|
Green Standards
The Green Standard Army (; Manchu: ''niowanggiyan turun i kūwaran'') was the name of a category of military units under the control of Qing dynasty in China. It was made up mostly of ethnic Han soldiers and operated concurrently with the Manchu-Mongol-Han Eight Banner armies. In areas with a high concentration of Hui people, Muslims served as soldiers in the Green Standard Army. After the Qing consolidated control over China, the Green Standard Army was primarily used as a police force. History Origins The original Green Standard troops were the soldiers of the Ming commanders who surrendered to the Qing in 1644 and after. Their troops enlisted voluntarily and for long terms of service; they usually came from the socially disadvantaged, and remained segregated from Chinese society, partly because of the latter's deep anti-military bias during the late Ming period, and partly because they were paid too poorly and irregularly to marry and support a family. The Qing relied on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Ming Dynasty
The transition from Ming to Qing, alternatively known as Ming–Qing transition or the Manchu conquest of China, from 1618 to 1683, saw the transition between two major dynasties in Chinese history. It was a decades-long conflict between the emerging Qing dynasty, the incumbent Ming dynasty, and several smaller factions (like the Shun dynasty and Xi dynasty). It ended with the consolidation of Qing rule, and the fall of the Ming and several other factions. Overview The transition from the Ming to Qing was a decades-long period of conflict between: # the Qing dynasty, established by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in contemporary Northeast China; # the Ming dynasty, the incumbent dynasty led by the Zhu clan; # and various other rebel powers in China, such as the short-lived Xi dynasty led by Zhang Xianzhong and the short-lived Shun dynasty led by Li Zicheng. Leading up to the Qing, in 1618, the Later Jin khan Nurhaci commissioned a document entitled the Seven Grievances, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gendarmerie
Wrong info! --> A gendarmerie () is a military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to " men-at-arms" (literally, "armed people"). In France and some Francophone nations, the gendarmerie is a branch of the armed forces that is responsible for internal security in parts of the territory (primarily in rural areas and small towns in the case of France), with additional duties as military police for the armed forces. It was introduced to several other Western European countries during the Napoleonic conquests. In the mid-twentieth century, a number of former French mandates and colonial possessions (such as Lebanon, Syria, the Ivory Coast and the Republic of the Congo) adopted a gendarmerie after independence. A similar concept exists in Eastern Europe in the form of Internal Troops, which are present in many countries of the former Soviet Union and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaanxi
Shaanxi (alternatively Shensi, see #Name, § Name) is a landlocked Provinces of China, province of China. Officially part of Northwest China, it borders the province-level divisions of Shanxi (NE, E), Henan (E), Hubei (SE), Chongqing (S), Sichuan (SW), Gansu (W), Ningxia (NW) and Inner Mongolia (N). Shaanxi covers an area of over with about 37 million people, the 16th highest in China. Xi'an – which includes the sites of the former Capitals of China, Chinese capitals Fenghao and Chang'an – is the Xi'an, provincial capital as well as the largest city in Northwest China and also one of the oldest cities in China and the oldest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals, being the capital for the Western Zhou, Western Han, Sima Jin, Jin, Sui dynasty, Sui and Tang dynasty, Tang List of Chinese dynasties, dynasties. Xianyang, which served as the Qin dynasty capital, is just north across Wei River. The other Prefectures of China, prefecture-level pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of the Sichuan Basin and the easternmost part of the Tibetan Plateau between the Jinsha River on the west, the Daba Mountains in the north and the Yungui Plateau to the south. Sichuan's capital city is Chengdu. The population of Sichuan stands at 83 million. Sichuan neighbors Qinghai to the northwest, Gansu to the north, Shaanxi to the northeast, Chongqing to the east, Guizhou to the southeast, Yunnan to the south, and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the west. In antiquity, Sichuan was the home of the ancient states of Ba and Shu. Their conquest by Qin strengthened it and paved the way for Qin Shi Huang's unification of China under the Qin dynasty. During the Three Kingdoms era, Liu Bei's state of Shu was based in Sichuan. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Yong (Qing Dynasty)
Zhang Yong may refer to: * Jack Yung Chang (Zhang Yong) (1911—1939), Chinese historian of mathematics, the second son of Zhang Shizhao * Zhang Yong (politician) (born 1953), former director of the China Food and Drug Administration * Zhang Yong (agronomist) (born 1956), Chinese agronomist * Zhang Yong (restaurateur), Chinese billionaire restaurateur, founder of Haidilao * Daniel Zhang or Zhang Yong (born 1972), CEO of Alibaba Group * Zhang Yong (real estate developer), founder of Xinyuan Real Estate * Zhang Yong (snooker player) (born 1995), Chinese snooker player {{hndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Jinbao
Wang may refer to: Names * Wang (surname) (王), a common Chinese surname * Wāng (汪), a less common Chinese surname * Titles in Chinese nobility * A title in Korean nobility * A title in Mongolian nobility Places * Wang River in Thailand * Wang Township, Minnesota, a township in the United States * Wang, Bavaria, a town in the district of Freising, Bavaria, Germany * Wang, Austria, a town in the district of Scheibbs in Lower Austria * An abbreviation for the town of Wangaratta, Australia * Wang Theatre, in Boston, Massacheussetts * Charles B. Wang Center, an Asian American center at Stony Brook University Other * Wang (Tibetan Buddhism), a form of empowerment or initiation * Wang tile, in mathematics, are a class of formal systems * ''Wang'' (musical), an 1891 New York musical * Wang Film Productions, Taiwanese-American animation studios * Wang Laboratories, an American computer company founded by Dr. An Wang * WWNG, a radio station (1330 AM) licensed to serve Havelock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Liangdong and Cong (jade)
Zhang may refer to: Chinese culture, etc. * Zhang (surname) (張/张), common Chinese surname ** Zhang (surname 章), a rarer Chinese surname * Zhang County (漳县), of Dingxi, Gansu * Zhang River (漳河), a river flowing mainly in Henan * ''Zhang'' (unit) (丈), a traditional Chinese unit of length equal to 10 ''chi'' (3–3.7 m) * Zhang Zetian, Chinese billionaire * 璋, a type of shaped stone or jade object in ancient Chinese culture thought to hold great value and protective properties; see also Bi (jade) The ''bi'' is a type of circular ancient Chinese jade artifact. The earliest ''bi'' were produced in the Neolithic period, particularly by the Liangzhu culture ( 3400– 2250 BCE). Other * Zhang, the proper name of the star Upsilon1 Hydrae, Upsilon¹ HydraeSee also * Zang (other) {{disambiguation, geo ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Fuchen
Wang Fuchen () (d. 1681) was a participant in the Revolt of the Three Feudatories during the Qing dynasty against the Kangxi Emperor. Wang was born in Datong, Shanxi Province, he was born to a poor family and grew up to be a bandit. His original surname was Li, nicknamed Horse-Sparrowhawk (馬鷂子) by the Manchu soldiers. Originally resisting the Manchu conquest of the Ming dynasty, ancient historians left behind records stating that Wang Fuchen was a handsome, tall and strong man with pale face, and thick eyebrows that resembled reclining silkworms. He was famous for his valour in battle and was known to the Manchus as a tough opponent, his presence was sometimes discouraging enough for the Manchu soldiers to retreat. He was highly regarded by Shunzhi Emperor and was won over to the Regent Dorgon. He assisted the former Ming dynasty generals Hong Chengchou and Wu Sangui in suppressing the Ming remnants of the Southern Ming. He followed Wu to Burma to capture and execute Zhu Youlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangxi Emperor
The Kangxi Emperor (4 May 1654– 20 December 1722), also known by his temple name Emperor Shengzu of Qing, born Xuanye, was the third emperor of the Qing dynasty, and the second Qing emperor to rule over China proper, reigning from 1661 to 1722. The Kangxi Emperor's reign of 61 years makes him the longest-reigning emperor in Chinese history (although his grandson, the Qianlong Emperor, had the longest period of ''de facto'' power, ascending as an adult and maintaining effective power until his death) and one of the longest-reigning rulers in history. However, since he ascended the throne at the age of seven, actual power was held for six years by four regents and his grandmother, the Grand Empress Dowager Xiaozhuang. The Kangxi Emperor is considered one of China's greatest emperors. He suppressed the Revolt of the Three Feudatories, forced the Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan and assorted Mongol rebels in the North and Northwest to submit to Qing rule, and blocked Tsarist R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Sangui
Wu Sangui (; 8 June 1612 – 2 October 1678), courtesy name Changbai () or Changbo (), was a notorious Ming Dynasty military officer who played a key role in the fall of the Ming dynasty and the founding of the Qing dynasty in China. In Chinese folklore, Wu Sangui is regarded as a disreputable Hanjian, Han Chinese traitor who played a pivotal role in several historical events, including the Battle of Shanhai Pass, Transition from Ming to Qing, Manchu invasion of China, the suppression of Southern Ming resistances and the execution of the Zhu Youlang, Yongli Emperor, and eventually double-crossed both of his masters, the Ming and the Qing dynasties. In 1644, after learning of the death of his father, the Ming general Wu Xiang (Ming dynasty), Wu Xiang in Beijing, Wu Sangui turned to the Manchu invaders (the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin) and offered up the gate of Shanhaiguan, allowing the Manchus to enter China and establish the Qing dynasty in Beijing. For his aid, the Qing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
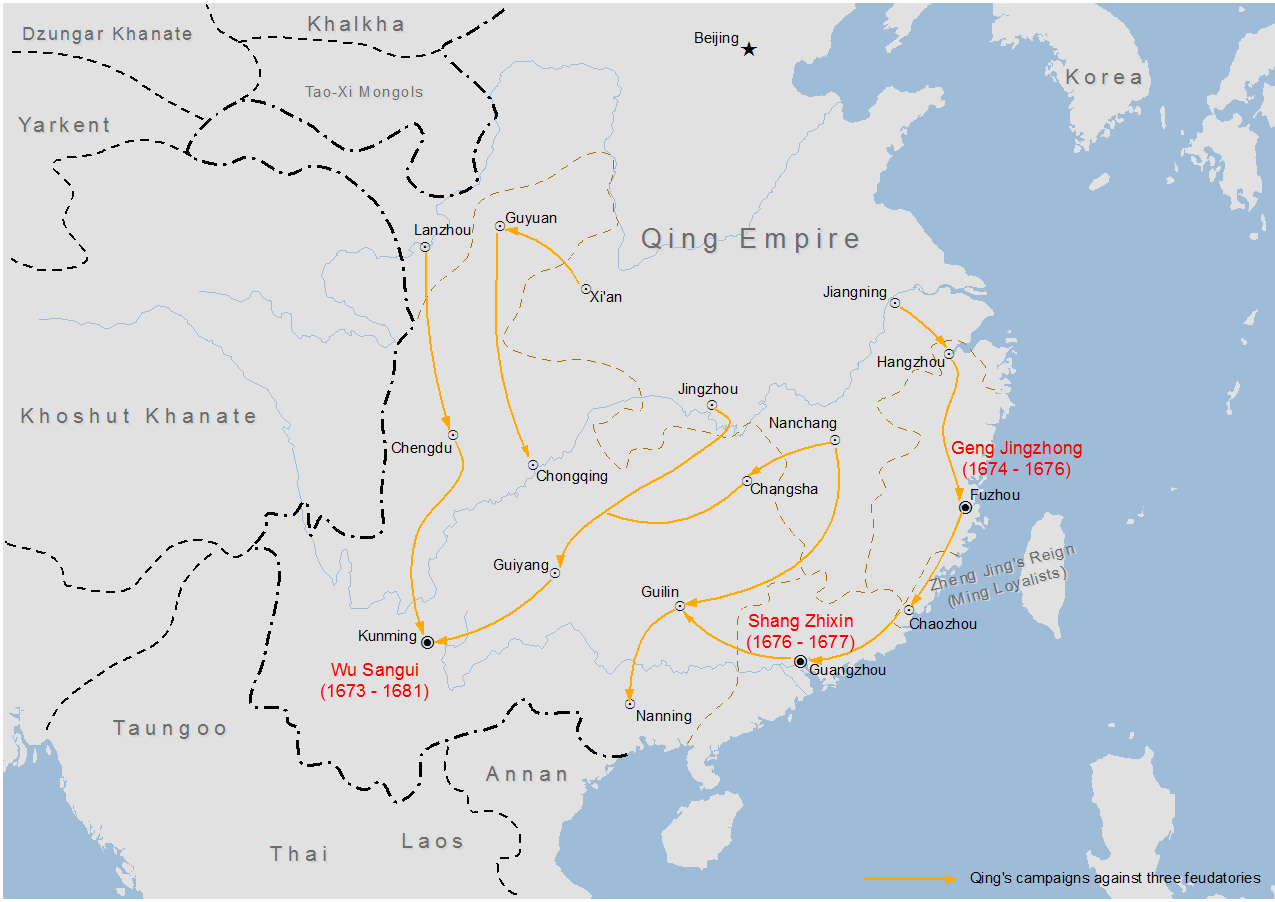
Revolt Of The Three Feudatories
The Revolt of the Three Feudatories, () also known as the Rebellion of Wu Sangui, was a rebellion in China lasting from 1673 to 1681, during the early reign of the Kangxi Emperor (r. 1661–1722) of the Qing dynasty (1644–1912). The revolt was led by the three lords of the fiefdoms in Yunnan, Guangdong and Fujian provinces against the Qing central government. These hereditary titles had been given to prominent Han Chinese defectors who had helped the Manchu conquer China during the transition from Ming to Qing. The feudatories were supported by Zheng Jing's Kingdom of Tungning in Taiwan, which sent forces to invade Mainland China. Additionally, minor Han military figures, such as Wang Fuchen and the Chahar Mongols, also revolted against Qing rule. After the last remaining Han resistance had been put down, the former princely titles were abolished. Background In the early years of the Qing Dynasty, during the reign of the Shunzhi Emperor, central government authority was not st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |