|
Ikeda Taenioides
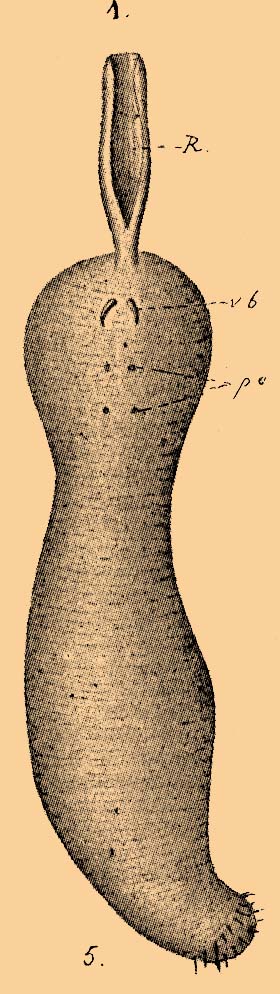
''Ikeda taenioides'' is a species of spoon worm in the family Ikedidae. It is native to the northern Pacific Ocean where it is found in the subtidal waters around Japan. Taxonomy This spoon worm was first described by the Japanese zoologist I. Ikeda in 1904 as ''Thalassema taenioides'', the type locality being Misaki, Sagami Bay, in Honshu, Japan. Examination of the musculature of the body wall led to the observation that the longitudinal muscle layer lay outside both the circular layer and the inner oblique layer, and as this was at odds with all other members of the subclass Echiura, it warranted the creation of a new order. However, examination of the original material by Teruaki Nishikawa in 2002, showed that the longitudinal muscle layer was in fact between the circular layer and the oblique layer, as in all other echurians, throwing the taxonomy of the species into doubt. Nishikawa advocates that the family Ikedidae be regarded as a junior synonym of Echiuridae. Descript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iwaki Ikeda
Iwaki (岩城、磐城) may refer to: Places *Iwaki, Fukushima (いわき市), a city in Japan *Iwaki, Akita (岩城町), a former town in Japan *Iwaki, Aomori (岩木町), a former town in Japan *Iwaki Province (718) (岩城国), an old province of Japan established in 718 and dissolved by 724 *Iwaki Province (1868) (磐城国), an old province of Japan established in 1868 *Iwaki River (岩木川), a river in Aomori Prefecture, Japan *Mount Iwaki (岩木山), a volcano on the Japanese island of Honshū Surname *Iwaki clan: a Japanese clan that ruled the Hamadōri area *Hiroyuki Iwaki (岩城 宏之), a Japanese musician and conductor *Mirai Iwaki, a fictional character in the manga ''Guru Guru Pon-chan'' {{disambiguation, geo, surname Japanese-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into segments, but echiurans have secondarily lost their segmentation. The majority of echiurans live in burrows in soft sediment in shallow water, but some live in rock crevices or under boulders, and there are also deep sea forms. More than 230 species have been described. Spoon worms are cylindrical, soft-bodied animals usually possessing a non-retractable proboscis which can be rolled into a scoop-shape to feed. In some species the proboscis is ribbon-like, longer than the trunk and may have a forked tip. Spoon worms vary in size from less than a centimetre in length to more than a metre. Most are deposit feeders, collecting detritus from the sea floor. Fossils of these worms are seldom found and the earliest known fossil specimen is from the Upper Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ikedidae
Ikedidae is a family of spoon worms in the suborder Bonelliida. It is a monotypic family, the only genus being ''Ikeda''. These worms burrow into soft sediment on the seabed. Examination of the original material of '' Ikeda taenoides'' by Teruaki Nishikawa in 2002 showed that the longitudinal muscle layer lay between the circular layer and the oblique layer, as in all other echiurans, throwing the validity of the family Ikedidae into doubt. Nishikawa advocates that the family be regarded as a junior synonym of Echiuridae. Species The World Register of Marine Species recognises the following species in the genus:- *'' Ikeda pirotansis'' ( Menon & DattaGupta, 1962) *''Ikeda taenioides'' (Ikeda Ikeda may refer to: * Ikeda (surname), a Japanese surname * Ikeda (comics), a character in ''Usagi Yojimbo'' * Ikeda clan, a Japanese clan * Ikeda map, chaotic attractor * ''Ikeda'' (annelid) a genus of the family Ikedidae Places * Ikeda, Osaka i ..., 1904) References {{Taxonbar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassema
Thalassema is a genus of spoonworms in the subclass Echiura. Species The World Register of Marine Species includes these species in this genus:- * '' Thalassema antarcticum'' Stephen, 1941 * '' Thalassema arcassonense'' Cuénot, 1902 * '' Thalassema diaphanes'' Sluiter, 1889 * '' Thalassema elapsum'' Sluiter, 1912 * '' Thalassema fuscum'' Ikeda, 1904 * '' Thalassema hartmani'' Fisher Fisher is an archaic term for a fisherman, revived as gender-neutral. Fisher, Fishers or The Fisher may also refer to: Places Australia *Division of Fisher, an electoral district in the Australian House of Representatives, in Queensland *Elect ..., 1947 * '' Thalassema jenniferae'' Biseswar, 1988 * '' Thalassema liliae'' Schaeffer, 1972 * '' Thalassema malakhovi'' Popkov, 1992 * '' Thalassema marshalli'' Prashad, 1935 * '' Thalassema mortenseni'' Fischer, 1923 * '' Thalassema ochotica'' Pergament, 1961 * '' Thalassema ovatum'' Sluiter, 1902 * '' Thalassema owstoni'' Ikeda, 1904 * '' Thalassem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagami Bay
lies south of Kanagawa Prefecture in Honshu, central Japan, contained within the scope of the Miura Peninsula, in Kanagawa, to the east, the Izu Peninsula, in Shizuoka Prefecture, to the west, and the Shōnan coastline to the north, while the island of Izu Ōshima marks the southern extent of the bay. It lies approximately southwest of the capital, Tokyo. Cities on the bay include Odawara, Chigasaki, Fujisawa, Hiratsuka, Itō, and Kamakura. History The center of the Great Kantō earthquake in 1923 was deep beneath Izu Ōshima Island in Sagami Bay. It devastated Tokyo, the port city of Yokohama, and the surrounding prefectures of Chiba, Kanagawa, and Shizuoka, and caused widespread damage throughout the Kantō region. The shallow nature of the seabed on the north of the bay, and the funnelling effect of tsunami and typhoon wave energy, contributed to certain parts of the Shonan coast having suffered considerable damage, including the destruction of the Kōtoku-in temple hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honshu
, historically called , is the largest and most populous island of Japan. It is located south of Hokkaidō across the Tsugaru Strait, north of Shikoku across the Inland Sea, and northeast of Kyūshū across the Kanmon Straits. The island separates the Sea of Japan, which lies to its north and west, from the North Pacific Ocean to the south and east. It is the seventh-largest island in the world, and the second-most populous after the Indonesian island of Java. Honshu had a population of 104 million , constituting 81.3% of the entire population of Japan, and is mostly concentrated in the coastal areas and plains. Approximately 30% of the total population resides in the Greater Tokyo Area on the Kantō Plain. As the historical center of Japanese cultural and political power, the island includes several past Japanese capitals, including Kyōto, Nara and Kamakura. Much of the island's southern shore forms part of the Taiheiyō Belt, a megalopolis that spans several of the Japane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echiuridae
Echiuridae is a family of spoon worms in the suborder Echiurida. It is a monotypic family, the only genus being ''Echiurus''. These worms burrow into soft sediment on the seabed. Species The World Register of Marine Species recognises the following species in the genus:- * '' Echiurus abyssalis'' Skorikow, 1906 * '' Echiurus antarcticus'' Spengel, 1912 * ''Echiurus echiurus ''Echiurus echiurus'' is a species of spoon worm in the family Echiuridae. It is found in the North Atlantic Ocean and a subspecies is found in Alaska. It burrows into soft sediment and under boulders and stones in muddy places. Description Th ...'' (Pallas, 1766) * '' Echiurus sitchaensis'' Brandt, 1835 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q2809389 Echiurans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations, landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances) above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. Unlike normal ocean waves, which are generated by wind, or tides, which are in turn generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun, a tsunami is generated by the displacement of water from a large event. Tsunami waves do not resemble normal undersea currents or sea waves because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide. For this reason, it is often referred to as a tidal wave, although this usage is not favoured by the scientific community because it might give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seagrass
Seagrasses are the only flowering plants which grow in marine environments. There are about 60 species of fully marine seagrasses which belong to four families (Posidoniaceae, Zosteraceae, Hydrocharitaceae and Cymodoceaceae), all in the order Alismatales (in the clade of monocotyledons). Seagrasses evolved from terrestrial plants which recolonised the ocean 70 to 100 million years ago. The name ''seagrass'' stems from the many species with long and narrow leaves, which grow by rhizome extension and often spread across large "meadows" resembling grassland; many species superficially resemble terrestrial grasses of the family Poaceae. Like all autotrophic plants, seagrasses photosynthesize, in the submerged photic zone, and most occur in shallow and sheltered coastal waters anchored in sand or mud bottoms. Most species undergo submarine pollination and complete their life cycle underwater. While it was previously believed this pollination was carried out without pollinators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatangoida
The heart urchins or Spatangoida are an order of sea urchins. Their body is a somewhat elongated oval in form, and is distinguished by the mouth being placed towards one end of the animal, and the anus towards the other. As a result, heart urchins, unlike most other sea urchins, are bilaterally symmetrical, and have a distinct anterior surface. The presence and position of the mouth and anus typically give members of this group the distinct "heart" shape from which they get their name. Heart urchins have no feeding lantern, and often have petaloids sunk into grooves. They are a relatively diverse order, with a number of varying species. Taxonomy According to World Register of Marine Species : * suborder Brissidina Stockley, Smith, Littlewood, Lessios & MacKenzie-Dodds, 2005 ** family Asterostomatidae Pictet, 1857 ** family Brissidae Gray, 1855 ** family Palaeotropidae Lambert, 1896 ** super-family Spatangidea Fischer, 1966 *** family Eupatagidae Lambert, 1905 *** family ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |