|
Gastrocotylidae
Gastrocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans.WoRMS (2019). Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119243 on 2019-02-15 All the species in this family are parasitic on fish. Systematics The gastrocotylids are known by their rather very diffuse distribution, and a marqued preference for scombroid fishes and carangids. The Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943 was erected to separate '' Gastrocotyle'' and its allies., named and described by reference to a diagram of the clamp type alone Sproston agreed on the importance of the difference in clamp structure in microcotylids, however, she reduced the Gastrocotylidae to sub-family status included in Microcotylidae Taschenberg, 1879. Palombi did not recognize Sproston's subfamily Gastrocotylinae and placed it in the subfamily Microcotylinae Monticelli, 1892 then in his own family Arreptocotylidae Palombi, 1949. This arrangement was refuted, and The Gastrocotylidae was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrocotylidae
Gastrocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans.WoRMS (2019). Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119243 on 2019-02-15 All the species in this family are parasitic on fish. Systematics The gastrocotylids are known by their rather very diffuse distribution, and a marqued preference for scombroid fishes and carangids. The Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943 was erected to separate '' Gastrocotyle'' and its allies., named and described by reference to a diagram of the clamp type alone Sproston agreed on the importance of the difference in clamp structure in microcotylids, however, she reduced the Gastrocotylidae to sub-family status included in Microcotylidae Taschenberg, 1879. Palombi did not recognize Sproston's subfamily Gastrocotylinae and placed it in the subfamily Microcotylinae Monticelli, 1892 then in his own family Arreptocotylidae Palombi, 1949. This arrangement was refuted, and The Gastrocotylidae was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudaxine
''Pseudaxine'' is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish. Morphology Species of ''Pseudaxine'' are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated. The clamps are distributed along one margin of the haptor. ''Pseudaxine'' resemble ''Axine'' in having a single row of 20 – 30 clamps on one side of the body. However, it differs from ''Axine'' in having their hooks situated at the posterior end of the clamp row. ''Pseudaxine'' also resembles ''Gastrocotyle'' in having a single row of clamps on one side, however, in ''Pseudaxine'' the haptor is oblique, while in ''Gastrocotyle'' the haptor is parallel to the body-axis, and extends to the ovarian zone. Systematics ''Pseudaxine'' was established to accommodate ''Pseudaxine trachuri'' from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
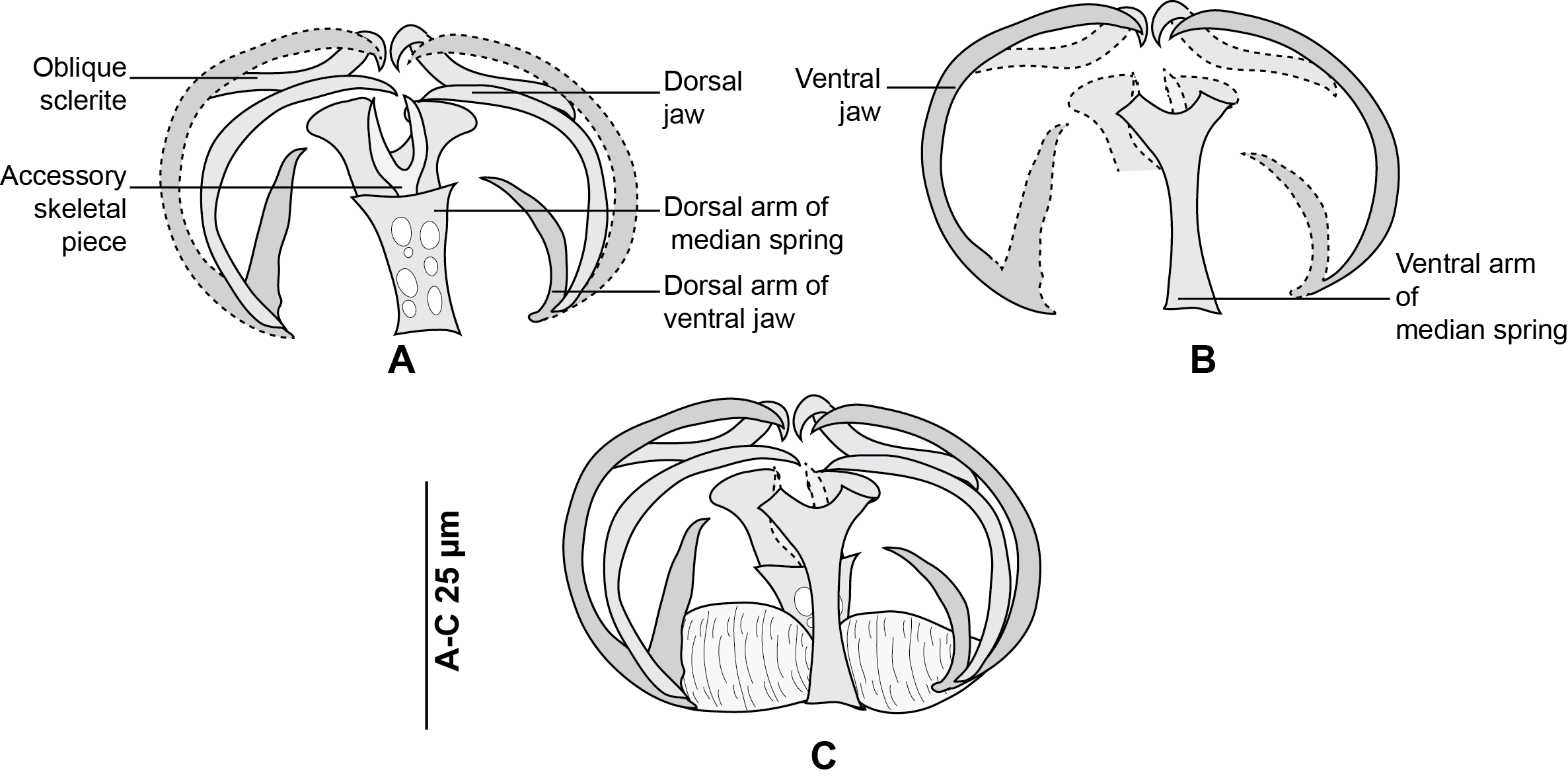
Allogastrocotyle
''Allogastrocotyle'' is a genus within the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea. The only species in this genus (''Allogastrocotyle bivaginalis'') is parasitic upon fish. Systematics ''Allogastrocotyle'' was established to accommodate ''Allogastrocotyle bivaginalis'' from the gills of the rough scad ''Trachurus lathami'', and designated as the type species of the genus. This genus resembles '' Gastrocotyle'' and ''Pseudaxine ''Pseudaxine'' is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish. Morphology Species of ''Pseudaxine'' are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larva ...'' especially in having a haptor developed on one side of the body. However, it differs by the following features: *Two ventro-lateral vaginal pores, one on each side of the body. *Clamps supported by short peduncles. *Haptor occupying two longitudinal thirds of the body. Species ''Allogastrocotyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrocotylinae
Gastrocotylinae is a sub-family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans. All the species in this family are parasitic on fish. Genera According to the Lebedev (1986) Lebedev, B.I. Monogenea: suborder Gastrocotylinea. Leningrad, USSR; Nauka (1986) 200pp.(In Russian) the sub-family includes 17 valid genera: *''Allogastrocotyle'' Nasir & Fuentes Zambrano, 1984 *''Amphipolycotyle'' Hargis, 1957 *''Areotestis'' Yamaguti, 1965 Yamaguti, S. (1965) New Monogenetic trematodes from Hawaiian fishes, I. Pacific Science, 19, 55–95PDF *''Churavera'' Unnithan, 1968 *''Cypselurobranchitrema'' Yamaguti, 1966Yamaguti, S. (1966). New monogenetic trematodes from Hawaiian fishes, II. Pacific Science, 20(4), 419-434. *''Engraulicola'' George, 1960 George, K. C. (1960). On a new gastrocotylid trematode, ''Engraulicola forcipopenis'' gen. Et sp. Nov. On white-bait, from southern India. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India, 2(2), 208-215PDF *''Engrauliphila'' Unnithan, 1967 *''Engraul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrocotyle (flatworm)
''Gastrocotyle'' is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Gastrocotylidae Gastrocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans.WoRMS (2019). Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119243 on 2019-02-15 All the species in this family are parasitic on fi .... The species of this genus are found in Europe and Northern America. Species: *'' Gastrocotyle buckleyi'' *'' Gastrocotyle indica'' *'' Gastrocotyle kurra'' *'' Gastrocotyle mozambiquensis'' *'' Gastrocotyle trachuri'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q22927432 Platyhelminthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyopisthocotylea
Polyopisthocotylea is a subclass of parasitic flatworms in the class Monogenea. WoRMS (2019). Polyopisthocotylea. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119220 on 2019-02-08Yamaguti, S. (1963). Systema Helminthum Volume IV Monogenea and Aspidocotylea: John Wiley & Sons.Hayward, C. (2005). Monogenea Polyopisthocotylea (ectoparasitic flukes). In K. Rohde (Ed.), Marine Parasitology (pp. 55-63): CSIRO, Collingwood, Australia & CABI, Oxon, UK. Classification There are only two subclasses in the class Monogenea: * Monopisthocotylea. The name means "a single posterior sucker" - the attachment organ (the haptor) is simple. * Polyopisthocotylea. The name means "several posterior suckers" - the attachment organ (the haptor) is complex, with several clamps or suckers. The subclass Polyopisthocotylea contains the four following orders: * Order Chimaericolidea * Order Diclybothriidea * Order Mazocraeidea * Order Polystomatidea Examples of species * '' Microco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogenea
Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.L.A. Tubbsa et al. (2005). "Effects of temperature on fecundity in vitro, egg hatching and reproductive development of ''Benedenia seriolae'' and ''Zeuxapta seriolae'' (Monogenea) parasitic on yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi". ''International Journal for Parasitology''(35), 315–327. Some monogeneans are oviparous (egg-laying) and some are viviparous (live-bearing). Oviparous varieties release eggs into the water. Viviparous varieties release larvae, which immediately attach to another host. The genus ''Gyrodactylus'' is an example of a viviparous variety, while the genus ''Dactylogyrus'' is an example of an oviparous variety. Signs and symptoms Freshwater fish that become infected with this parasite become let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scombridae
The mackerel, tuna, and bonito family, Scombridae, includes many of the most important and familiar food fishes. The family consists of 51 species in 15 genera and two subfamilies. All species are in the subfamily Scombrinae, except the butterfly kingfish, which is the sole member of subfamily Gasterochismatinae. Scombrids have two dorsal fins and a series of finlets behind the rear dorsal fin and anal fin. The caudal fin is strongly divided and rigid, with a slender, ridged base. The first (spiny) dorsal fin and the pelvic fins are normally retracted into body grooves. Species lengths vary from the of the island mackerel to the recorded for the immense Atlantic bluefin tuna. Scombrids are generally predators of the open ocean, and are found worldwide in tropical and temperate waters. They are capable of considerable speed, due to a highly streamlined body and retractable fins. Some members of the family, in particular the tunas, are notable for being partially endothermic (warm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carangid
The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish which includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes. They are marine fishes found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans. Most species are fast-swimming predatory fishes that hunt in the waters above reefs and in the open sea; some dig in the sea floor for invertebrates. The largest fish in the family, the greater amberjack, ''Seriola dumerili'', grows up to 2 m in length; most fish in the family reach a maximum length of 25–100 cm. The family contains many important commercial and game fish, notably the Pacific jack mackerel, ''Trachurus symmetricus'', and the other jack mackerels in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcotylidae
Microcotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans.WoRMS (2018). Microcotylidae Taschenberg, 1879. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119247 on 2018-12-03 All the species in this family are parasitic on fish. Subfamilies According to the World Register of Marine Species The World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS) is a taxonomic database that aims to provide an authoritative and comprehensive list of names of marine organisms. Content The content of the registry is edited and maintained by scientific specialist ..., the family includes 7 subfamilies: * Anchoromicrocotylinae Bravo-Hollis, 1981 Bravo-Hollis, M. (1981). Helmintos de peces del Pacífico mexicano XXXVI. Sobre un género y subfamilia nuevos de la familia Microcotylidae Taschenberg, 1879. Emend. Anales del Instituto de Ciencias del Mar y Limnología, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, 8, 305-314 * Atriasterinae Maillard & Noisy, 1979 Maillard, C., & Noisy, D. (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |