|
Gold Nanorods
In nanotechnology, nanorods are one morphology of nanoscale objects. Each of their dimensions range from 1–100 nm. They may be synthesized from metals or semiconducting materials. Standard aspect ratios (length divided by width) are 3-5. Nanorods are produced by direct chemical synthesis. A combination of ligands act as shape control agents and bond to different facets of the nanorod with different strengths. This allows different faces of the nanorod to grow at different rates, producing an elongated object. One potential application of nanorods is in display technologies, because the reflectivity of the rods can be changed by changing their orientation with an applied electric field. Another application is for microelectromechanical systems (MEMS). Nanorods, along with other noble metal nanoparticles, also function as theragnostic agents. Nanorods absorb in the near IR, and generate heat when excited with IR light. This property has led to the use of nanorods as can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
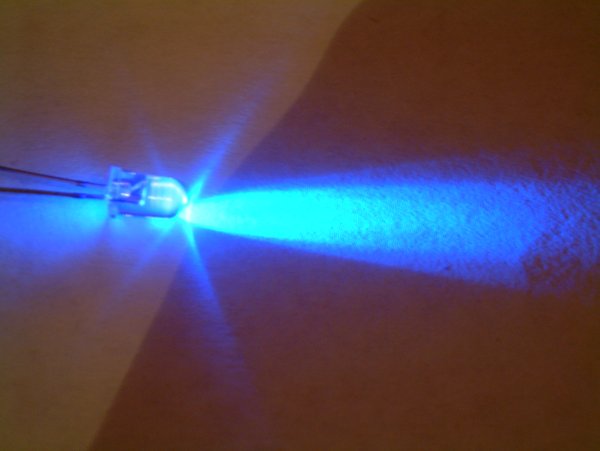
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surfactant
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsion#Emulsifiers , emulsifiers, foaming agents, or dispersants. The word "surfactant" is a Blend word, blend of ''surface-active agent'', coined . Agents that increase surface tension are "surface active" in the literal sense but are not called surfactants as their effect is opposite to the common meaning. A common example of surface tension increase is salting out: by adding an inorganic salt to an aqueous solution of a weakly polar substance, the substance will precipitate. The substance may itself be a surfactant – this is one of the reasons why many surfactants are ineffective in sea water. Composition and structure Surfactants are usually organic compounds that are amphiphilic, meaning each molecule contains both a hydrophilic "water-seeking" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide
Cetrimonium bromide ( C16H33)N(CH3)3r; cetyltrimethylammonium bromide; hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide; CTAB) is a quaternary ammonium surfactant. It is one of the components of the topical antiseptic cetrimide. The cetrimonium (hexadecyltrimethylammonium) cation is an effective antiseptic agent against bacteria and fungi. It is also one of the main components of some buffers for the extraction of DNA. It has been widely used in synthesis of gold nanoparticles (''e.g.'', spheres, rods, bipyramids), mesoporous silica nanoparticles (''e.g.'', MCM-41), and hair conditioning products. The closely related compounds cetrimonium chloride and cetrimonium stearate are also used as topical antiseptics and may be found in many household products such as shampoos and cosmetics. CTAB, due to its relatively high cost, is typically only used in select cosmetics. As with most surfactants, CTAB forms micelles in aqueous solutions. At 303 K (30 °C) it forms micelles with aggregation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascorbic Acid
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) and wrinkles on the face. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Most animals are able to synthesize their own vitamin C. However, apes (including humans) and monkeys (but not all primates), most bats, some rodents, and certain other animals must acquire it from dietary sources. There is some evidence that regular use of supplements may reduce the duration of the common cold, but it does not appear to prevent infection. It is unclear whether s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QD-OLED
A quantum dot display is a display device that uses quantum dots (QD), semiconductor nanocrystals which can produce pure monochromatic red, green, and blue light. ''Photo-emissive'' quantum dot particles are used in LCD backlights and/or display color filters. Quantum dots are excited by the blue light from the display panel to emit pure basic colors, which reduces light losses and color crosstalk in color filters, improving display brightness and color gamut. Light travels through QD layer film and traditional RGB filters made from color pigments, or through QD filters with red/green QD color converters and blue passthrough. Although the QD color filter technology is primarily used in LED-backlit LCDs, it is applicable to other display technologies which use color filters, such as blue/UV AMOLED/ QNED/ MicroLED display panels. LED-backlit LCDs are the main application of photo-emissive quantum dots, though blue OLED panels with QD color filters are being researched. ''Electro- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InGaN
Indium gallium nitride (InGaN, ) is a semiconductor material made of a mix of gallium nitride (GaN) and indium nitride (InN). It is a ternary group III/group V direct bandgap semiconductor. Its bandgap can be tuned by varying the amount of indium in the alloy. InxGa1−xN has a direct bandgap span from the infrared (0.69 eV) for InN to the ultraviolet (3.4 eV) of GaN. The ratio of In/Ga is usually between 0.02/0.98 and 0.3/0.7. Applications LEDs Indium gallium nitride is the light-emitting layer in modern blue and green LEDs and often grown on a GaN buffer on a transparent substrate as, e.g. sapphire or silicon carbide. It has a high heat capacity and its sensitivity to ionizing radiation is low (like other group III nitrides), making it also a potentially suitable material for solar photovoltaic devices, specifically for arrays for satellites. It is theoretically predicted that spinodal decomposition of indium nitride should occur for compositions between 15% and 85%, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Oxidation
In microfabrication, thermal oxidation is a way to produce a thin layer of oxide (usually silicon dioxide) on the surface of a wafer. The technique forces an oxidizing agent to diffuse into the wafer at high temperature and react with it. The rate of oxide growth is often predicted by the Deal–Grove model. Thermal oxidation may be applied to different materials, but most commonly involves the oxidation of silicon substrates to produce silicon dioxide. The chemical reaction Thermal oxidation of silicon is usually performed at a temperature between 800 and 1200 °C, resulting in so called High Temperature Oxide layer (HTO). It may use either water vapor (usually UHP steam) or molecular oxygen as the oxidant; it is consequently called either ''wet'' or ''dry'' oxidation. The reaction is one of the following: :\rm Si + 2H_2O \rightarrow SiO_2 + 2H_ :\rm Si + O_2 \rightarrow SiO_2 \, The oxidizing ambient may also contain several percent of hydrochloric acid (HCl). The chlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOCVD
Metalorganic vapour-phase epitaxy (MOVPE), also known as organometallic vapour-phase epitaxy (OMVPE) or metalorganic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD), is a chemical vapour deposition method used to produce single- or polycrystalline thin films. It is a process for growing crystalline layers to create complex semiconductor multilayer structures. In contrast to molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE), the growth of crystals is by chemical reaction and not physical deposition. This takes place not in vacuum, but from the gas phase at moderate pressures (10 to 760 Torr). As such, this technique is preferred for the formation of devices incorporating thermodynamically metastable alloys, and it has become a major process in the manufacture of optoelectronics, such as Light-emitting diodes. It was invented in 1968 at North American Aviation (later Rockwell International) Science Center by Harold M. Manasevit. Basic principles In MOCVD ultrapure precursor gases are injected into a reactor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |