can be made sense of as random d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richardson Extrapolation
In numerical analysis, Richardson extrapolation is a Series acceleration, sequence acceleration method used to improve the rate of convergence of a sequence of estimates of some value A^\ast = \lim_ A(h). In essence, given the value of A(h) for several values of h, we can estimate A^\ast by extrapolating the estimates to h=0. It is named after Lewis Fry Richardson, who introduced the technique in the early 20th century, though the idea was already known to Christiaan Huygens in Christiaan_Huygens#De_Circuli_Magnitudine_Inventa, his calculation of \pi. In the words of Garrett Birkhoff, Birkhoff and Gian-Carlo Rota, Rota, "its usefulness for practical computations can hardly be overestimated."Page 126 of Practical applications of Richardson extrapolation include Romberg integration, which applies Richardson extrapolation to the trapezoid rule, and the Bulirsch–Stoer algorithm for solving ordinary differential equations. General formula Notation Let A_0(h) be an approximation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eötvös Loránd University
Eötvös Loránd University (, ELTE, also known as ''University of Budapest'') is a Hungarian public research university based in Budapest. Founded in 1635, ELTE is one of the largest and most prestigious public higher education institutions in Hungary. The 28,000 students at ELTE are organized into nine faculties, and into research institutes located throughout Budapest and on the scenic banks of the Danube. ELTE is affiliated with 5 Nobel laureates, as well as winners of the Wolf Prize, Fulkerson Prize and Abel Prize, the latest of which was Abel Prize winner László Lovász in 2021. The predecessor of Eötvös Loránd University was founded in 1635 by Cardinal Péter Pázmány in Nagyszombat, Kingdom of Hungary (today Trnava, Slovakia) as a Catholic university for teaching theology and philosophy. In 1770, the university was transferred to Buda. It was named Royal University of Pest until 1873, then University of Budapest until 1921, when it was renamed Royal Hungarian Pá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |