|
Ipswich Railway Station
Ipswich railway station is on the Great Eastern Main Line in the East of England, serving the town of Ipswich, Suffolk. It is down the line from London Liverpool Street and, on the main line, it is situated between to the south and to the north. Ipswich is also the terminus of the East Suffolk Line to , a branch line to and a branch line to , Cambridgeshire. Its three-letter station code is IPS. The station is operated by Greater Anglia, which also operates all trains serving it, as part of the East Anglia franchise. History The Eastern Union Railway (EUR) opened its first terminus in Ipswich, called , in 1846 on Station Road at the other end of the current tunnel, close to the old quay for the steamboats and the aptly named Steamboat Tavern. The Ipswich Steam Navigation Company had been formed in 1824/25 during a period of "steamship mania" and briefly offered services from the quay between Ipswich and London calling at . The current station is just to the north o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line railway and the A12 road; it is north-east of London, east-southeast of Cambridge and south of Norwich. Ipswich is surrounded by two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB): Suffolk Coast and Heaths and Dedham Vale. Ipswich's modern name is derived from the medieval name ''Gippeswic'', probably taken either from an Anglo-Saxon personal name or from an earlier name given to the Orwell Estuary (although possibly unrelated to the name of the River Gipping). It has also been known as ''Gyppewicus'' and ''Yppswyche''. The town has been continuously occupied since the Saxon period, and is contested to be one of the oldest towns in the United Kingdom.Hills, Catherine"England's Oldest Town" Retrieved 2 August 2015. Ipswich was a settleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sancton Wood
Sancton Wood (27 April 1814 – 18 April 1886) was an English architect and surveyor, known for his work on railway buildings. Life and family Sancton Wood was born on 27 April 1814 in Nursery Place, Hackney Terrace, Hackney, London. He was the son of John Wood and Harriet Russell. He had 5 sisters. Wood's birth was registered in the Protestant dissenters’ birth registry. His mother was a niece of the painter, Richard Smirke. His paternal family were cotton merchants originally from Cumberland. He was named Sancton after his paternal uncle by marriage, Philip Sancton, a London merchant. He attended a private school in Devon, and later a school run by T. W. Hill at Hazelwood, Birmingham. On 11 March 1839, Wood married Elizabeth Sarah Simson (1810–1878), at Dedham, Essex. The couple had two sons, Herbert Sancton Wood (1844–1883) and William Winder Wood (1846–1876). The family moved to 11 Putney Hill, London in 1850, a house which Wood designed. He died there on 18 Apr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNER Gresley Classes A1 And A3
The London and North Eastern Railway LNER Gresley Classes A1 and A3 locomotives represented two distinct stages in the history of the British "Pacific" steam locomotives designed by Nigel Gresley. They were designed for main line passenger services and later express passenger services, initially on the Great Northern Railway (GNR), a constituent company of the London and North Eastern Railway after the amalgamation of 1923, for which they became a standard design. The change in class designation to A3 reflected the fitting to the same chassis of a higher pressure boiler with a greater superheating surface and a small reduction in cylinder diameter, leading to an increase in locomotive weight. Eventually all of the A1 locomotives were rebuilt, most to A3 specifications, but no. 4470 was completely rebuilt as Class A1/1. The names for the locomotives came from a variety of sources. The first, ''Great Northern'', was named after its parent company. Others were given the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNER Class W1
