|
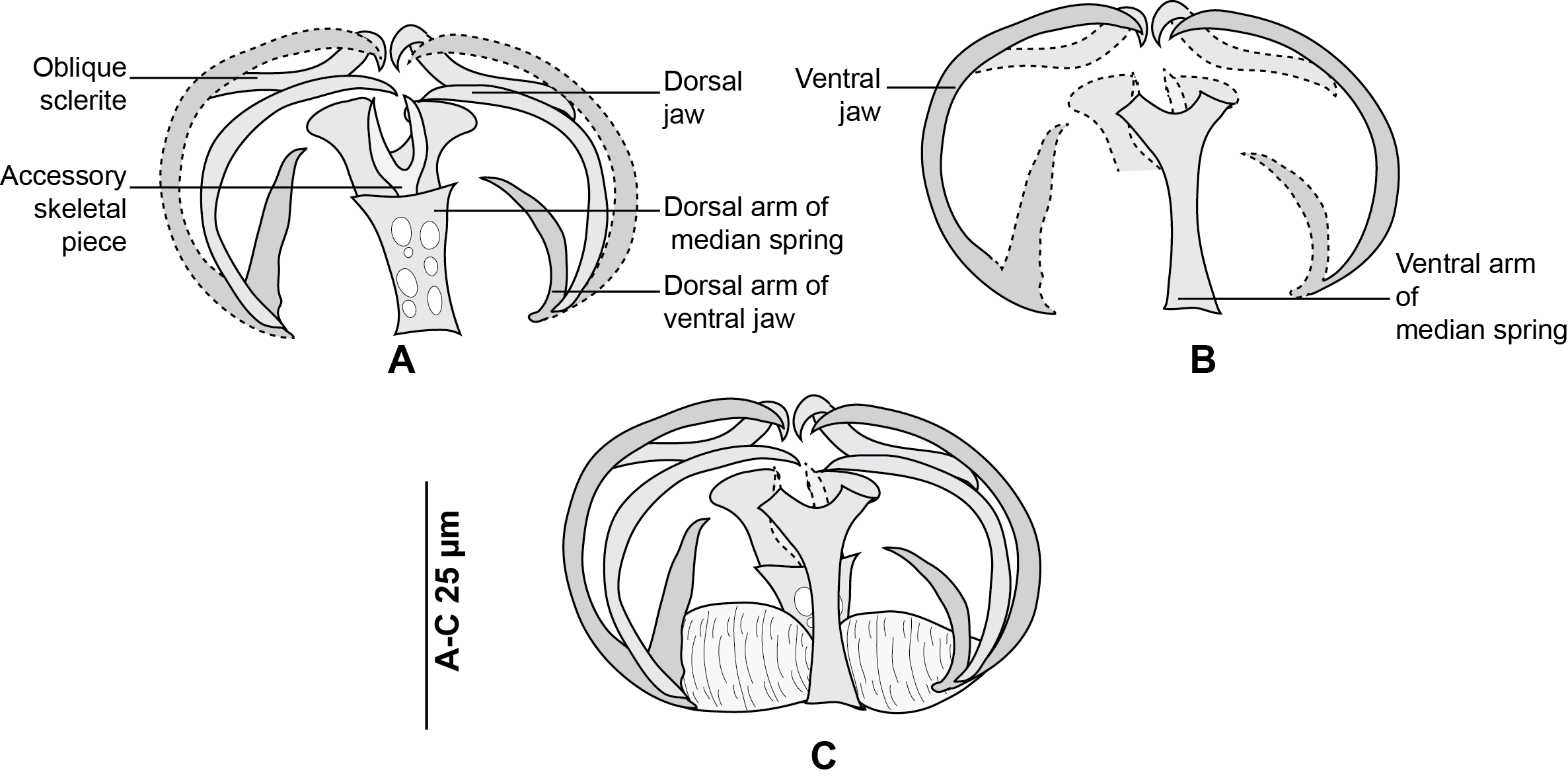
Allogastrocotyle
''Allogastrocotyle'' is a genus within the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea. The only species in this genus (''Allogastrocotyle bivaginalis'') is parasitic upon fish. Systematics ''Allogastrocotyle'' was established to accommodate ''Allogastrocotyle bivaginalis'' from the gills of the rough scad ''Trachurus lathami'', and designated as the type species of the genus. This genus resembles '' Gastrocotyle'' and ''Pseudaxine ''Pseudaxine'' is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish. Morphology Species of ''Pseudaxine'' are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larva ...'' especially in having a haptor developed on one side of the body. However, it differs by the following features: *Two ventro-lateral vaginal pores, one on each side of the body. *Clamps supported by short peduncles. *Haptor occupying two longitudinal thirds of the body. Species ''Allogastrocotyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allogastrocotyle Bivaginalis
''Allogastrocotyle bivaginalis'' is a species of monogenean flatworm, which is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Gastrocotylidae. Nasir, P. & Fuentes, J.L. (1983). "Algunos trematodos monogeneticos Venezolanos". ''Revista de Parasitologia''. 44: 335-380. (In Spanish). The species was described and illustrated from two specimens from the gills the rough scad ''Trachurus lathami'' ( Carangidae) off Venezuela, and designated as the type species of the genus. In 2019, Bouguerche et al. examined specimens of monogeneans similar to ''Allogastrocotyle bivaginalis'', collected from the gills of the Blue jack mackerel '' Trachurus picturatus'' ( Carangidae) from off the Algerian coast, Mediterranean Sea. They claimed that they could not distinguish the Mediterranean specimens from ''A. bivaginalis'', neither on the base of morphology nor on molecules (because molecular information was lacking on ''A. bivaginalis'' from Venezuela). Gallery ''Allog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrocotylidae
Gastrocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans.WoRMS (2019). Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119243 on 2019-02-15 All the species in this family are parasitic on fish. Systematics The gastrocotylids are known by their rather very diffuse distribution, and a marqued preference for scombroid fishes and carangids. The Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943 was erected to separate '' Gastrocotyle'' and its allies., named and described by reference to a diagram of the clamp type alone Sproston agreed on the importance of the difference in clamp structure in microcotylids, however, she reduced the Gastrocotylidae to sub-family status included in Microcotylidae Taschenberg, 1879. Palombi did not recognize Sproston's subfamily Gastrocotylinae and placed it in the subfamily Microcotylinae Monticelli, 1892 then in his own family Arreptocotylidae Palombi, 1949. This arrangement was refuted, and The Gastrocotylidae was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platyhelminthes
The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") are a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates (having no coelom, body cavity), and have no specialized circulatory system, circulatory and respiratory system, respiratory organ (anatomy), organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion (intake of nutrients) and egestion (removal of undigested wastes); as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously. In traditional medicinal texts, Platyhelminthes are divided into Turbellaria, which are mostly non-parasitic animals such as planarians, and three entirely p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogenea
Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.L.A. Tubbsa et al. (2005). "Effects of temperature on fecundity in vitro, egg hatching and reproductive development of ''Benedenia seriolae'' and ''Zeuxapta seriolae'' (Monogenea) parasitic on yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi". ''International Journal for Parasitology''(35), 315–327. Some monogeneans are oviparous (egg-laying) and some are viviparous (live-bearing). Oviparous varieties release eggs into the water. Viviparous varieties release larvae, which immediately attach to another host. The genus ''Gyrodactylus'' is an example of a viviparous variety, while the genus ''Dactylogyrus'' is an example of an oviparous variety. Signs and symptoms Freshwater fish that become infected with this parasite become let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyopisthocotylea
Polyopisthocotylea is a subclass of parasitic flatworms in the class Monogenea. WoRMS (2019). Polyopisthocotylea. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119220 on 2019-02-08Yamaguti, S. (1963). Systema Helminthum Volume IV Monogenea and Aspidocotylea: John Wiley & Sons.Hayward, C. (2005). Monogenea Polyopisthocotylea (ectoparasitic flukes). In K. Rohde (Ed.), Marine Parasitology (pp. 55-63): CSIRO, Collingwood, Australia & CABI, Oxon, UK. Classification There are only two subclasses in the class Monogenea: * Monopisthocotylea. The name means "a single posterior sucker" - the attachment organ (the haptor) is simple. * Polyopisthocotylea. The name means "several posterior suckers" - the attachment organ (the haptor) is complex, with several clamps or suckers. The subclass Polyopisthocotylea contains the four following orders: * Order Chimaericolidea * Order Diclybothriidea * Order Mazocraeidea * Order Polystomatidea Examples of species * '' Microco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; plural: phyla) is a level of classification or taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. Traditionally, in botany the term division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about 8 phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships between phyla, which are contained in larger clades, like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguished them as a group ("a self-contained unity" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Class (biology)
In biological classification, class ( la, classis) is a taxonomic rank, as well as a taxonomic unit, a taxon, in that rank. It is a group of related taxonomic orders. Other well-known ranks in descending order of size are life, domain, kingdom, phylum, order, family, genus, and species, with class fitting between phylum and order. History The class as a distinct rank of biological classification having its own distinctive name (and not just called a ''top-level genus'' ''(genus summum)'') was first introduced by the French botanist Joseph Pitton de Tournefort in his classification of plants that appeared in his ''Eléments de botanique'', 1694. Insofar as a general definition of a class is available, it has historically been conceived as embracing taxa that combine a distinct ''grade'' of organization—i.e. a 'level of complexity', measured in terms of how differentiated their organ systems are into distinct regions or sub-organs—with a distinct ''type'' of construction, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachurus Lathami
''Trachurus lathami'' is a species of fish in the family Carangidae and the genus ''Trachurus'', the jack mackerels. Common names include rough scad and horse mackerelVergani, M., et al. (2008)Food of the yellowtail amberjack ''Seriola lalandi'' from the south-west Atlantic.''Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the UK'' 88(4) 851-52. in English, as well as ''chinchard frappeur'' ( French), ''chicharro garretón'' (Spanish), ''jurel'' (in Argentina and Uruguay), and ''carapau'', ''garaçuma'', ''surel'', and ''xixarro'' (in Brazil).Common names of ''Trachurus lathami''. FishBase. It is native to parts of the western |
Gastrocotyle (flatworm)
''Gastrocotyle'' is a genus of flatworms belonging to the family Gastrocotylidae Gastrocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans.WoRMS (2019). Gastrocotylidae Price, 1943. Accessed at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=119243 on 2019-02-15 All the species in this family are parasitic on fi .... The species of this genus are found in Europe and Northern America. Species: *'' Gastrocotyle buckleyi'' *'' Gastrocotyle indica'' *'' Gastrocotyle kurra'' *'' Gastrocotyle mozambiquensis'' *'' Gastrocotyle trachuri'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q22927432 Platyhelminthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudaxine
''Pseudaxine'' is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish. Morphology Species of ''Pseudaxine'' are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated. The clamps are distributed along one margin of the haptor. ''Pseudaxine'' resemble ''Axine'' in having a single row of 20 – 30 clamps on one side of the body. However, it differs from ''Axine'' in having their hooks situated at the posterior end of the clamp row. ''Pseudaxine'' also resembles ''Gastrocotyle'' in having a single row of clamps on one side, however, in ''Pseudaxine'' the haptor is oblique, while in ''Gastrocotyle'' the haptor is parallel to the body-axis, and extends to the ovarian zone. Systematics ''Pseudaxine'' was established to accommodate ''Pseudaxine trachuri'' from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |