|
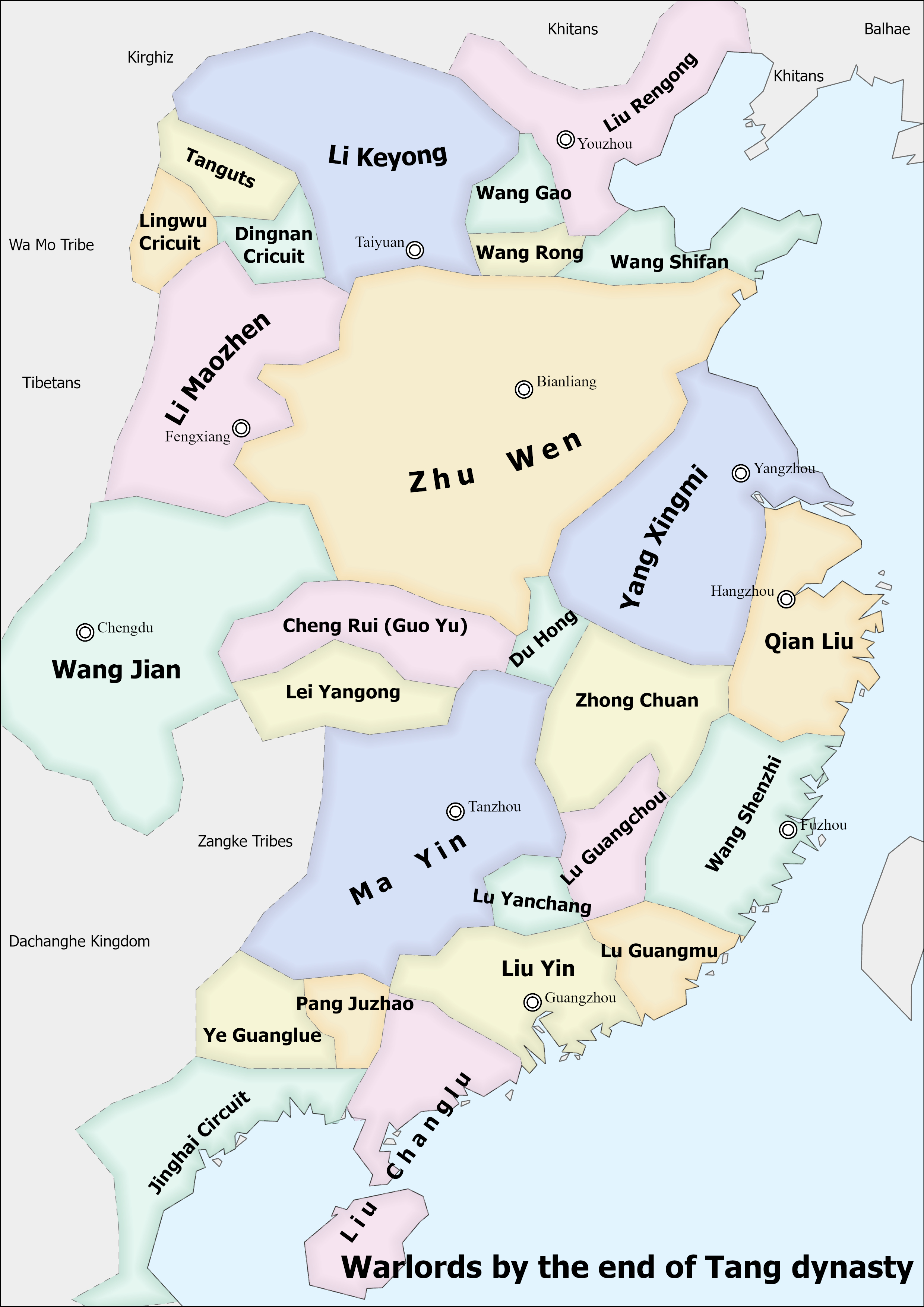
Liu Rengong
Liu Rengong () (died 914) was a warlord late in the Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty who controlled Lulong Circuit (盧龍, headquartered in modern Beijing) from 895 (when his one-time lord Li Keyong conquered Lulong and left him in charge of it) to 907 (when he was overthrown by his son Liu Shouguang and put under house arrest). He was initially a Lulong officer, but later fled to Li Keyong's Hedong Circuit (河東, headquartered in modern Taiyuan, Shanxi). After Li conquered Lulong and left him in charge, he turned against Li and became an independent warlord, although at times he and Li would still act in concert. His domain later became the basis of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period state Yan that Liu Shouguang established. In 913, however, Li Keyong's son and successor Li Cunxu the Prince of Jin conquered Yan and captured both Liu Shouguang and Liu Rengong; he put them to death the next year. Background It is not known when Liu Rengong was born—although he was sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapters, 11th century BC), the '' Bamboo Annals'' (c. 296 BC) and the ''Records of the Grand Historian'' (c. 91 BC) describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is among the world's oldest civilizations and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization. The Zhou dynasty (1046–256 BC) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Quanzhong
Li Quanzhong () (d. 886) was a warlord late in the History of China, Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty, who controlled Lulong Circuit (盧龍, headquartered in modern Beijing) from 885, when he overthrew the prior military governor (''Jiedushi'') Li Keju, to his death in 886. His sons Li Kuangwei and Li Kuangchou successively served as military governors after he died. Background It is not known when Li Quanzhong was born, but it is known that he was from Lulong Circuit's capital Fanyang (). During Emperor Xizong of Tang, Emperor Xizong's ''Guangming'' era (880-881), he served as the military advisor to the prefect of Di Prefecture (棣州, in modern Binzhou, Shandong). After that term, he returned to Lulong and served under the military governor Li Keju.''Old Book of Tang'', :zh:s:舊唐書/卷180, vol. 180. Seizure of Lulong In spring 885, Li Keju and his ally Wang Rong (warlord), Wang Rong the military governor of Chengde Circuit (成德, headquartered in modern Shijiazhuang, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Cunshen
Li Cunshen () (862'' History of the Five Dynasties'', vol. 56.-June 16, 924Academia Sinicabr>Chinese-Western Calendar Converter), né Fu Cun (), often referred to in historical sources as Fu Cunshen (), courtesy name Dexiang (), was a Chinese military general, politician, and singer of the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period dynasty Later Tang and Later Tang's predecessor state Jin. He was an adoptive son of Jin's first prince Li Keyong and later served in a number of major campaigns under the reign of Li Keyong's son (Li Cunshen's adoptive brother) Li Cunxu, helping Li Cunxu to establish Later Tang as its Emperor Zhuangzong. Background Fu Cun was born in 862, during the reign of Emperor Yizong of Tang. His family was from Wanqiu (宛丘, in modern Zhoukou, Henan), and his father Fu Chu () was an officer for the army of Chen Prefecture (陳州, in modern Zhumadian, Henan), which Wanqiu was a part of. When he was young, there was an occasion when he was to be ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu Yanwei
Lu Yanwei () was a warlord late in the Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty, who controlled Yichang Circuit (義昌, headquartered in modern Cangzhou, Hebei) from 885 to 898, most of that time as its military governor (''Jiedushi''). Background and seizure of Yichang Circuit Little is known about Lu Yanwei's background, as neither of the official histories of Tang Dynasty — the '' Old Book of Tang'' and the '' New Book of Tang'' — contained a biography for him. The first reference to him in the ''Zizhi Tongjian'' was in 885, when a mutiny at Yichang's capital Cang Prefecture () led to the expulsion of the previously military governor Yang Quanmei (), who fled to neighboring Lulong Circuit (盧龍, headquartered in modern Beijing). The soldiers supported Lu to be their acting military governor. Then-reigning Emperor Xizong, however, did not make Lu military governor, instead commissioning the imperial guard officer Cao Cheng () as military governor and Lu as the prefect of one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xingtai
Xingtai (), formerly known as Xingzhou and Shunde, is a prefecture-level city in southern Hebei province, People's Republic of China. It has a total area of and administers 4 districts, 2 county-level cities and 12 counties. At the 2020 census, its population was 7,111,106 inhabitants. It borders Shijiazhuang and Hengshui in the north, Handan in the south, and the provinces of Shandong and Shanxi in the east and west respectively. History Xingtai is the oldest city in North China. The history of Xingtai can be traced back 3500 years ago. During the Shang Dynasty, Xingtai functioned as a capital city. During the Zhou Dynasty, the State of Xingfrom which the present name deriveswas founded in the city. During the Warring States period, the state of Zhao made Xingtai its provisional capital. The city was known as Xindu for most of the Qin Dynasty, but after the 207 BC Battle of Julu (within present-day Pingxiang County, not today's Julu County), it became known as Xiangguo. Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Cunxiao
Li Cunxiao () (d. 894), né An Jingsi (), was an adoptive son of the late-Tang Dynasty warlord Li Keyong who contributed much to Li Keyong's campaigns, but who later rebelled against his adoptive father. He subsequently was defeated by Li Keyong and executed by dismemberment after he surrendered, although Li Keyong soon regretted his death. Background It is not known when An Jingsi was born, but it is known that he, or his family, was originally from Feihu (飛狐, in modern Zhangjiakou, Hebei). He was taken captive by Li Keyong during one of Li Keyong's raids in the region, and Li Keyong raised him as an adoptive son, changing his name to Li Cunxiao. He thereafter became a cavalry officer in Li Keyong's army.''New History of the Five Dynasties'', vol. 36. It was said that after he grew up, he was capable in horsemanship and archery, and no officer in Li Keyong's army rivaled him in ferocity. He often served as Li Keyong's forward commander, and during Li Keyong's campaig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gai Yu
Gai Yu () (died 905), formally the Duke of Chengyang (), was a key strategist of Li Keyong, a major warlord late in the History of China, Chinese dynasty Tang Dynasty. Background It is not known when Gai Yu was born, but it was known that he was from Wei Prefecture (蔚州, in modern Zhangjiakou, Hebei), and that both his grandfather Gai Zuo () and father Gai Qing () served as officer at Wei Prefecture.''Old History of the Five Dynasties, History of the Five Dynasties'', :zh:s:舊五代史/卷55, vol. 55. When the ethnically-Shatuo officer Li Keyong rose against Duan Wenchu () the defender of Datong Circuit (大同, headquartered at Datong, Shanxi) (which Wei Prefecture belonged to) at Datong's capital Yun Prefecture () in 878, Gai was one of the proponents, and he became a close associate of Li's. Services under Li Keyong After Li Keyong resubmitted to Tang authority and was made the military governor (''Jiedushi'') of Yanmen Circuit (traditional characters, t or simplified c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juyong Pass
Juyong Pass () is a mountain pass located in the Changping District of Beijing Municipality, over from central Beijing. The Great Wall of China passes through, and the Cloud Platform was built here in the year 1342. Mountain pass Geography Juyongguan (pass) is in the -long Guangou Valley. The pass is one of the three greatest mountain passes of the Great Wall of China. The other two are Jiayuguan and Shanhaiguan (passes). Juyongguan Pass has two 'sub-passes,' one at the valley's south and the other at the north. The southern one is called "Nan (pass)" and the northern is called "Badaling". History The pass had many different names during former Chinese dynasties. However, the name "Juyongguan" was used by more than three dynasties. It was first used in the Qin Dynasty when Emperor Qinshihuang ordered the building of the Great Wall. Juyongguan pass was connected to the Great Wall in the Southern and Northern Dynasties era. The present pass route was built in the Ming Dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Li Kuangchou
Li, li, or LI may refer to: Businesses and organizations * Landscape Institute, a British professional body for landscape architects * Leadership Institute, a non-profit organization located in Arlington, Virginia, US, that teaches "political technology." * Li Auto (Nasdaq: LI), a Chinese manufacturer of electric vehicles * Liberal International, a political federation for liberal parties * Linux International, an international non-profit organization * Lyndon Institute, an independent high school in the U.S. state of Vermont * The Light Infantry, a British Army infantry regiment Names * Li (surname), including: ** List of people with surname Li ** Li (surname 李), one of the most common surnames in the world ** Li (surname 黎), the 84th most common surname in China ** Li (surname 栗), the 249th most common surname in China ** Li (surname 利), the 299th most common surname in China ** Li (surname 厉), a Chinese surname ** Li (surname 郦), a Chinese surname ** Li (surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhangjiakou
Zhangjiakou (; ; ) also known as Kalgan and by several other names, is a prefecture-level city in northwestern Hebei province in Northern China, bordering Beijing to the southeast, Inner Mongolia to the north and west, and Shanxi to the southwest. By 2019, its population was 4,650,000 inhabitants on , divided into 17 Counties and Districts. The built-up (''or metro'') area made of Qiaoxi, Qiaodong, Chongli, Xuanhua, Xiahuayuan Districts largely being conurbated had 1,500,000 inhabitants in 2019 on . Since ancient times, Zhangjiakou has been a stronghold of military significance and vied for by multiple sides. Hence, Zhangjiakou is nicknamed the Northern Gate of Beijing. Due to its strategic position on several important transport arteries, it is a critical node for travel between Hebei and Inner Mongolia and connecting northwest China, Mongolia, and Beijing. Dajingmen, an important gate and junction of the Great Wall of China is located here. In the south, Zhangjiakou is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana, that is, freedom from ignorance, craving, rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind that includes meditation and instruction in Buddhist ethics such as right effort, mindfulness, and ''jhana''. He die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)