|
Gerald Lankester Harding
Gerald Lankester Harding (8 December 1901 – 11 February 1979) was a British archaeologist who was the director of the Department of Antiquities of Jordan from 1936 to 1956. His tenure spanned the period in which the Dead Sea Scrolls were discovered and brought to public awareness. Without his efforts many of the scrolls might have disappeared into private collections never to be seen again. Life Harding was born in Tientsin, North China in 1901, but spent his childhood from age two to 13 in Singapore. He returned to the UK with his parents in 1913, but his father was killed in World War I, and Harding earned his living in a number of jobs from the ages of 16 to 25. During this time, he became fascinated by Egyptian hieroglyphics and eventually joined the evening classes run by the distinguished Egyptologist Dr Margaret Murray. Recognising his brilliance, she encouraged him to write to Sir Flinders Petrie and apply to go on one of his excavations. In 1926, Petrie was excavating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tientsin
Tianjin (; ; Mandarin: ), alternately romanized as Tientsin (), is a municipality and a coastal metropolis in Northern China on the shore of the Bohai Sea. It is one of the nine national central cities in Mainland China, with a total population of 13,866,009 inhabitants during the 2020 Chinese census. Its built-up (''or metro'') area, made up of 12 central districts (all but Baodi, Jizhou, Jinghai and Ninghe), was home to 11,165,706 inhabitants and is also the world's 29th-largest agglomeration (between Chengdu and Rio de Janeiro) and 11th- most populous city proper. It is governed as one of the four municipalities under the direct administration of Chinese central government and is thus under direct administration of the State Council. Tianjin borders Hebei Province and Beijing Municipality, bounded to the east by the Bohai Gulf portion of the Yellow Sea. Part of the Bohai Economic Rim, it is the largest coastal city in Northern China and part of the Jing-Jin-Ji megap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasan Awad
Hasan ʿAwad al-Qatshan (born 1912–13) was a Bedouin archaeologist associated with the Jordanian Department of Antiquities. Working with his partner Gerald Lankester Harding and other western archaeologists, he played a role in a number of major discoveries, including those of the Lachish letters and the Dead Sea Scrolls. Archaeological career ʿAwad was born to the Negev Bedouin Hanajira of Beersheba. Though not formally educated in archaeology, he began his training as a teenager, on Flinders Petrie's excavations at Tell Jemmeh (1926–1927). He went on to acquire a reputation as a skilled excavator and the "best archaeological foreman in Jordan", working with James Leslie Starkey at Tell ed-Duweir (Lachish, 1932–1939), George Ernest Wright at Tell Balata (Shechem, 1956–1973), the American Schools of Oriental Research at Dhiban (1950–1953), Henri de Contenson at Tell esh-Shuna (1953), and Diana Kirkbride at Petra (1955–1956). Harding credited ʿAwad with the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Horsfield
George Horsfield (1882-1956) was a British architect and archaeologist. He was Chief Inspector of Antiquities in Transjordan in 1928–36. Horsfield began the initial clearance and conservation of Jerash in 1925, and excavated at Petra with his future wife, Agnes Conway in 1929. Personal life George Horsfield was born in Meanwood, Leeds, Yorkshire, England on 19 April 1882 to Richard Horsfield and his wife Sarah. He attended Leeds Grammar School and moved to London to train in architecture in the office of noted Gothic architect George Frederick Bodley. Horsfield then moved to the United States to work for the architectural firm Cram, Goodhue & Ferguson. Horsfield returned to the UK in 1914 at the outbreak of war and volunteered for service in the Royal Naval Brigade. He saw action in the Gallipoli campaign in 1915, after which he was commissioned into the 7th West Yorkshire Regiment and took part in the Battle of the Somme in 1916. After contracting trench fever he was po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Further complicating the issue was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Inge
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch and German, have retained the word in two separate senses. In the particular case of Dutch, ''Karel'' refers to the given name, whereas the noun ''kerel'' means "a bloke, fellow, man". Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its depre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleo-Hebrew Alphabet
The Paleo-Hebrew script ( he, הכתב העברי הקדום), also Palaeo-Hebrew, Proto-Hebrew or Old Hebrew, is the writing system found in Canaanite inscriptions from the region of biblical Israel and Judah. It is considered to be the script used to record the original texts of the Hebrew Bible due to its similarity to the Samaritan script, as the Talmud stated that the Hebrew ancient script was still used by the Samaritans. The Talmud described it as the "Libona'a script" ( he, לִיבּוֹנָאָה ''Lībōnāʾā''), translated by some as "Lebanon script". Use of the term "Paleo-Hebrew alphabet" is due to a 1954 suggestion by Solomon Birnbaum, who argued that " apply the term Phoenician to the script of the Hebrews is hardly suitable". The first Paleo-Hebrew inscription identified in modern times was the '' Shebna inscription'', found in 1870, and then referred to as "two large ancient Hebrew inscriptions in Phoenician letters".Clermont-Ganneau, 1899Archaeological Resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lachish Letters
The Lachish Letters or ''Lachish Ostraca'', sometimes called ''Hoshaiah Letters'', are a series of letters written in carbon ink containing Canaanite inscriptions in Ancient Hebrew on clay ostraca. The letters were discovered at the excavations at Lachish (Tell ed-Duweir). The ostraca were discovered by James Leslie Starkey in January–February 1935, during the third campaign of the Wellcome excavations. They were published in 1938 by Harry Torczyner (name later changed to Naftali Herz Tur-Sinai) and have been much studied since then. Seventeen of them are currently located in the British Museum in London, a smaller number (including Letter 6) are on permanent display at the Rockefeller Museum in East Jerusalem. The primary inscriptions are known as KAI 192–199. Interpretation The individual ostraca probably come from the same broken clay pot and were most likely written in a short period of time. They were written to Yaush (or Ya'osh), possibly the commanding officer at Lac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Lachish
Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. The current '' tell'' (ruin) by that name, known as Tel Lachish ( he, תל לכיש) or Tell ed-Duweir (),, has been identified with the biblical Lachish. Today, it is an Israeli national park operated and maintained by the Israel Nature and Parks Authority. The park was established on lands of the depopulated Palestinian village of Qobebet Ibn ‘Awwad which was north of the Tel. It lies near the present-day moshav of Lakhish. Lachish was first mentioned in the Amarna letters. In the Book of Joshua, Lachish is mentioned as one of the cities destroyed by the Israelites for joining the league against the Gibeonites (). The territory was later assigned to the tribe of Judah () and became part of the United Kingdom of Israel. Following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Ed-Duweir
Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. The current '' tell'' (ruin) by that name, known as Tel Lachish ( he, תל לכיש) or Tell ed-Duweir (),, has been identified with the biblical Lachish. Today, it is an Israeli national park operated and maintained by the Israel Nature and Parks Authority. The park was established on lands of the depopulated Palestinian village of Qobebet Ibn ‘Awwad which was north of the Tel. It lies near the present-day moshav of Lakhish. Lachish was first mentioned in the Amarna letters. In the Book of Joshua, Lachish is mentioned as one of the cities destroyed by the Israelites for joining the league against the Gibeonites (). The territory was later assigned to the tribe of Judah () and became part of the United Kingdom of Israel. Following the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tall Al-Ajjul
Tall al-Ajjul or Tell el-'Ajul is an archaeological mound or '' tell'' in the Gaza Strip. The fortified city excavated at the site dates as far back as ca. 2000-1800 BCE and was inhabited during the Bronze Age. It is located at the mouth of Wadi Ghazzah just south of the town of Gaza. History Bronze Age Archaeologists have excavated remains dated mainly to the Middle and Late Bronze Age. Middle Bronze In the MBII, Tell el-Ajjul was an important city in the Southern Levant. In the MBIIB, Tell el-Ajjul had the largest number of Egyptian Second Intermediate Period imports. Late Bronze Large quantities of pumice were deposited during the Late Bronze Age, which may have been caused by the Thera (Santorini) volcanic eruption. If proven correct, this would offer a good correlation and dating tool. Treaty of Tell Ajul (1229) The Sixth Crusade came to an end with the so-called Treaty of Jaffa and Tell Ajul. These were in fact two different treaties, the first being the one sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
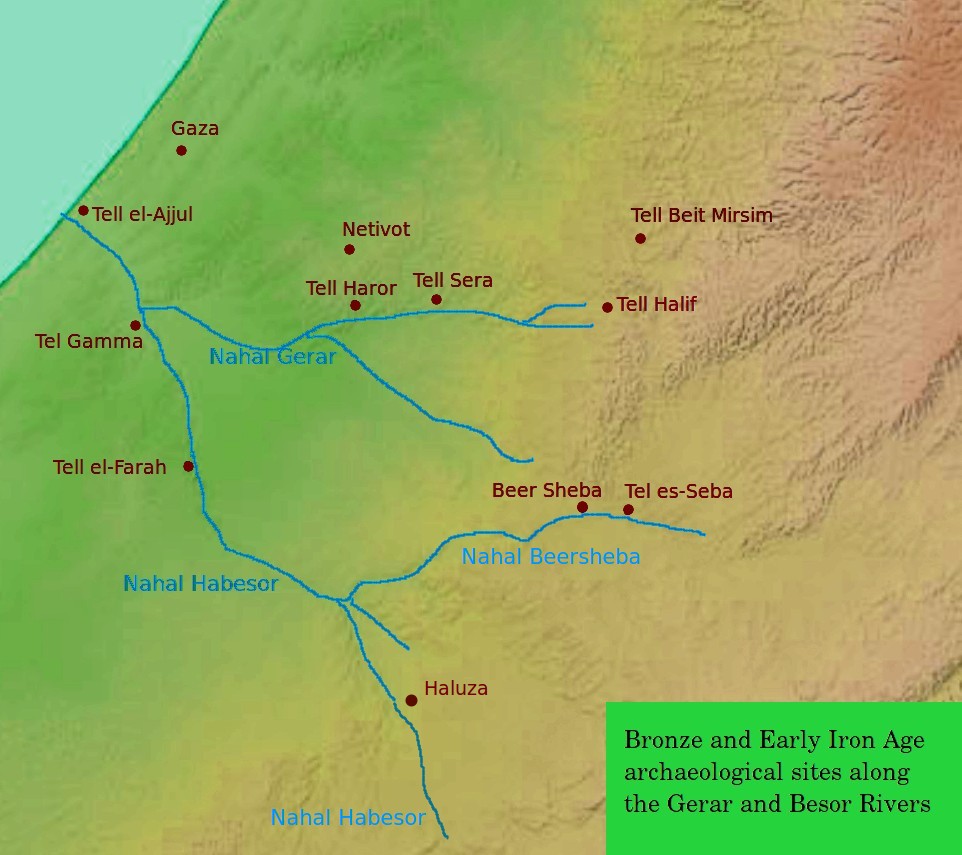
HaBesor Stream
The Besor ( he, נחל הבשור, ''Nahal HaBesor'') is a wadi in southern Israel. The stream begins at Mount Boker (near Sde Boker), and spills into the Mediterranean Sea near Al-Zahra in the Gaza Strip, where it is called Wadi Gaza ( ar, وادي غزة, Wadi Ghazzeh), also spelled Wadi Ghazza or Wadi 'Azza. Further upstream it is marked as Wadi esh-Shallaleh on the 1878 Survey of Western Palestine map. There are several important archaeological sites located in this area. The stream is the largest in the northern Negev, and together with its largest tributaries, the Nahal Gerar, and the Beersheba stream, reaches as far east into the desert as Sde Boker, Yeruham, Dimona and Arad/ Tel Arad. The Gaza section of the Coastal Aquifer is the only significant source of water in the Gaza Strip. The Wadi Gaza runs through a wetland, the Gaza Valley, and as of 2012 it is used as a wastewater dump. History In the Old Testament Besor was a ravine or brook in the extreme south-west of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)