|
Institute Of Archaeology Of The Chinese Academy Of Social Sciences
The Institute of Archaeology (IA; ) is a constituent institute of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS), based in Beijing, China. It was founded on 1 August 1950, as part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Its original 20 or so researchers came from the Beiping Research Academy and the Institute of History and Philology, Academia Sinica of the Republic of China. In 1977, the institute became part of the newly established CASS. Academic departments *Department of Prehistoric Archaeology, established 1953 *Department of Xia, Shang and Zhou Archaeology, established 1953 *Research Department of Han to Tang Archaeology, established 1953 *Research Center for Frontier Archaeology and Foreign Archaeology, established 2002 *Center for Scientific Archaeology, established 1995 *Archaeology Press, established 1955 *Center for Archaeological Data and Information, established 1996 In addition, the Research Center for Ancient Civilizations and the Conservation and Research Center of Cultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Academy Of Social Sciences
The Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS) is a Chinese research institute and think tank. The institution is the premier comprehensive national academic research organization in the People's Republic of China for the study in the fields of philosophy and social sciences, with the obligation of advancing and innovating in the scientific research of philosophy, social sciences and policies. It was described by '' Foreign Policy'' magazine as the top think tank in Asia. CASS is under the auspices of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. It is the country's second oldest such institution, after the Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences in Shanghai. It also holds the Graduate School of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences and later become the University of Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. History The CASS was established in May 1977, based on the 14 research units of the Department of Philosophy and Social Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, with the aim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ledu District
Ledu District () is a district of the city of Haidong, Qinghai province, China. Nearby are Ping'an District and the city of Xining. Ledu used to be named Nianbo county before 1929. The county dates back to 1724. On 8 February 2013 Ledu was upgraded from a county into a district. Ledu District is served by the G6 Beijing–Lhasa Expressway. See also * Liuwan Museum of Ancient Painted Pottery References External links Map of Ledu, Qinghai, Chinafrom Multimap In computer science, a multimap (sometimes also multihash, multidict or multidictionary) is a generalization of a map or associative array abstract data type in which more than one value may be associated with and returned for a given key. Both m ... Liuwan Tombs the largest tombs of primitive China County-level divisions of Qinghai Haidong {{Qinghai-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sui Dynasty
The Sui dynasty (, ) was a short-lived imperial dynasty of China that lasted from 581 to 618. The Sui unified the Northern and Southern dynasties, thus ending the long period of division following the fall of the Western Jin dynasty, and laying the foundations for the much longer lasting Tang dynasty. Founded by Emperor Wen of Sui, the Sui dynasty capital was Chang'an (which was renamed Daxing, modern Xi'an, Shaanxi) from 581–605 and later Luoyang (605–18). Emperors Wen and his successor Yang undertook various centralized reforms, most notably the equal-field system, intended to reduce economic inequality and improve agricultural productivity; the institution of the Five Departments and Six Board (五省六曹 or 五省六部) system, which is a predecessor of Three Departments and Six Ministries system; and the standardization and re-unification of the coinage. They also spread and encouraged Buddhism throughout the empire. By the middle of the dynasty, the newly unifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0.3% Mongol. Three Mandarin dialects are spoken: Jilu Mandarin, Beijing Mandarin and Jin. Hebei borders the provinces of Shanxi to the west, Henan to the south, Shandong to the southeast, Liaoning to the northeast, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north. Its economy is based on agriculture and manufacturing. The province is China's premier steel producer, although the steel industry creates serious air pollution. Five UNESCO World Heritage Sites can be found in the province, the: Great Wall of China, Chengde Mountain Resort, Grand Canal, Eastern Qing tombs, and Western Qing tombs. It is also home to five National Famous Historical and Cultural Cities: Handan, Baoding, Chengde, Zhengding and Shanhaiguan. Historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mancheng Han Tomb
Mancheng District () is a district of west-central Hebei province, China, in the eastern foothills of the Taihang Mountains. It is administratively part of Baoding prefecture-level city, of which the Mancheng is a northwestern suburb. Mancheng is the site of the Han dynasty tombs of Prince Jing of Zhongshan, Liu Sheng and his wife Dou Wan. Administrative divisions There is 1 subdistrict, 5 towns and 7 townships under the county's administration. Subdistricts: * Huiyang Subdistrict () Towns: *Mancheng Mancheng District () is a district of west-central Hebei province, China, in the eastern foothills of the Taihang Mountains. It is administratively part of Baoding prefecture-level city, of which the Mancheng is a northwestern suburb. Mancheng is ... (), Daceying (), Shenxing (), Nanhancun (), Fangshunqiao () Townships: * Yujiazhuang Township (), Xiantai Township (), Yaozhuang Township (), Bailong Township (), Shijing Township (), Tuonan Township (), Liujiatai Townshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin Shi Huang of the Qin dynasty, China's first emperor, held his imperial court, and constructed his massive mausoleum guarded by the Terracotta Army. From its capital at Xianyang, the Qin dynasty ruled a larger area than either of the preceding dynasties. The imperial city of Chang'an during the Han dynasty was located northwest of today's Xi'an. During the Tang dynasty, the area that came to be known as Chang'an included the area inside the Ming Xi'an fortification, plus some small areas to its east and west, and a substantial part of its southern suburbs. Thus, Tang Chang'an was eight times the size of the Ming Xi'an, which was reconstructed upon the site of the former imperial quarters of the Sui and Tang city. During its heyday, Chang'an w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang, Henan, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five out of six urban districts (except the Jili District not continuously urbanized) and Yanshi District, now being conurbated. Situated on the Central Plain (China), central plain of China, Luoyang is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#East Asia, oldest cities in China and one of the History of China#Ancient China, cradles of Chinese civilization. It is the earliest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
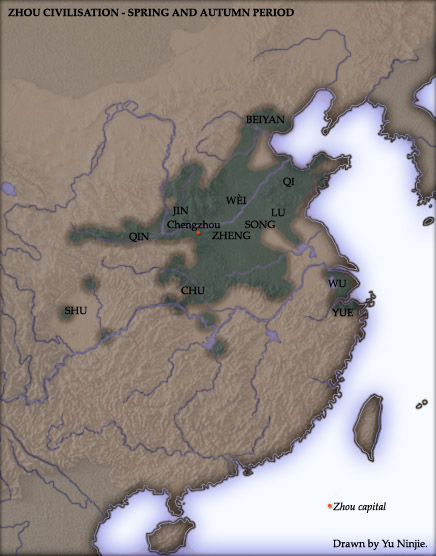
Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (; zh, c=, p=Dōngzhōu, w=Tung1-chou1, t= ; 771–256 BC) was a royal dynasty of China and the second half of the Zhou dynasty. It was divided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn and the Warring States. History In 770 BCE, the capital of the Zhou Kingdom was moved from Haojing (Chang'an County in Xi'an City) to Luoyi (known today as Luoyang, Henan Province). This brought about the beginning of the Eastern Zhou dynasty (as opposed to Western Zhou dynasty), so named due to Luoyi being situated to the east of Haojing. Over 25 kings reigned over the Eastern Zhou Dynasty, lasting 515 years in all. With the death of King You of Zhou, the last king of the Western Zhou Dynasty, ascended Crown Prince Yijiu was proclaimed the new king by the nobles from the states of Zheng, Lü, Qin and the Marquess of Shen. He was King Ping of Zhou. In the second year of his reign, he moved the capital east to Luoyi as Quanrong invaded Haojing, indicating the end of the Weste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenghao
Fenghao () is the modern name of the twin city formed by the Western Zhou dynasty, Western Zhou capitals of Feng and Haojing, Hao on opposite banks of the Feng River near its confluence with the Wei River in Shaanxi, China. History As King Wen of Zhou, Duke Wen (ruled c. 1099–1050 BCE) expanded the territory of duchy of Zhou, Zhou east into Shanxi in preparation for an assault on his nominal Shang dynasty, Shang overlords, he constructed a new capital on the west bank of the Feng about downstream from Zhou's original capital on the Wei River below Qishan County, Mount Qi. This city was called Feng, Fengxi, or Fengjing (, ''Fēngjīng''). After his son Fa defeated the Shang at battle of Muye, Muye and ascended the throne as King Wu of Zhou, King Wu (ruled c. 1046–1043 BCE), the capital was moved to a new establishment on the east bank called Hao or Haojing. The two formed a twin capital, with Feng continuing to serve the rituals of the Zhou ancestral hall, Ancestral Shrine an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anyang
Anyang (; ) is a prefecture-level city in Henan province, China. The northernmost city in Henan, Anyang borders Puyang to the east, Hebi and Xinxiang to the south, and the provinces of Shanxi and Hebei to its west and north respectively. It had a total population of 5,477,614 as of the 2020 census, 2,675,523 of whom lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of four urban districts and Anyang and Tangyin counties, now largely agglomerated with the city proper. Anyang is the location of the ancient city of Yin, which was the capital of the Shang dynasty and the first stable capital of China. Henan once had the largest population in China. History Early history Xiaonanhai, on the far western edge of the city, was home to prehistoric cavemen during the Stone Age. Over 7,000 artifacts (including stone tools and animal bone fossils) have been unearthed here, representing what has been dubbed the Xiaonanhai culture. Around 2000 BC, the legendary sage-kings Zhuanxu and Emperor Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yinxu
Yinxu (modern ; ) is the site of one of the ancient and major historical capitals of China. It is the source of the archeological discovery of oracle bones and oracle bone script, which resulted in the identification of the earliest known Chinese writing. The archeological remnants (or ruins) known as Yinxu represent the ancient city of Yin, the last capital of China's Shang dynasty which existed through eight generations for 255 years, and through the reign of 12 kings. Yinxu was discovered, or rediscovered, in 1899. It is now one of China's oldest and largest archeological sites, and was selected as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006. Yinxu is located in northernmost Henan province near the modern city of Anyang, and near the Hebei and Shanxi province borders. Public access to the site is permitted. Traditional history According to the 2nd century ''Shuowen Jiezi'' dictionary (說文解字), the Chinese character "" (''yīn'') originally referred to "vibrant music-maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |