|
Isabella Fyvie Mayo
Isabella Fyvie Mayo (pen name, Edward Garrett; 10 December 1843 – 13 May 1914) was a Scottish poet, novelist, suffragist, and reformer. With the help of friends, Fyvie Mayo published poems and stories, using the pseudonym, Edward Garrett. Fyvie Mayo spent most of her life living in Aberdeen, where she was the first woman elected to a public board. Fyvie Mayo was described as an "ethical anarchist, pacifist, anti-imperialist and anti-racist campaigner"; and her "home was an asylum for Asian Indians." Early years and education Isabella Fyvie was born on 10 December 1843 in London of Scottish parents George Fyvie and Margaret Thomson. As a child, her father told her the legends of Buchan, and the stories that he brought with him from his father's farm, where his ancestors had been settled for three hundred years. His people were staunch Scottish Episcopalians, one of them being the Dean of Moray and Ross. Her mother's ancestors, on the paternal side, belonged to the Border countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Hislop
Alexander Hislop (1807 – 13 March 1865) was a Free Church of Scotland minister known for his criticisms of the Roman Catholic Church. He was the son of Stephen Hislop (died 1837), a mason by occupation and an elder of the Relief Church. Alexander's brother was also named Stephen Hislop (lived 1817–1863) and became well known in his time as a missionary to India and a naturalist. Alexander was born and raised in Duns, Berwickshire. He was for a time parish schoolmaster of Wick, Caithness. In 1831 he married Jane Pearson. He was for a time editor of the ''Scottish Guardian'' newspaper. As a probationer he joined the Free Church of Scotland at the Disruption of 1843. He was ordained in 1844 at the East Free Church, Arbroath, where he became senior minister in 1864. He died of a paralytic stroke in Arbroath the next year after being ill for about two years. He wrote several books, his most famous being '' The Two Babylons: Papal Worship Proved to be the Worship of Nimro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's College London
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public research university located in London, England. King's was established by royal charter in 1829 under the patronage of King George IV and the Duke of Wellington. In 1836, King's became one of the two founding colleges of the University of London. It is one of the oldest university-level institutions in England. In the late 20th century, King's grew through a series of mergers, including with Queen Elizabeth College and Chelsea College of Science and Technology (in 1985), the Institute of Psychiatry (in 1997), the United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy's and St Thomas' Hospitals and the Florence Nightingale School of Nursing and Midwifery (in 1998). King's has five campuses: its historic Strand Campus in central London, three other Thames-side campuses (Guy's, St Thomas' and Waterloo) nearby and one in Denmark Hill in south London. It also has a presence in Shrivenham, Oxfordshire, for its professional mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-suffragism
Anti-suffragism was a political movement composed of both men and women that began in the late 19th century in order to campaign against women's suffrage in countries such as Australia, Canada, Ireland, the United Kingdom and the United States. To some extent, Anti-suffragism was a Classical Conservative movement that sought to keep the status quo for women and which opposed the idea of giving women equal suffrage rights. It was closely associated with "domestic feminism," the belief that women had the right to complete freedom within the home. In the United States, these activists were often referred to as "remonstrants" or "antis." Background The anti-suffrage movement was a counter movement opposing the social movement of women's suffrage in various countries. It could also be considered a counterpublic that espoused a democratic defense of the status quo for women and men in society. As a counter movement, the anti-suffrage movement did not gain traction or start to or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Fraser (feminist)
Helen Miller Fraser, later Moyes (14 September 1881 – 2 December 1979),Leah Leneman, "Moyes , Helen Miller (1881–1979)", ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, 200accessed 11 Feb 2014/ref> was a Scottish suffragist, feminist, educationalist and Liberal Party politician who later emigrated to Australia. Background Fraser was born in Leeds, Yorkshire to Scottish parents. She was educated at Queen's Park Higher Grade School, Glasgow. She opened a studio in Glasgow that specialised in black and white illustration work and embroidery. Political career She joined the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) after hearing Teresa Billington speak in Glasgow. She travelled to England to help the WSPU campaign at the 1906 Huddersfield by-election. She became Treasurer of the Glasgow WSPU and a WSPU Scottish Organiser, one of the fifty-eight funded branches in the UK. On 20 December 1906, with Flora Drummond, Fraser and three others attempted to enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmeline Pankhurst
Emmeline Pankhurst ('' née'' Goulden; 15 July 1858 – 14 June 1928) was an English political activist who organised the UK suffragette movement and helped women win the right to vote. In 1999, ''Time'' named her as one of the 100 Most Important People of the 20th Century, stating that "she shaped an idea of objects for our time" and "shook society into a new pattern from which there could be no going back". She was widely criticised for her militant tactics, and historians disagree about their effectiveness, but her work is recognised as a crucial element in achieving women's suffrage in the United Kingdom. Born in the Moss Side district of Manchester to politically active parents, Pankhurst was introduced at the age of 14 to the women's suffrage movement. She founded and became involved with the Women's Franchise League, which advocated suffrage for both married and unmarried women. When that organisation broke apart, she tried to join the left-leaning Independent Labour P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek War Of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by the British Empire, Bourbon Restoration in France, Kingdom of France, and the Russian Empire, while the Ottomans were aided by their North African vassals, particularly the eyalet of Egypt Eyalet, Egypt. The war led to the formation of modern Greece. The revolution is Celebration of the Greek Revolution, celebrated by Greeks around the world as Greek Independence Day, independence day on 25 March. Greece, with the exception of the Ionian Islands, came under Ottoman rule in the 15th century, in the decades before and after the fall of Constantinople. During the following centuries, there were sporadic but unsuccessful Ottoman Greece#Uprisings before 1821, Greek uprisings against Ottoman rule. In 1814, a secret organization called Filiki Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Mayhew Edmonds
Elizabeth Mayhew Edmonds (c1821-1907) was an English writer active in the 1880s who wrote about modern Greece. Her focus on publishing in magazines and journals as well as in books brought modern Greek life to increased prominence in Britain. Early life Elizabeth Mayhew Edmonds was born and baptised as Elizabeth Waller on 19 January 1821 at St Mary Magdalen, Bermondsey. Her father, John Waller, was a former Royal Navy officer and her mother, Susanna Green, was the daughter of a surgeon from Hoxne, Suffolk. Elizabeth was one of seven children, and was educated at home by her elder brother, the artist John Waller. He introduced her to great literature in English, French, Italian and Latin. She was also encouraged by her cousin, the writer Mary Matilda Betham to write poetry. In December 1849, Elizabeth married Augustus Robert Edmonds. He worked as a lighterman, foreign merchant and a master barge builder. They moved to Blackheath, London, and he encouraged her to return to writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Liberal Association
The Women's Liberal Federation was an organisation that was part of the Liberal Party in the United Kingdom. History The Women's Liberal Federation (WLF) was formed on the initiative of Sophia Fry, who in 1886 called a meeting at her house of fifteen local Women's Liberal Associations.Patricia Hollis, ''Ladies Elect: Women in English Local Government 1865-1914'', p.57 The establishment of a national organisation was agreed, and this occurred in 1887, when members of forty associations met in London. It was reported that the federation membership was about 6,000,''The Liberal Year Book'', 1905 but this grew rapidly, reaching 75,000 in 1892. By 1904 there were 494 affiliated associations and a membership of approximately 67,600. By 1907 there were 613 affiliated association, and a membership of 83,000.''The Liberal Year Book'', 1908 Although the Women’s Liberal Federation (WLF) was initiated by Lady Sophia Fry Pease in 1886, the federation was under the presidency of the daught ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's Social And Political Union
The Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU) was a women-only political movement and leading militant organisation campaigning for women's suffrage in the United Kingdom from 1903 to 1918. Known from 1906 as the suffragettes, its membership and policies were tightly controlled by Emmeline Pankhurst and her daughters Christabel and Sylvia; Sylvia was eventually expelled. The WSPU membership became known for civil disobedience and direct action. Emmeline Pankhurst described them as engaging in a "reign of terror". Group members heckled politicians, held demonstrations and marches, broke the law to force arrests, broke windows in prominent buildings, set fire to or introduced chemicals into postboxes thus injuring several postal workers, and committed a series of arsons that killed at least five people and injured at least 24. When imprisoned, the group's members engaged in hunger strikes and were subject to force-feeding. Emmeline Pankhurst said the group's goal was "to make En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Union Of Women's Suffrage Societies
The National Union of Women Suffrage Societies (NUWSS), also known as the ''suffragists'' (not to be confused with the suffragettes) was an organisation founded in 1897 of women's suffrage societies around the United Kingdom. In 1919 it was renamed the National Union of Societies for Equal Citizenship. Formation and campaigning The team was founded in 1897 by the merger of the National Central Society for Women's Suffrage and the Central Committee of the National Society for Women's Suffrage, the groups having originally split in 1888. The groups united under the leadership of Millicent Fawcett, who was the president of the society for more than twenty years. The organisation was democratic and non-militant, aiming to achieve women's suffrage through peaceful and legal means, in particular by introducing Parliamentary Bills and holding meetings to explain and promote their aims. In 1903 the Women's Social and Political Union (WSPU, the "suffragettes"), who wished to undertak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. With a population of approximately 1.2 million people, Surrey is the 12th-most populous county in England. The most populated town in Surrey is Woking, followed by Guildford. The county is divided into eleven districts with borough status. Between 1893 and 2020, Surrey County Council was headquartered at County Hall, Kingston-upon-Thames (now part of Greater London) but is now based at Woodhatch Place, Reigate. In the 20th century several alterations were made to Surrey's borders, with territory ceded to Greater London upon its creation and some gained from the abolition of Middlesex. Surrey is bordered by Greater London to the north east, Kent to the east, Berkshire to the north west, West Sussex to the south, East Sussex to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
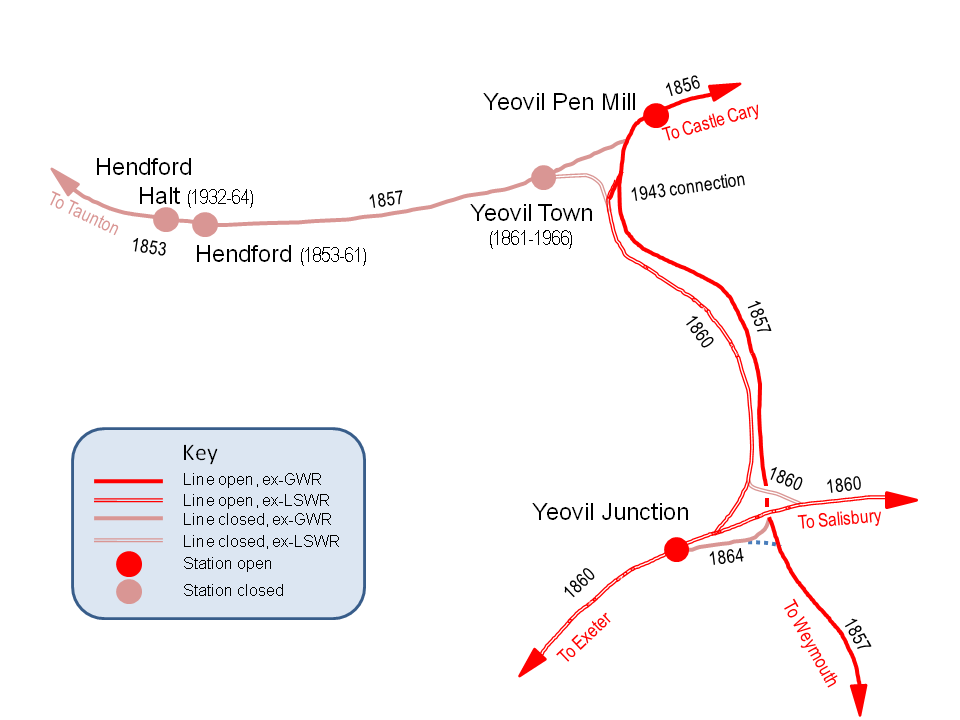
Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with Dorset, from London, south of Bristol, from Sherborne and from Taunton. The aircraft and defence industries which developed in the 20th century made it a target for bombing in the Second World War; they are still major employers. Yeovil Country Park, which includes Ninesprings, is one of several open spaces with educational, cultural and sporting facilities. Religious sites include the 14th-century Church of St John the Baptist, Yeovil, Church of St John the Baptist. The town is on the A30 road, A30 and A37 road, A37 roads and has two railway stations. History Archaeological surveys have yielded Palaeolithic burial and settlement sites mainly to the south of the modern town, particularly in Hendford, where a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)