The LNER W1 No. 10000 (also known as the ''Hush-Hush'' due to its secrecy) was an experimental steam locomotive fitted with a high pressure water-tube boiler. Nigel Gresley was impressed by the results of using high-pressure steam in marine applications and so in 1924 he approached Harold Yarrow of shipyard and boilermakers Yarrow & Company of Glasgow to design a suitable boiler for a railway locomotive, based on Yarrow's design. Boiler The boiler was not the usual Yarrow design. In operation, particularly its circulation paths, the boiler had more in common with other three-drum designs such as the Woolnough. It has also been described as an evolution of the Brotan-Deffner water-tube firebox, with the firebox extended to become the entire boiler. The boiler resembled two elongated marine Yarrow boilers, joined end to end. Both had the usual Yarrow triangular arrangement of a central large steam drum above two separated water drums, linked by multiple rows of slightly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Churchman, 1st Baron Woodbridge
Lieutenant-Colonel Arthur Charles Churchman, 1st Baron Woodbridge, DL (7 September 1867 – 3 February 1949), known as Sir Arthur Churchman, Bt, between 1917 and 1932, was a British tobacco manufacturer, soldier and Conservative politician. Background and education Churchman was the son of Henry Charles Churchman, of Paget House, Ipswich, Suffolk, by Mary Anna Eade, daughter of Charles Eade. Sir William Churchman, 1st Baronet, was his elder brother. He was educated at Ipswich School. Business and political career Churchman went into partnership with his brother, William, in the family tobacco firm which had been founded by their great-grandfather in 1790. This was renamed W.A. & A.C. Churchman. It was later absorbed by the tobacco combines and Churchman became vice-chairman of the British American Tobacco Company. Churchman was elected Mayor of Ipswich in 1901, a post he held until the following year (his brother William had been mayor between 1899 and 1900). He was lieutena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was the second largest (after LMS) of the " Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain. It operated from 1 January 1923 until nationalisation on 1 January 1948. At that time, it was divided into the new British Railways' Eastern Region, North Eastern Region, and partially the Scottish Region. History The company was the second largest created by the Railways Act 1921. The principal constituents of the LNER were: * Great Eastern Railway * Great Central Railway * Great Northern Railway * Great North of Scotland Railway * Hull and Barnsley Railway * North British Railway * North Eastern Railway The total route mileage was . The North Eastern Railway had the largest route mileage of , whilst the Hull and Barnsley Railway was . It covered the area north and east of London. It included the East Coast Main Line from London to Edinburgh via York and Newcastle upon Tyne and the routes from Edinburgh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Engineers
The Corps of Royal Engineers, usually called the Royal Engineers (RE), and commonly known as the ''Sappers'', is a corps of the British Army. It provides military engineering and other technical support to the British Armed Forces and is headed by the Chief Royal Engineer. The Regimental Headquarters and the Royal School of Military Engineering are in Chatham in Kent, England. The corps is divided into several regiments, barracked at various places in the United Kingdom and around the world. History The Royal Engineers trace their origins back to the military engineers brought to England by William the Conqueror, specifically Bishop Gundulf of Rochester Cathedral, and claim over 900 years of unbroken service to the crown. Engineers have always served in the armies of the Crown; however, the origins of the modern corps, along with those of the Royal Artillery, lie in the Board of Ordnance established in the 15th century. In Woolwich in 1716, the Board formed the Royal Regime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Yeomanry
The Norfolk Yeomanry was a volunteer cavalry (Yeomanry) regiment of Britain's Territorial Army accepted onto the establishment of the British Army in 1794. After seeing action in the Second Boer War, it served dismounted at Gallipoli, in Palestine and on the Western Front during the First World War. Between the wars it converted to the Royal Artillery (TA), and served as an anti-tank regiment in France, the Western Desert, Italy and North West Europe during the Second World War. After the war it served as a TA air defence unit and then as an Army Air Corps unit. History Formation and early history A volunteer unit, the Norfolk Rangers, was raised as a home defence force in the county of Norfolk in 1782, during the American Revolutionary War, by the Hon George Townshend. Lord Ferrers of Chartley (later 2nd Marquess Townshend). It consisted of a troop of cavalry and an infantry company. The unit was accepted as Yeomanry Cavalry in 1794, and during the Napoleonic Wars there were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratford TMD
Stratford TMD was a traction maintenance depot located in Stratford, London, England close to the Great Eastern Main Line. It was located just west of Stratford station, on a site now occupied by Stratford International station. The depot was at one time the biggest on the London and North Eastern Railway with locomotives covering duties from express services to freight workings in London's docks. Locomotive construction took place at the adjacent Stratford Works and Stratford TMD was initially located on this site in the V between the Lea Bridge and Great Eastern Main Lines. In 1871 the depot moved to the 'teardrop' of lines to the west of the present Stratford Regional station. The depot closed in 2001, as part of the construction of the Channel Tunnel Rail Link. History Opening and early years Stratford Depot was built by the Northern and Eastern Railway whose line from Stratford to Broxbourne opened in 1840. By 1843, the main building was a 16 road roundhouse whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
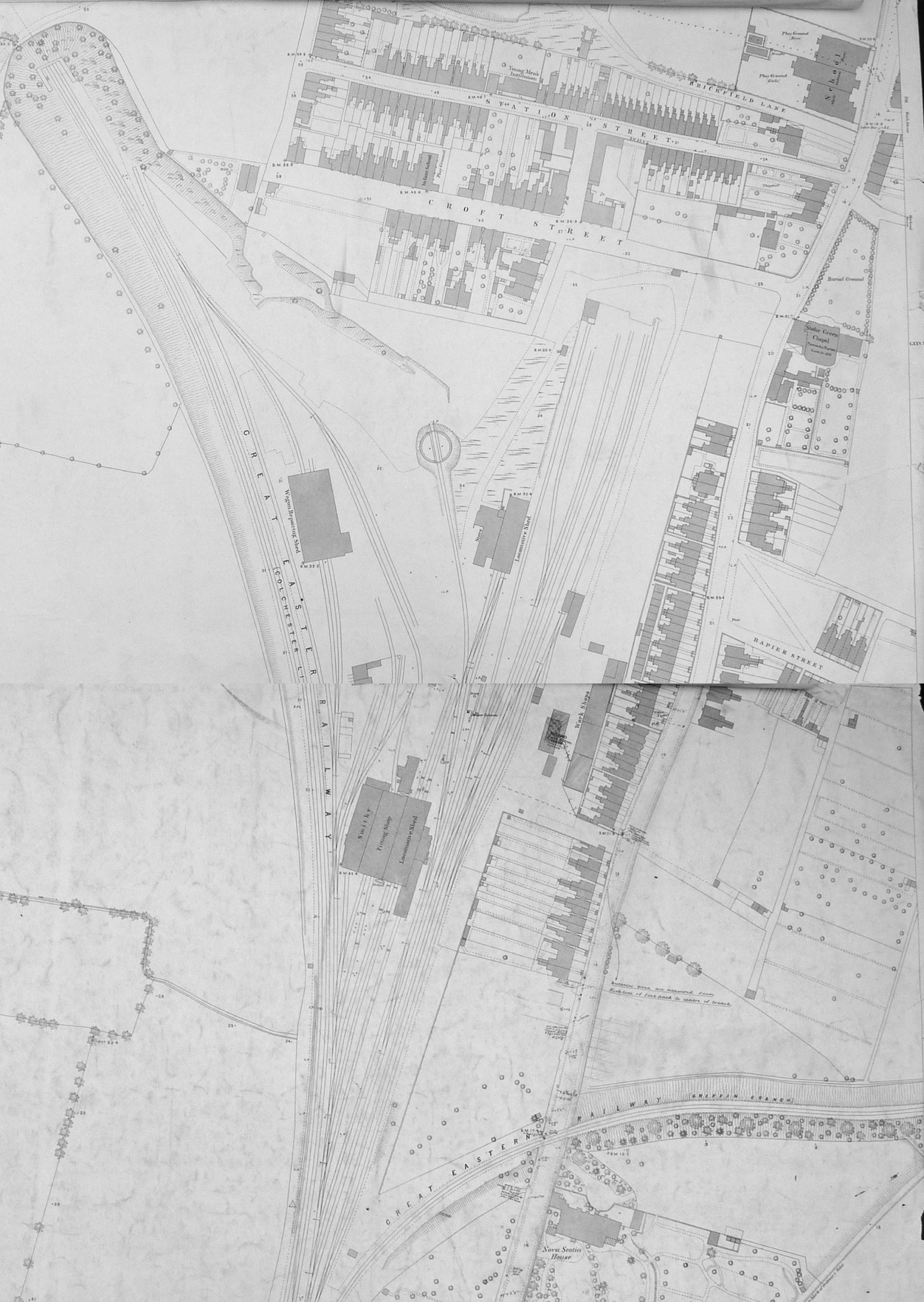
Ipswich Engine Shed
Ipswich engine shed was an engine shed located in Ipswich, Suffolk on the Great Eastern Main Line. It was located just south of Stoke tunnel and the current Ipswich railway station. Locomotives accessed the site from Halifax Junction which was also the junction for the Griffin Wharf branch of Ipswich docks. The depot opened in 1846 and closed in 1968 although the site remained in railway use for a further thirty years. In British Railways days it was allocated the code 32B. History Opening and early years Locomotive activity started on the depot site with the opening of the original Ipswich station located at Croft Street and (presumably the newly named) Station St in June 1846 by the Eastern Union Railway. Locomotives belonging to sister company the Ipswich and Bury Railway would also have used the facilities when their line opened in November 1846 although the two railway companies were worked as one from January the following year. In June 1851 the EUR had 31 locomotive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Platform
An island platform (also center platform, centre platform) is a station layout arrangement where a single platform is positioned between two tracks within a railway station, tram stop or transitway interchange. Island platforms are popular on twin-track routes due to pragmatic and cost reasons. They are also useful within larger stations where local and express services for the same direction of travel can be provided from opposite sides of the same platform thereby simplifying transfers between the two tracks. An alternative arrangement is to position side platforms on either side of the tracks. The historical use of island platforms depends greatly upon the location. In the United Kingdom the use of island platforms is relatively common when the railway line is in a cutting or raised on an embankment, as this makes it easier to provide access to the platform without walking across the tracks. Advantages and tradeoffs Island platforms are necessary for any station with many th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)

_(IWM_Q12647).jpeg)