|
Gao Xingzhou
Gao Xingzhou () (885'' History of the Five Dynasties'', vol. 123. – September 10, 952''History of the Five Dynasties'', vol. 112.Academia Sinicabr>Chinese-Western Calendar Converter), courtesy name Shangzhi (), formally Prince Wuyi of Qin (), was a Chinese military general, monarch, and politician that served the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period states Jin, Jin's successor state Later Tang, Later Jin, Liao Dynasty, Later Han, and Later Zhou. His son Gao Huaide was later a famed general in the succeeding Song Dynasty. Background Gao Xingzhou was born in 885, during the reign of Emperor Xizong of Tang. His family was originally from You Prefecture (幽州, in modern Beijing), but his male-line ancestors had served for several generations (since his great-grandfather Gao Shunli () at Huairong Base () at Gui Prefecture (媯州, in modern Zhangjiakou, Hebei), which belonged to Lulong Circuit (盧龍, headquartered at You Prefecture), and Gao Xingzhou was born at the fortre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old History Of The Five Dynasties
The ''Old History of the Five Dynasties'' (''Jiù Wǔdài Shǐ'') was an official history mainly focus on Five Dynasties era (907–960), which controlled much of northern China. And it also includes some history of other south states during the era. It was compiled by the Song dynasty official-scholar Xue Juzheng in the first two decades of the Song dynasty, which was founded in 960. It is one of the Twenty-Four Histories recognized through Chinese history. The book comprises 150 chapters, and was in effect divided into 7 books, they are: ''Book of Liang'' (24 volume), ''Book of Tang'' (50 volume), ''Book of Jin'' (24 volume), ''Book of Han'' (11 volume), ''Book of Zhou'' (22 volume), '' Liezhuan'' (7 volume) and ''Zhi'' (12 volume), respectively''.'' After the ''New History of the Five Dynasties'' by Ouyang Xiu was published, it was no longer popular. In the 12th century it was removed from the Imperial Library and was no longer published by order of the Jin dynasty. The book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebei
Hebei or , (; alternately Hopeh) is a northern province of China. Hebei is China's sixth most populous province, with over 75 million people. Shijiazhuang is the capital city. The province is 96% Han Chinese, 3% Manchu, 0.8% Hui, and 0.3% Mongol. Three Mandarin dialects are spoken: Jilu Mandarin, Beijing Mandarin and Jin. Hebei borders the provinces of Shanxi to the west, Henan to the south, Shandong to the southeast, Liaoning to the northeast, and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to the north. Its economy is based on agriculture and manufacturing. The province is China's premier steel producer, although the steel industry creates serious air pollution. Five UNESCO World Heritage Sites can be found in the province, the: Great Wall of China, Chengde Mountain Resort, Grand Canal, Eastern Qing tombs, and Western Qing tombs. It is also home to five National Famous Historical and Cultural Cities: Handan, Baoding, Chengde, Zhengding and Shanhaiguan. Historic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
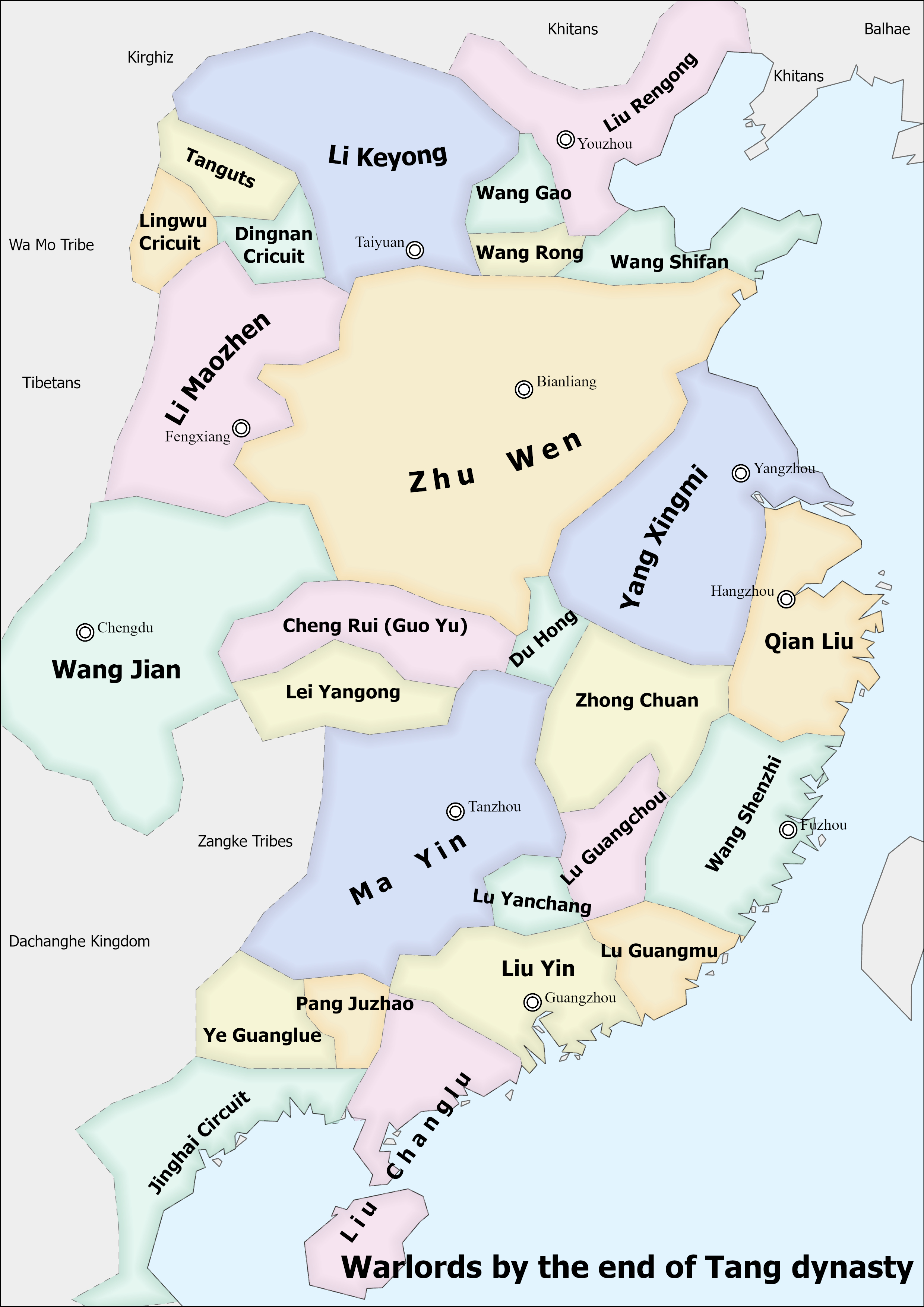
Liu Shouguang
Liu Shouguang () (died February 16, 914) was a warlord early in the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period who controlled Lulong (盧龍, headquartered in modern Beijing) and Yichang (義昌, headquartered in modern Cangzhou, Hebei) Circuits, after seizing control from his father Liu Rengong and defeating his brother Liu Shouwen. He claimed the title of Emperor of Yan in 911, but was subsequently defeated and executed by Li Cunxu the Prince of Jin, who absorbed Yan into his Jin state. Background It is not known when Liu Shouguang was born. He was a son of Liu Rengong, who became military governor (''Jiedushi'') of Lulong Circuit in 895 after Liu Rengong's then-liege Li Keyong the military governor of Hedong Circuit (河東, headquartered in modern Taiyuan, Shanxi) conquered Lulong Circuit in 894. Liu Rengong eventually broke away from Li and became an independent warlord in 897.''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 261. It is not known when Liu Shouguang's birth was in relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Zhuangzong Of Later Tang
Emperor Zhuangzong of Later Tang (), personal name Li Cunxu (), nickname Yazi (), stage name Li Tianxia (), was the ruling prince of the Former Jin dynasty (r. 908–923) and later became the founding emperor of the Later Tang dynasty (r. 923–926) during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period of Chinese history.Cihai: Page 1266. He was the son of Li Keyong, an ethnic Shatuo Jiedushi of the Tang dynasty. Li Cunxu was considered one of the most militarily capable rulers of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. When he succeeded his father Li Keyong as the Prince of Jin, Jin had been weakened in the late years of Li Keyong's rule and not considered capable of posing a military threat to its archrival to the south, Later Liang, whose founding emperor Zhu Quanzhong had seized the Tang throne. Li Cunxu carefully rebuilt the Jin state, using a series of conquests and alliances to take over most of the territory north of the Yellow River, before starting a lengthy campai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yan (Five Dynasties)
Yan (), sometimes known in historiography as Jie Yan (), was a short-lived monarchical state in the vicinity of present-day Beijing at the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Yan, established by Liu Shouguang in 911, only lasted for two years before its destruction by Li Cunxu of the Former Jin dynasty. As the only ruler of Yan, Liu Shouguang was noted for his cruelty. The state of Yan was therefore sometimes referred to as ''Jie Yan'', in reference to the tyrannical ruler Jie of the Xia dynasty The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In tradi .... References * {{5d10k Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Former countries in Chinese history 911 establishments 910s disestablishments States and territories established in the 910s States and territories d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Rengong
Liu Rengong () (died 914) was a warlord late in the Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty who controlled Lulong Circuit (盧龍, headquartered in modern Beijing) from 895 (when his one-time lord Li Keyong conquered Lulong and left him in charge of it) to 907 (when he was overthrown by his son Liu Shouguang and put under house arrest). He was initially a Lulong officer, but later fled to Li Keyong's Hedong Circuit (河東, headquartered in modern Taiyuan, Shanxi). After Li conquered Lulong and left him in charge, he turned against Li and became an independent warlord, although at times he and Li would still act in concert. His domain later became the basis of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period state Yan that Liu Shouguang established. In 913, however, Li Keyong's son and successor Li Cunxu the Prince of Jin conquered Yan and captured both Liu Shouguang and Liu Rengong; he put them to death the next year. Background It is not known when Liu Rengong was born—although he was said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New History Of The Five Dynasties
The ''Historical Records of the Five Dynasties'' (''Wudai Shiji'') is a Chinese history book on the Five Dynasties period (907–960), written by the Song dynasty official Ouyang Xiu in private. It was drafted during Ouyang's exile from 1036 to 1039 but not published until 1073, a year after his death. An abridged English translation by Richard L. Davis was published in 2004. One of the official Twenty-Four Histories of China, the book is frequently referred to as the ''New History of the Five Dynasties'' (''Xin Wudai Shi'') in order to distinguish it from the ''Old History of the Five Dynasties'' which was published in 974. Though both books follow a similar format, Ouyang's book is more concise and markedly more analytical. Contents ''New History of the Five Dynasties'' covers the Later Liang, Later Tang, Later Jin, Later Han, and Later Zhou dynasties. The book consists of 74 chapters total. It includes biographies, annuals, case studies, family histories, genealogies, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Kuangchou
Li, li, or LI may refer to: Businesses and organizations * Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects * Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political technology." * Li Auto (Nasdaq: LI), a Chinese manufacturer of electric vehicles * Liberal International, a political federation for liberal parties * Linux International, an international non-profit organization * Lyndon Institute, an independent high school in the U.S. state of Vermont * The Light Infantry, a British Army infantry regiment Names * Li (surname), including: ** List of people with surname Li ** Li (surname 李), one of the most common surnames in the world ** Li (surname 黎), the 84th most common surname in China ** Li (surname 栗), the 249th most common surname in China ** Li (surname 利), the 299th most common surname in China ** Li (surname 厉), a Chinese surname ** Li (surname 郦), a Chinese surname ** Li (surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Kuangwei
Li Kuangwei () (d. 893) was a warlord late in the Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty, who controlled Lulong Circuit (盧龍, headquartered in modern Beijing) after inherited it from his father Li Quanzhong in 886, until he was overthrown by his brother Li Kuangchou in 893. After he was overthrown, he resided briefly at the domain of his ally Wang Rong the military governor of Chengde Circuit (成德, headquartered in modern Shijiazhuang, Hebei). He subsequently tried to seize control of the circuit from Wang, but was killed by Chengde soldiers faithful to Wang. Background It is not known when Li Kuangwei was born, but it is known that his family was from Lulong Circuit's capital Fanyang.''Old Book of Tang'', vol. 180. The first historical reference to him was in 886, when his father, the military governor (''Jiedushi'') Li Quanzhong, who had seized control of Lulong in 885 after overthrowing the prior military governor Li Keju, died, and Li Kuangwei thereafter claimed the title of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |