|
Garcia De Orta
Garcia de Orta (or Garcia d'Orta) (1501 – 1568) was a Sephardic Jewish physician, herbalist and naturalist of the Portuguese Renaissance, who worked primarily in the former Portuguese capital of Goa and the Bombay territory (Chaul, Bassein & Damaon) of Portuguese India. A pioneer of tropical medicine, pharmacognosy & ethnobotany, Garcia used an experimental approach to the identification and the use of herbal medicines, rather than the older approach of received knowledge (oral tradition). His most famous work is ''Colóquios dos simples e drogas da India'', a book on simples (herbs used individually and not mixed with others) and drugs. Published in 1563, it is the earliest treatise on the medicinal and economic plants of India. Carolus Clusius translated it into Latin, which was widely used as a standard reference text on medicinal plants. Although Garcia de Orta did not, apparently, suffer the Goa Inquisition, his sister Catarina was burnt at the stake in 1569 for being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veloso Salgado
José Maria Veloso Salgado (2 April 1864 22 July 1945) was a Galicia (Spain), Galician-born Portugal, Portuguese artist. He is regarded as one of the country's foremost masters of Realism (art movement), Naturalism with many distinguished works in History painting, historical painting, landscapes, and portraits. Biography José Maria Veloso Salgado was born in Galicia (Spain), Galicia (Spain), in Melón (a small town in the province of Province of Ourense, Ourense, not far from the Portugal–Spain border, Portuguese border), where he lived until the age of 10. He was the son of two farmers, José Pérez and Dolores Veloso Rodrigues Salgado. In 1874, his parents sent him to live with his maternal uncle, Miguel Veloso Rodrigues Salgado, who run a lithography workshop (''Litografia Lemos'') in Lisbon, Portugal. Veloso Salgado started working as an apprentice at his uncle's workshop. From 1878 to 1880, he attended evening classes for workers at the School of the Lisbon Academy of Fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnobotany
Ethnobotany is the study of a region's plants and their practical uses through the traditional knowledge of a local culture and people. An ethnobotanist thus strives to document the local customs involving the practical uses of local flora for many aspects of life, such as plants as medicines, foods, intoxicants and clothing. Richard Evans Schultes, often referred to as the "father of ethnobotany", explained the discipline in this way: Ethnobotany simply means ... investigating plants used by societies in various parts of the world. Since the time of Schultes, the field of ethnobotany has grown from simply acquiring ethnobotanical knowledge to that of applying it to a modern society, primarily in the form of pharmaceuticals. Intellectual property rights and benefit-sharing arrangements are important issues in ethnobotany. History The idea of ethnobotany was first proposed by the early 20th century botanist John William Harshberger. While Harshberger did perform ethnobotanical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
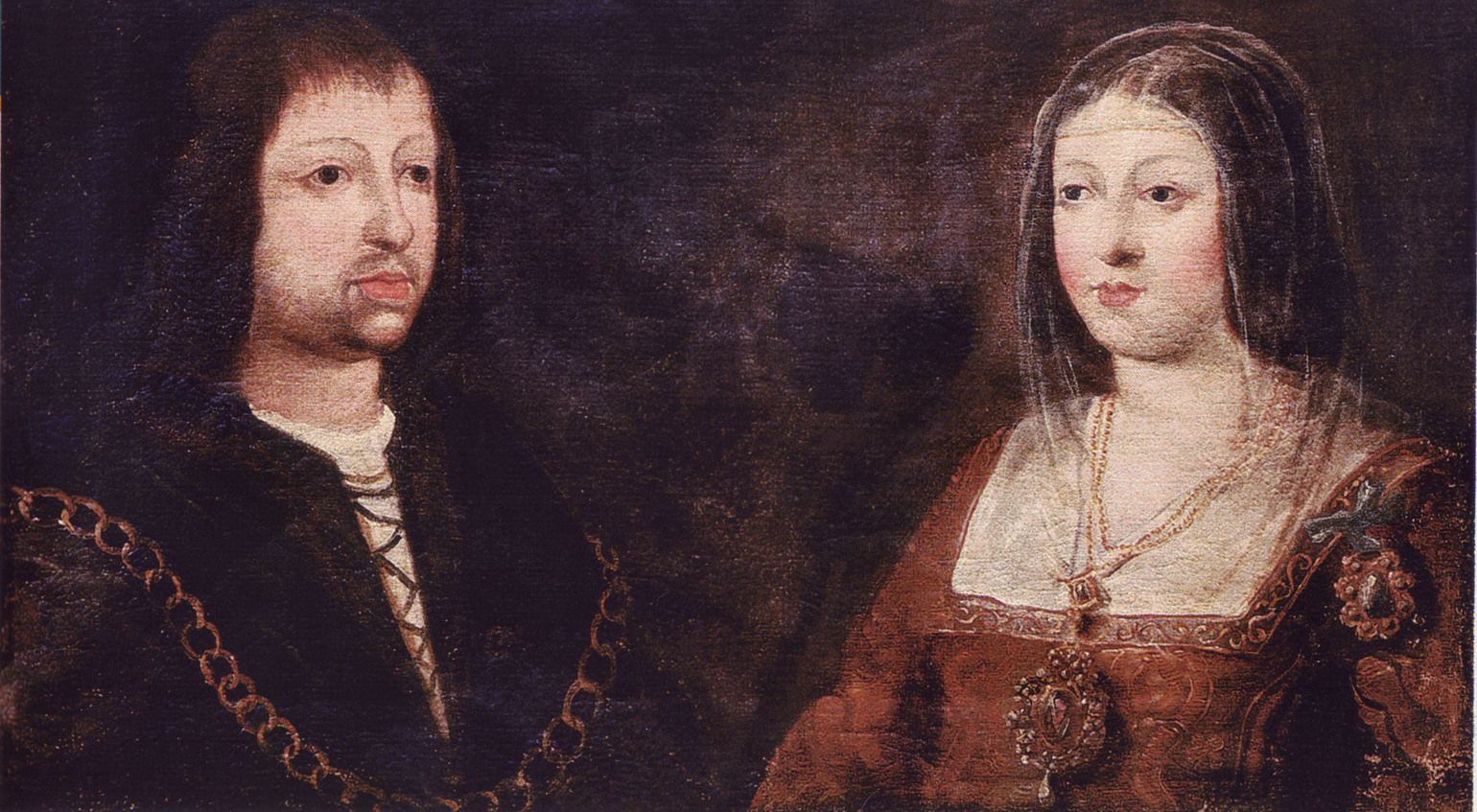
Isabella I Of Castile
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as List of Aragonese royal consorts, Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 by virtue of her marriage to King Ferdinand II of Aragon. Reigning together over a Dynastic union, dynastically unified Spain, Isabella and Ferdinand are known as the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, Catholic Monarchs. After a struggle to claim the throne, Isabella reorganized the governmental system, brought the crime rate to the lowest it had been in years, and unburdened the kingdom of the enormous debt her half-brother Henry IV of Castile, King Henry IV had left behind. Isabella's marriage to Ferdinand in 1469 created the basis of the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. Her reforms and those she made with her husband had an influence that extended well beyond the borders of their united kingdoms. Isabella I of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand II Of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia from 1479, King of Sicily from 1468, King of Naples (as Ferdinand III) from 1504 and King of Navarre (as Ferdinand I) from 1512 until his death in 1516. He was also the nominal Duke of the ancient Duchies of Athens and Neopatria. He was King of Castile and León (as Ferdinand V) from 1475 to 1504, alongside his wife Queen Isabella I. From 1506 to 1516, he was the Regent of the Crown of Castile, making him the effective ruler of Castile. From 1511 to 1516, he styled himself as ''Imperator totius Africa'' (Emperor of All Africa) after having conquered Tlemcen and making the Zayyanid Sultan, Abu Abdallah V, his vassal. He was also the Grandmaster of the Spanish Military Orders of Santiago (1499-1516), Calatrava (1487-1516), Alcantara (1492- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; to remove the obstacle that this consanguinity would otherwise have posed to their marriage under canon law, they were given a papal dispensation by Sixtus IV. They married on October 19, 1469, in the city of Valladolid; Isabella was eighteen years old and Ferdinand a year younger. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the unification of Spain can essentially be traced back to the marriage of Ferdinand and Isabella. Spain was formed as a dynastic union of two crowns rather than a unitary state, as Castile and Aragon remained separate kingdoms until the Nueva Planta decrees of 1707–16. The court of Ferdinand and Isabella was constantly on the move, in order to bolster local support for the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira. It features the westernmost point in continental Europe, and its Iberian portion is bordered to the west and south by the Atlantic Ocean and to the north and east by Spain, the sole country to have a land border with Portugal. Its two archipelagos form two autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Lisbon is the capital and largest city by population. Portugal is the oldest continuously existing nation state on the Iberian Peninsula and one of the oldest in Europe, its territory having been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. It was inhabited by pre-Celtic and Celtic peoples who had contact with Phoenicians and Ancient Greek traders, it was ruled by the Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valencia De Alcántara
Valencia de Alcántara (Population: 6178) is a municipality located in the province of Cáceres, in the autonomous community of Extremadura, Spain. It is near the Portuguese border (District of Portalegre), separated from it by the Sever. History From the 16th century to the 18th Valencia was a celebrated border fortress; it was captured by the Portuguese in 1664 and 1698. Battle of 1762 The Battle of Valencia de Alcántara took place in 1762 as part of the Spanish invasion of Portugal. Portuguese-British troops under John Burgoyne attacked and captured the town, which was a Spanish supply base, setting back the invasion and contributing to the British victory that year. Nineteenth century The beginning of the nineteenth century, traditionally associated with the beginnings of the modern age, is particularly troublesome in the case of Valencia de Alcántara as it was caught up in two important conflicts, including the fleeting conflict known as the War of the Oranges (1801) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auto-da-fé
An ''auto-da-fé'' ( ; from Portuguese , meaning 'act of faith'; es, auto de fe ) was the ritual of public penance carried out between the 15th and 19th centuries of condemned heretics and apostates imposed by the Spanish, Portuguese, or Mexican Inquisition as punishment and enforced by civil authorities. Its most extreme form was death by burning. History From the 8th to the 15th centuries, much of Spain was controlled by Muslims, under whose laws Jews and Christians were given dhimmi status. This meant that they were required to pay a special tax, the jizya, for "protection", intended, as Islamic legal texts indicated, to remind them of their submission. The tax was imposed on the "people of the Book", as Jews and Christians were known, to humble them. Jews could sometimes rise to important positions in the political structure; anti-Jewish violence could also erupt. In the 1066 Granada massacre, much of the Jewish population of Granada was killed by a Muslim mob. The tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crypto-Jews
Crypto-Judaism is the secret adherence to Judaism while publicly professing to be of another faith; practitioners are referred to as "crypto-Jews" (origin from Greek ''kryptos'' – , 'hidden'). The term is especially applied historically to Spanish Jews who outwardly professed Catholicism, also known as Conversos, Marranos, or the Anusim. The phenomenon is especially associated with Renaissance Spain, following the Massacre of 1391 and the expulsion of the Jews in 1492.Levine Melammed, Renee. "Women in Medieval Jewish Societies," in ''Women and Judaism: New Insights and Scholarship''. Ed. Frederick E. Greenspahn. New York: New York University Press, 2009. 105–106. Europe Officially, Jews who converted in Spain during the 14th and 15th centuries were known as ''Cristianos Nuevos'' (New Christians), but were commonly called '' conversos'' (converts o Christianity. Spain and Portugal passed legislation restricting their rights in the mother countries of Spain and Portuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goa Inquisition
The Goa Inquisition ( pt, Inquisição de Goa) was an extension of the Portuguese Inquisition in Portuguese India. Its objective was to enforce Catholic Orthodoxy and allegiance to the Apostolic See of Rome (Pontifex). The inquisition primarily focused on the New Christians accused of secretly practicing their former religions, and Old Christians accused of involvement in the Protestant Revolution of the 16th century. It was established in 1560, briefly suppressed from 1774 to 1778, continued thereafter until it was finally abolished in 1812. Those targeted were predominately accused of crypto-Hinduism. Those accused were imprisoned and depending on the criminal charge, could even be sentenced to death if convicted. The Inquisitors also seized and burnt any books written in Sanskrit, Dutch, English, or Konkani, on the suspicions that they contained deviationist or Protestant material. The aims of the Portuguese Empire in Asia were combating Islam, spreading Christianity, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_-_Veloso_Salgado_(MNAC).png)