|
Hemimastigophora
Hemimastigophora is a group of single-celled eukaryotic organisms with a single family, Spironemidae, first identified in 1988. Over the next 30 years, different authors proposed placing these organisms in various branches of the eukaryotes. In 2018 Lax ''et al''. reported the first genetic information for Spironemidae, and suggest that they are from an ancient lineage of eukaryotes which constitute a separate clade from all other eukaryotic kingdoms. It is potentially related to the Telonemia. History of classification Hemimastigophora was established in 1988 by Foissner ''et al''., as a new phylum with a single family, Spironemidae. Its placement on the eukaryote tree of life was unclear, but the authors suggested that the structure of its pellicle and cell nucleus indicated a close relationship with Euglenozoa. For 30 years after the description of the group, no genetic information was available. During that time, researchers proposed that it should be classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemimastigophora
Hemimastigophora is a group of single-celled eukaryotic organisms with a single family, Spironemidae, first identified in 1988. Over the next 30 years, different authors proposed placing these organisms in various branches of the eukaryotes. In 2018 Lax ''et al''. reported the first genetic information for Spironemidae, and suggest that they are from an ancient lineage of eukaryotes which constitute a separate clade from all other eukaryotic kingdoms. It is potentially related to the Telonemia. History of classification Hemimastigophora was established in 1988 by Foissner ''et al''., as a new phylum with a single family, Spironemidae. Its placement on the eukaryote tree of life was unclear, but the authors suggested that the structure of its pellicle and cell nucleus indicated a close relationship with Euglenozoa. For 30 years after the description of the group, no genetic information was available. During that time, researchers proposed that it should be classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
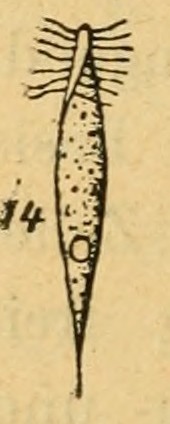
Stereonema
Spironemidae is a family of heterotrophic flagellates, in the group Hemimastigophora. They vary in size and shape from the ellipsoid ''Hemimastix amphikineta'' (14 × 7 μm) to the vermiform ''Spironema terricola'' (43 × 3 μm), and are united by the possession of two rows of cilia, called kineties. Phylogenomic analysis shows that Hemimastigophora are a distinct and ancient lineage of eukaryotic organisms, forming a possible sister clade to the supergroup Diaphoretickes. Taxonomy * Order Hemimastigida Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 [Hemimastigophora Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 sensu Cavalier-Smith 1993; Hemimastigea Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988; Hemimastigidea] ** Family Spironematellidae *** Genus '' Hemimastix'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. amphikineta'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. kukwesjijk'' Eglit & Simpson, 2018 *** Genus '' Stereonema'' Foissner& Foissner, 1993 non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spironema (flagellate)
Spironemidae is a family of heterotrophic flagellates, in the group Hemimastigophora. They vary in size and shape from the ellipsoid ''Hemimastix amphikineta'' (14 × 7 μm) to the vermiform ''Spironema terricola'' (43 × 3 μm), and are united by the possession of two rows of cilia, called kineties. Phylogenomic analysis shows that Hemimastigophora are a distinct and ancient lineage of eukaryotic organisms, forming a possible sister clade to the supergroup Diaphoretickes. Taxonomy * Order Hemimastigida Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 [Hemimastigophora Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 sensu Cavalier-Smith 1993; Hemimastigea Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988; Hemimastigidea] ** Family Spironematellidae *** Genus '' Hemimastix'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. amphikineta'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. kukwesjijk'' Eglit & Simpson, 2018 *** Genus ''Stereonema'' Foissner& Foissner, 1993 non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemimastix
Spironemidae is a family of heterotrophic flagellates, in the group Hemimastigophora. They vary in size and shape from the ellipsoid ''Hemimastix amphikineta'' (14 × 7 μm) to the vermiform ''Spironema terricola'' (43 × 3 μm), and are united by the possession of two rows of cilia, called kineties. Phylogenomic analysis shows that Hemimastigophora are a distinct and ancient lineage of eukaryotic organisms, forming a possible sister clade to the supergroup Diaphoretickes. Taxonomy * Order Hemimastigida Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 [Hemimastigophora Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 sensu Cavalier-Smith 1993; Hemimastigea Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988; Hemimastigidea] ** Family Spironematellidae *** Genus '' Hemimastix'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. amphikineta'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. kukwesjijk'' Eglit & Simpson, 2018 *** Genus ''Stereonema'' Foissner& Foissner, 1993 non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemimastigida
Spironemidae is a family of heterotrophic flagellates, in the group Hemimastigophora. They vary in size and shape from the ellipsoid ''Hemimastix amphikineta'' (14 × 7 μm) to the vermiform ''Spironema terricola'' (43 × 3 μm), and are united by the possession of two rows of cilia, called kineties. Phylogenomic analysis shows that Hemimastigophora are a distinct and ancient lineage of eukaryotic organisms, forming a possible sister clade to the supergroup Diaphoretickes. Taxonomy * Order Hemimastigida Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 [Hemimastigophora Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 sensu Cavalier-Smith 1993; Hemimastigea Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988; Hemimastigidea] ** Family Spironematellidae *** Genus ''Hemimastix'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. amphikineta'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. kukwesjijk'' Eglit & Simpson, 2018 *** Genus ''Stereonema'' Foissner& Foissner, 1993 non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spironemidae
Spironemidae is a family of heterotrophic flagellates, in the group Hemimastigophora. They vary in size and shape from the ellipsoid ''Hemimastix amphikineta'' (14 × 7 μm) to the vermiform ''Spironema terricola'' (43 × 3 μm), and are united by the possession of two rows of cilia, called kineties. Phylogenomic analysis shows that Hemimastigophora are a distinct and ancient lineage of eukaryotic organisms, forming a possible sister clade to the supergroup Diaphoretickes. Taxonomy * Order Hemimastigida Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 [Hemimastigophora Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988 sensu Cavalier-Smith 1993; Hemimastigea Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner 1988; Hemimastigidea] ** Family Spironematellidae *** Genus ''Hemimastix'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. amphikineta'' Foissner, Blatterer & Foissner, 1988 **** Species '' H. kukwesjijk'' Eglit & Simpson, 2018 *** Genus ''Stereonema'' Foissner& Foissner, 1993 non ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote Phylogeny
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Eukar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolate
The alveolates (meaning "pitted like a honeycomb") are a group of protists, considered a major clade and Biological classification, superphylum within Eukarya. They are currently grouped with the stramenopiles and Rhizaria among the protists with tubulocristate mitochondria, the group being referred to as SAR supergroup, SAR. Characteristics The most notable shared characteristic is the presence of cortical (near the surface) alveoli (sacs). These are flattened vesicle (biology), vesicles (sacs) arranged as a layer just under the cell membrane, membrane and supporting it, typically contributing to a flexible pellicle (thin skin). In armored dinoflagellates they may contain stiff plates. Alveolates have mitochondrion, mitochondria with tubular cristae (invaginations), and cells often have pore-like intrusions through the cell surface. The group contains free-living and parasitic organisms, predatory flagellates, and photosynthetic organisms. Almost all sequenced mitochondrial g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenomics
Phylogenomics is the intersection of the fields of evolution and genomics. The term has been used in multiple ways to refer to analysis that involves genome data and evolutionary reconstructions. It is a group of techniques within the larger fields of phylogenetics and genomics. Phylogenomics draws information by comparing entire genomes, or at least large portions of genomes. Phylogenetics compares and analyzes the sequences of single genes, or a small number of genes, as well as many other types of data. Four major areas fall under phylogenomics: * Prediction of gene function * Establishment and clarification of evolutionary relationships * Gene family evolution * Prediction and retracing lateral gene transfer. The ultimate goal of phylogenomics is to reconstruct the evolutionary history of species through their genomes. This history is usually inferred from a series of genomes by using a genome evolution model and standard statistical inference methods (e.g. Bayesian inference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |