|
Fulham Pottery
The Fulham Pottery was founded in Fulham, London, by John Dwight (potter), John Dwight in 1672, at the junction of New King's Road and Burlington Road, Fulham, not far from Putney Bridge. Dwight is the earliest clearly documented maker of stoneware in England, although immigrant Dutch or German potters were probably active several decades before. By 1690 there was a rival stoneware operation in Fulham, run by the Dutch Elers brothers, who after a few years went off to become important early figures in transforming the Staffordshire pottery industry. In its first years it was a pioneering force in English pottery in several respects, in particular salt-glazed wares and figures. After Dwight's death in 1703 the pottery made less ambitious stonewares until a revival in the later 19th century. It operated on the same site until 1956, and then until at least the 1980s as a base for studio pottery to be fired. Today, all that remains of the original pottery is one large bottle kiln, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulham Pottery, September 2016 01
Fulham () is an area of the London Borough of Hammersmith & Fulham in West London, England, southwest of Charing Cross. It lies on the north bank of the River Thames, bordering Hammersmith, Kensington and Chelsea, London, Chelsea. The area faces Wandsworth, Putney, Barn Elms and the London Wetland Centre in Barnes, London, Barnes. on the far side of the river. First recorded by name in 691, Fulham was a manor and ancient parish which originally included Hammersmith. Between 1900 and 1965, it was the Metropolitan Borough of Fulham, before its merger with the Metropolitan Borough of Hammersmith created the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham (known as the London Borough of Hammersmith from 1965 to 1979). The district is split between the W postcode area, western and SW postcode area, south-western postal areas. Fulham has a history of industry and enterprise dating back to the 15th century, with pottery, tapestry-weaving, paper-making and brewing in the 17th and 18th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of modern chemistry, and one of the pioneers of modern experimental scientific method. He is best known for Boyle's law, which describes the inversely proportional relationship between the absolute pressure and volume of a gas, if the temperature is kept constant within a closed system. Among his works, '' The Sceptical Chymist'' is seen as a cornerstone book in the field of chemistry. He was a devout and pious Anglican and is noted for his writings in theology. Biography Early years Boyle was born at Lismore Castle, in County Waterford, Ireland, the seventh son and fourteenth child of The 1st Earl of Cork ('the Great Earl of Cork') and Catherine Fenton. Lord Cork, then known simply as Richard Boyle, had arrived in Dublin from England i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architectural Ceramics
Architectural terracotta refers to a fired mixture of clay and water that can be used in a non-structural, semi-structural, or structural capacity on the exterior or interior of a building. Terracotta pottery, as earthenware is called when not used for vessels, is an ancient building material that translates from Latin as " baked earth". Some architectural terracotta is actually the stronger stoneware. It can be unglazed, painted, slip glazed, or glazed. A piece of terracotta is composed of a hollow clay web enclosing a void space or cell. The cell can be installed in compression with mortar or hung with metal anchors. All cells are partially backfilled with mortar. By the late 19th century the version with a ceramic glaze, namely glazed architectural terracotta became more popular. Chemistry Terracotta is made of a clay or silt matrix, a fluxing agent, and grog or bits of previously fired clay. Clays are the remnants of weathered rocks that are smaller than 2 microns. They ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
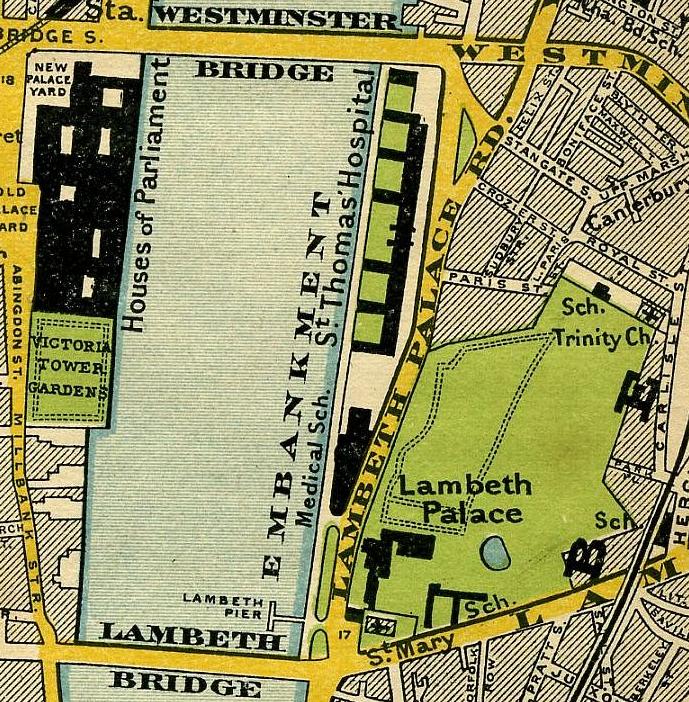
Lambeth
Lambeth () is a district in South London, England, in the London Borough of Lambeth, historically in the County of Surrey. It is situated south of Charing Cross. The population of the London Borough of Lambeth was 303,086 in 2011. The area experienced some slight growth in the medieval period as part of the manor of Lambeth Palace. By the Victorian era the area had seen significant development as London expanded, with dense industrial, commercial and residential buildings located adjacent to one another. The changes brought by World War II altered much of the fabric of Lambeth. Subsequent development in the late 20th and early 21st centuries has seen an increase in the number of high-rise buildings. The area is home to the International Maritime Organization. Lambeth is home to one of the largest Lusophone, Portuguese-speaking communities in the UK, and is the second most commonly spoken language in Lambeth after English language, English. History Medieval The origins of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Doulton
Royal Doulton is an English ceramic and home accessories manufacturer that was founded in 1815. Operating originally in Vauxhall, London, and later moving to Lambeth, in 1882 it opened a factory in Burslem, Stoke-on-Trent, in the centre of English pottery. From the start, the backbone of the business was a wide range of utilitarian wares, mostly stonewares, including storage jars, tankards and the like, and later extending to pipes for drains, lavatories and other bathroom ceramics. From 1853 to 1901, its wares were marked Doulton & Co., then from 1901, when a royal warrant was given, Royal Doulton. It always made some more decorative wares, initially still mostly stoneware, and from the 1860s, the firm made considerable efforts to get a reputation for design, in which it was largely successful, as one of the first British makers of art pottery. Initially this was done through artistic stonewares made in Lambeth, but in 1882 the firm bought a Burslem factory, which was main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doulton & Co
Royal Doulton is an English ceramic and home accessories manufacturer that was founded in 1815. Operating originally in Vauxhall, London, and later moving to Lambeth, in 1882 it opened a factory in Burslem, Stoke-on-Trent, in the centre of English pottery. From the start, the backbone of the business was a wide range of utilitarian wares, mostly stonewares, including storage jars, tankards and the like, and later extending to pipes for drains, lavatories and other bathroom ceramics. From 1853 to 1901, its wares were marked Doulton & Co., then from 1901, when a royal warrant was given, Royal Doulton. It always made some more decorative wares, initially still mostly stoneware, and from the 1860s, the firm made considerable efforts to get a reputation for design, in which it was largely successful, as one of the first British makers of art pottery. Initially this was done through artistic stonewares made in Lambeth, but in 1882 the firm bought a Burslem factory, which was main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Doulton
John Doulton (17 November 1793 – 26 May 1873) was an English businessman and manufacturer of pottery, a founder of the firm that later became known as ''Royal Doulton''. John Doulton married Jane Duneau, a widow from Bridgnorth in Shropshire, who died on 9 April 1841. They had eight children, including Sir Henry, MP Frederick, Josiah and Alfred. Biography In 1815, soon after John Doulton had completed his apprenticeship as a potter at the Fulham Pottery in London, he invested his life savings of £100 in the Vauxhall Walk pottery of Martha Jones, Lambeth. Her foreman, John Watts, was also taken into partnership and the firm became known as ''Jones, Watts and Doulton''. It specialized in industrial ware, brown stoneware, drain pipes as well as stoneware bottles for chemicals, beer, and other industrial liquids among others. Martha Jones withdrew from the partnership in 1820 and the company moved to new premises in Lambeth High Street in 1826. In 1835 John's 15-year-old son Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auckland Museum
The Auckland War Memorial Museum Tāmaki Paenga Hira (or simply the Auckland Museum) is one of New Zealand's most important museums and war memorials. Its collections concentrate on New Zealand history (and especially the history of the Auckland Region), natural history, and military history. The present museum building was constructed in the 1920s in the neo-classicist style, and sits on a grassed plinth (the remains of a dormant volcano) in the Auckland Domain, a large public park close to the Auckland CBD. Auckland Museum's collections and exhibits began in 1852. In 1867 Aucklanders formed a learned society – the Auckland Philosophical Society, later the Auckland Institute. Within a few years the society merged with the museum and '' Auckland Institute and Museum'' was the organisation's name until 1996. Auckland War Memorial Museum was the name of the new building opened in 1929, but since 1996 was more commonly used for the institution as well. From 1991 to 2003 the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For government statistical purposes, it forms part of the East of England region. Hertfordshire covers . It derives its name – via the name of the county town of Hertford – from a hart (stag) and a ford, as represented on the county's coat of arms and on the flag. Hertfordshire County Council is based in Hertford, once the main market town and the current county town. The largest settlement is Watford. Since 1903 Letchworth has served as the prototype garden city; Stevenage became the first town to expand under post-war Britain's New Towns Act of 1946. In 2013 Hertfordshire had a population of about 1,140,700, with Hemel Hempstead, Stevenage, Watford and St Albans (the county's only ''city'') each having between 50,000 and 100,000 r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickmansworth
Rickmansworth () is a town in southwest Hertfordshire, England, about northwest of central London and inside the perimeter of the M25 motorway. The town is mainly to the north of the Grand Union Canal (formerly the Grand Junction Canal) and the River Colne. The town of Watford is to the northeast. Rickmansworth is the administrative seat of the Three Rivers District Council. The confluence of the River Chess and the River Gade with the Colne in Rickmansworth inspired the district's name. The enlarged Colne flows south to form a major tributary of the River Thames. The town is served by the Metropolitan line of the London Underground and Chiltern Railways from London Marylebone to Aylesbury railway station. Toponymy The name Rickmansworth comes from the Saxon name ''Ryckmer'', the local landowner, and ''worth'' meaning a farm or stockade. In the Domesday Book of 1086 it was recorded as the Manor of Prichemaresworde. Other spellings include Rykemarwurthe (1119–46), Richema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like series of pictures called "modern moral subjects", and he is perhaps best known for his series ''A Harlot's Progress'', ''A Rake's Progress'' and '' Marriage A-la-Mode''. Knowledge of his work is so pervasive that satirical political illustrations in this style are often referred to as "Hogarthian". Hogarth was born in London to a lower-middle-class family. In his youth he took up an apprenticeship with an engraver, but did not complete the apprenticeship. His father underwent periods of mixed fortune, and was at one time imprisoned in lieu of outstanding debts, an event that is thought to have informed William's paintings and prints with a hard edge. Influenced by French and Italian painting and engraving, Hogarth's works are mostly sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

