|
Haryanka
The Haryanka dynasty was the third ruling dynasty of Magadha, an empire of ancient India, which succeeded the Pradyota dynasty and Barhadratha dynasty. Initially, the capital was Rajagriha. Later, it was shifted to Pataliputra, near the present-day Patna in India during the reign of Udayin. Bimbisara is considered as the main founder of the dynasty. According to the Buddhist text, the Mahavamsa, Bimbisara was appointed king by his father, Bhattiya, at the age of fifteen. This dynasty was succeeded by the Shishunaga dynasty. Governance The governance structure of Haryanka dynasty is mentioned in ancient texts. They mention ''gramakas'' (village headmen) who headed village assemblies and ''mahamatras'' (high-ranking officials) who had executive, judicial and military functions. Historically, this period coincided with the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley during the rule of Darius I from about 517/516 BCE. Rulers Bimbisara Bimbisara reigned from 545 to 493 BCE. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bimbisara
Bimbisāra (in Buddhist tradition) or Shrenika () and Seniya () in the Jain histories (c. 558 – c. 491 BCE or during the late 5th century BCE) was a King of Magadha (V. K. Agnihotri (ed.), ''Indian History''. Allied Publishers, New Delhi 262010p. 166f. or c. 400 BCE) and belonged to the Haryanka dynasty.Peter N. Stearns (2001), ''The Encyclopedia of World History''. Houghton Mifflin, p. 76 ff. . He was the son of Bhattiya. His expansion of the kingdom, especially his annexation of the kingdom of Anga to the east, is considered to have laid the foundations for the later expansion of the Mauryan Empire. According to Jain Tradition, he is said to be the first Tirthankara (''will be named as Padmanabha / Mahapadma'') out of 24th Tirthankara of the future cosmic age. He frequently visited Samavasarana of Lord Mahavira seeking answers to his queries. According to Buddhist Tradition, he is also known for his cultural achievements and was a great friend and protector of the Budd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udayin
Udayin (c. 460-444 BCE) also known as Udayabhadra was a king of Magadha in ancient India. According to the Buddhist and Jain accounts, he was the son and successor of the Haryanka king Ajatashatru. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at the confluence of two rivers, the Son and the Ganges. He shifted his capital from Rajgriha to Patliputra due to the latter's central location in the empire. Ancestry According to the Buddhist accounts, the successors of the Magadha ruler Bimbisara were Ajatashatru, Udayabhadda (Udayin), Anuruddha, Munda and Nagadasaka. The Jain tradition mentions Udayin as the son and successor of Ajatashatru. Kings Bimbisara (c. 558–491 BCE), Ajatashatru (c. 492–460 BCE), and Udayin (c. 460–440 BCE) of the Haryanka dynasty were patrons of Jainism. However, the Puranas name the successors of Bimbisara as Ajatashatru, Darshaka, Udayin, Nandivardhana and Mahanandin. The ''Matsya Purana'' names Vamsaka as the successor of Ajatashatru. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka." However, the earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Settled life, which involves the transition from foraging to farming and pastoralism, began in South Asia around 7000 BCE. At the site of Mehrgarh presence can be documented of the domestication of wheat and barley, rapidly followed by that of goats, sheep, and cattle. By 4500 BCE, settled life had spread more widely, and began to gradually evolve into the Indus Valley civilisation, an early civilisation of the Old World, which was contemporaneous with Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia. This civilisation flourished between 2500 BCE and 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
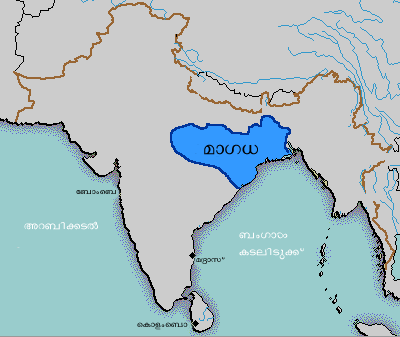
Magadha
Magadha was a region and one of the sixteen sa, script=Latn, Mahajanapadas, label=none, lit=Great Kingdoms of the Second Urbanization (600–200 BCE) in what is now south Bihar (before expansion) at the eastern Ganges Plain. Magadha was ruled by Brihadratha dynasty, Pradyota dynasty (682–544 BCE), Haryanka dynasty (544–413 BCE), the Shaishunaga dynasty (413–345 BCE) and the Mauryan dynasty by the end of it. Villages had their own assemblies under their local chiefs called ''Gramakas''. Their administrations were divided into executive, judicial, and military functions. Magadha played an important role in the development of Jainism and Buddhism. It was succeeded by four of northern India's greatest empires, the Nanda Empire (c. 345–322 BCE), Maurya Empire (c. 322–185 BCE), Shunga Empire (c. 185–78 BCE) and Gupta Empire (c. 319–550 CE). The Pala Empire also ruled over Magadha and maintained a royal camp in Pataliputra. The Pithipatis of Bodh Gaya referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ajatashatru
Ajatasattu (Pāli ) or Ajatashatru (Sanskrit ) in Buddhist tradition, or Kunika () and Kuniya () in the Jain histories, (c. 492 to 460 BCE or early 5th century BCE) was one of the most important kings of the Haryanka dynasty of Magadha in East India. He was the son of King Bimbisara and was a contemporary of both Mahavira and Gautama Buddha. He forcefully took over the kingdom of Magadha from his father and imprisoned him. He fought a war against the Vajjika League, led by the Licchavis, and conquered the republic of Vaishali. The city of Pataliputra was formed by fortification of a village by Ajatashatru. Ajatashatru followed policies of conquest and expansion. He defeated his neighbours including the king of Kosala; his brothers, at odds with him, went to Kashi, which had been given to Bimbisara as dowry and led to a war between Magadha and Kosala. Ajatashatru occupied Kashi and captured the smaller kingdoms. Magadha under Ajatashatru became the most powerful kingdom in Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nāgadāsaka
Nāgadāsaka was the last ruler of Haryanka dynasty from 437 to 413 BCE and son of Munda. He murdered his father and ruled for twenty-four years. The people deposed him and made Shishunaga king in his place. Shishunaga was the founder of Shishunaga dynasty. According to Buddhist tradition, he was the last of Haryanka rulers who was replaced by his '' amatya'' (minister), Shishunaga Shishunaga ( IAST: Śiśunāga, or Shusunaga) (c. 413 – 395 BCE) was the founder of the Shishunaga dynasty of the Magadha Empire in the present day northern India. Initially, he was an ''amatya'' (official) of the Magadha empire under the Hary .... References Citations Sources * {{DEFAULTSORT:Nagadasaka 5th-century BC Indian monarchs Kings of Magadha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shishunaga Dynasty
The Shaishunaga dynasty (IAST: Śaiśunāga, literally "of Shishunaga") is the fourth ruling dynasty of Magadha, an empire of ancient India. According to the Hindu ''Puranas'', this dynasty was the second ruling dynasty of Magadha, succeeding Nagadashaka of the Haryanka dynasty. Shishunaga, the founder of the dynasty, was initially an ''amatya'' or "minister" of the last Haryanka dynasty ruler Nāgadāsaka and ascended to the throne after a popular rebellion in c. 413 BCE. The capital of this dynasty initially was Vaishali; but later shifted to Pataliputra, near the present day Patna, during the reign of Kalashoka. According to tradition, Kalashoka was succeeded by his ten sons. This dynasty was succeeded by the Nanda Empire in c. 345 BCE. Establishment According to Buddhist tradition, Shishunaga was ''amatya'' in Haryanka kingdom, who revolted and became the king. Rulers Shishunaga Shishunaga founded his dynasty in 413 BCE with its capital in Rajgir and later Pataliputra (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliputra at the confluence of two rivers, the Son River, Son and the Ganges. He shifted his capital from Rajgir, Rajgriha to Patliputra due to the latter's central location in the empire. It became the capital of major powers in ancient India, such as the Shaishunaga dynasty, Shishunaga Empire (c. 413–345 BCE), Nanda Empire (c. 460 or 420–325 BCE), the Maurya Empire (c. 320–180 BCE), the Gupta Empire (c. 320–550 CE), and the Pala Empire (c. 750–1200 CE). During the Maurya period (see below), it became one of the List of largest cities throughout history, largest cities in the world. As per the Greek diplomat, traveler and historian Megasthenes, during the Mauryan Empire (c. 320–180 BCE) it was among the first cities in the world to have a high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pradyota Dynasty
Pradyota dynasty, also called ''Prthivim Bhoksyanti'' (lit. enjoying the earth), is an ancient Indian dynasty, which ruled over Avanti and Magadha, though most of the Puranas ''(except a manuscript of the Brahmanda Purana, preserved in the University of Dhaka)'' say that this dynasty succeeded the Brihadratha dynasty in Magadha. The dynasty ruled for 138 years. ''Pradyota'' is the founder of the dynasty and ruler of Avanti & Magadha. Pradyota dynasty was Second dynasty who ruled Magadha. Pradyota was son of Pulika (''Punika''), who is said to have killed Ripunjaya of Brihadratha dynasty at Rajagriha, to make his son the king. Pradyota dynasty was preceded by Brihadratha dynasty and succeeded by Haryanka dynasty of Magadha. Pradyota is said to have ruled for 23 years. Palaka's reign started in (659–635 BCE) according to ''Visarasreni'' of Merutunga. He was the son of Chanda Pradyota of Magadha. He is said to have conquered Kosambi. Palaka is said to have ruled for 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patna
Patna ( ), historically known as Pataliputra, is the capital and largest city of the state of Bihar in India. According to the United Nations, as of 2018, Patna had a population of 2.35 million, making it the 19th largest city in India. Covering and over 2.5 million people, its urban agglomeration is the 18th largest in India. Patna serves as the seat of Patna High Court. The Buddhist, Hindu and Jain pilgrimage centres of Vaishali, Rajgir, Nalanda, Bodh Gaya and Pawapuri are nearby and Patna City is a sacred city for Sikhs as the tenth Sikh Guru, Guru Gobind Singh was born here. The modern city of Patna is mainly on the southern bank of the river Ganges. The city also straddles the rivers Sone, Gandak and Punpun. The city is approximately in length and wide. One of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world, Patna was founded in 490 BCE by the king of Magadha. Ancient Patna, known as Pataliputra, was the capital of the Magadh Empire through Haryanka, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajagriha
Rajgir, meaning "The City of Kings," is a historic town in the district of Nalanda in Bihar, India. As the ancient seat and capital of the Haryanka dynasty, the Pradyota dynasty, the Brihadratha dynasty and the Mauryan Empire, as well as the dwelling ground of such historical figures as The Buddha and The Mahavira, the city holds a place of prominence in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain scriptures. As of 2011, the population of the town was reported to be 71,459 while the population in the community development block was about 88,500. Rajgir was the first capital of the ancient kingdom of Magadha, a state that would eventually evolve into the Mauryan Empire. It finds mention in India's renowned literary epic, the Mahabharata, through its king Jarasandha. The town's date of origin is unknown, although ceramics dating to about 1000 BC have been found in the city. The 2,500-year-old cyclopean wall is also located in the region. The town is also notable in Jainism and Buddhism. It w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajgir
Rajgir, meaning "The City of Kings," is a historic town in the district of Nalanda in Bihar, India. As the ancient seat and capital of the Haryanka dynasty, the Pradyota dynasty, the Brihadratha dynasty and the Mauryan Empire, as well as the dwelling ground of such historical figures as The Buddha and The Mahavira, the city holds a place of prominence in Hindu, Buddhist and Jain scriptures. As of 2011, the population of the town was reported to be 71,459 while the population in the community development block was about 88,500. Rajgir was the first capital of the ancient kingdom of Magadha, a state that would eventually evolve into the Mauryan Empire. It finds mention in India's renowned literary epic, the Mahabharata, through its king Jarasandha. The town's date of origin is unknown, although ceramics dating to about 1000 BC have been found in the city. The 2,500-year-old cyclopean wall is also located in the region. The town is also notable in Jainism and Buddhism. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)
.png)
.jpg)