|
Iduronic Acid
-Iduronic acid (IUPAC abbr.: IdoA) is the major uronic acid component of the glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) dermatan sulfate, and heparin. It is also present in heparan sulfate, although here in a minor amount relative to its carbon-5 epimer glucuronic acid. IdoA is a hexapyranose sugar. Most hexapyranoses are stable in one of two chair conformations 1C4 or 4C1. -iduronate is different and adopts more than one solution conformation, with an equilibrium existing between three low-energy conformers. These are the 1C4 and 4C1 chair forms and an additional 2S0 skew-boat conformation. IdoA may be modified by the addition of an ''O''-sulfate group at carbon position 2 to form 2-''O''-sulfo--iduronic acid (IdoA2S). In 2000, LK Hallak described the importance of this sugar in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection. Dermatan sulfate and heparan sulfate were the only GAGs containing IdoA, and they were the only ones that inhibited RSV infection in cell culture. When internally position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case of the sulfated glycosaminoglycan keratan, where, in place of the uronic sugar there is a galactose unit. GAGs are found in vertebrates, invertebrates and bacteria. Because GAGs are highly polar molecules and attract water; the body uses them as lubricants or shock absorbers. Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders in which abnormal accumulations of glycosaminoglycans occur due to enzyme deficiencies. Production Glycosaminoglycans vary greatly in molecular mass, disaccharide structure, and sulfation. This is because GAG synthesis is not template driven, as are proteins or nucleic acids, but constantly altered by processing enzymes. GAGs are classified into four groups, based on their core disaccharide structures. Hepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatan Sulfate
Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan (formerly called a mucopolysaccharide) found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs. It is also referred to as chondroitin sulfate B, although it is no longer classified as a form of chondroitin sulfate by most sources. The formula is C14H21NO15S. This carbohydrate is composed of linear polymers of disaccharide units that contain, N-acetyl galactosamine (GalNAc) and iduronic acid (IdoA). These repeating units are sulfated at a variety of positions. Dermatan sulfate is a component of the compound sulodexide. Function Dermatan sulfate may have roles in coagulation, cardiovascular disease, carcinogenesis, infection, wound repair, maintains the shape of galactosamine 4-sulfate skin and fibrosis. Pathology Dermatan sulfate accumulates abnormally in several of the mucopolysaccharidosis disorders. An excess of dermatan sulfate in the mitral valve is characteristic of myxomatous degeneration of the leaflet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
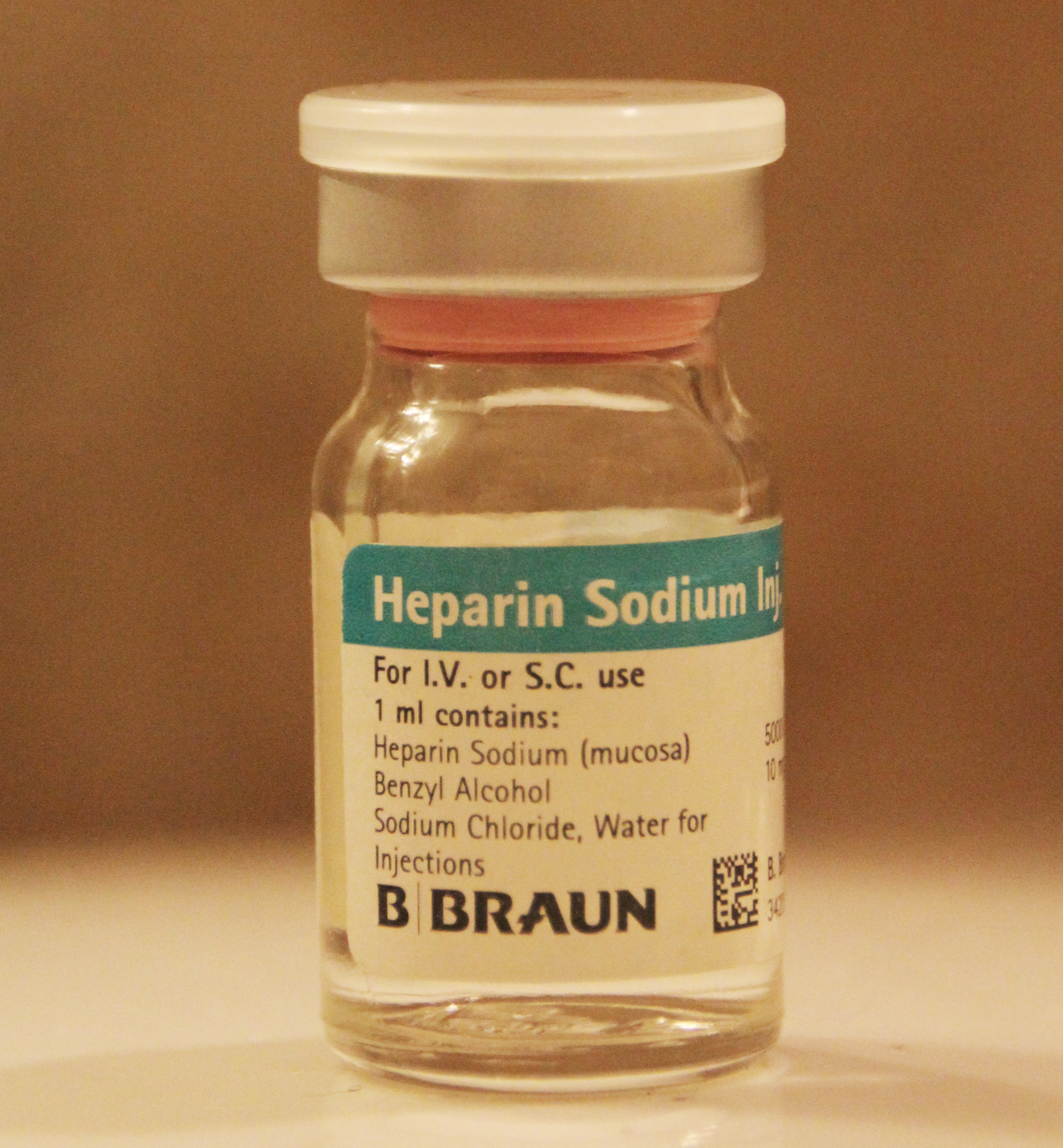
Heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatment of heart attacks and unstable angina. It is given intravenously or by injection under the skin. Other uses for its anticoagulant properties include inside blood specimen test tubes and kidney dialysis machines. Common side effects include bleeding, pain at the injection site, and low blood platelets. Serious side effects include heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Greater care is needed in those with poor kidney function. Heparin is contraindicated for suspected cases of vaccine-induced pro-thrombotic immune thrombocytopenia (VIPIT) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination, as heparin may further increase the risk of bleeding in an anti-PF4/heparin complex autoimmune manner, in favor of alternative anticoagulant medications (such as arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparan Sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. It is in this form that HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB (Granzyme B), and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2. Proteoglycans The major cell membrane HSPGs are the transmembrane syndecans and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored glypicans. Other minor forms of membrane HSPG include betaglycan and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epimer
In stereochemistry, an epimer is one of a pair of diastereomers. The two epimers have opposite configuration at only one stereogenic center out of at least two. All other stereogenic centers in the molecules are the same in each. Epimerization is the interconversion of one epimer to the other epimer. Doxorubicin and epirubicin are two epimers that are used as drugs. Examples The stereoisomers β-D- glucopyranose and β-D- mannopyranose are epimers because they differ only in the stereochemistry at the C-2 position. The hydroxy group in β-D-glucopyranose is equatorial (in the "plane" of the ring), while in β-D-mannopyranose the C-2 hydroxy group is axial (up from the "plane" of the ring). These two molecules are epimers but, because they are not mirror images of each other, are not enantiomers. (Enantiomers have the same name, but differ in D and L classification.) They are also not sugar anomers, since it is not the anomeric carbon involved in the stereochemistry. Simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucuronic Acid
Glucuronic acid (from Greek γλεῦκος "''wine, must''" and οὖρον "''urine''") is a uronic acid that was first isolated from urine (hence the name). It is found in many gums such as gum arabic (c. 18%), xanthan, and kombucha tea and is important for the metabolism of microorganisms, plants and animals. Properties Glucuronic acid is a sugar acid derived from glucose, with its sixth carbon atom oxidized to a carboxylic acid. In living beings, this primary oxidation occurs with UDP-α-D-glucose (UDPG), not with the free sugar. Glucuronic acid, like its precursor glucose, can exist as a linear (carboxo-) aldohexose ( 60,000 are too large for renal excretion and will be excreted with bile into the intestine. Neonates are deficient in this conjugating system, making them particularly vulnerable to drugs such as chloramphenicol, which is inactivated by the addition of glucuronic acid, resulting in gray baby syndrome. Bilirubin is excreted in the bile as bilirubin dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate Conformation
Carbohydrate conformation refers to the overall three-dimensional structure adopted by a carbohydrate (saccharide) molecule as a result of the through-bond and through-space physical forces it experiences arising from its molecular structure. The physical forces that dictate the three-dimensional shapes of all molecules—here, of all monosaccharide, oligosaccharide, and polysaccharide molecules—are sometimes summarily captured by such terms as " steric interactions" and " stereoelectronic effects" (see below). Saccharide and other chemical conformations can be reasonably shown using two-dimensional structure representations that follow set conventions; these capture for a trained viewer an understanding of the three-dimensional structure via structure drawings (see organic chemistry article, and "3D Representations" section in molecular geometry article); they are also represented by stereograms on the two dimensional page, and increasingly using 3D display technologies on compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), also called human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) and human orthopneumovirus, is a common, contagious virus that causes infections of the respiratory tract. It is a negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. Its name is derived from the large cells known as ''syncytia'' that form when infected cells fuse. RSV is the single most common cause of respiratory hospitalization in infants, and reinfection remains common in later life: it is a notable pathogen in all age groups. Infection rates are typically higher during the cold winter months, causing bronchiolitis in infants, common colds in adults, and more serious respiratory illnesses such as pneumonia in the elderly and immunocompromised. RSV can cause outbreaks both in the community and in hospital settings. Following initial infection via the eyes or nose, the virus infects the epithelial cells of the upper and lower airway, causing inflammation, cell damage, and airway obstruction. A varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMR Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei. The sample is placed in a magnetic field and the NMR signal is produced by excitation of the nuclei sample with radio waves into nuclear magnetic resonance, which is detected with sensitive radio receivers. The intramolecular magnetic field around an atom in a molecule changes the resonance frequency, thus giving access to details of the electronic structure of a molecule and its individual functional groups. As the fields are unique or highly characteristic to individual compounds, in modern organic chemistry practice, NMR spectroscopy is the definitive method to identify monomolecular organic compounds. The principle of NMR usually involves three sequential steps: # The alignment (polarization) of the magnetic nuclear spins in an applied, constant magnetic field B0. # The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |