|
Frederick Hamilton (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Frederick Tower Hamilton (8 March 1856 – 4 October 1917) was a senior Royal Navy officer who went on to be Second Sea Lord and Chief of Naval Personnel. Naval career Hamilton joined the Royal Navy in 1869 as a cadet on the training ship Britannia. He fought in Naval Brigade in the Zulu War in 1879, for which service he was mentioned in despatches. After promotion to Lieutenant he specialised into the Torpedo Branch and in 1884 after training was appointed a staff officer at the Torpedo Schoolship HMS Vernon. In 1892 he was promoted to commander and serving aboard the battleship HMS ''Hood''. He was appointed in command of the torpedo school ship HMS ''Defiance'' at Devonport on 1 November 1897, promoted to captain on 1 January 1898, and re-appointed in command of the ''Defiance'' the same day. On 18 March 1902 he was appointed flag captain of the battleship HMS ''Bulwark'', which in May was to become flagship of Admiral Sir Compton Domvile, Commander-in-Chief ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Dodd (artist)
Francis Edgar Dodd (29 November 1874 – 7 March 1949) was a British portrait painter, landscape artist and printmaker. Biography Dodd was born in Holyhead, Anglesey, Wales, the son of a Wesleyan minister. He trained at the Glasgow School of Art alongside Muirhead Bone, who married Dodd's sister, Gertrude. At Glasgow, Dodd won the Haldane Scholarship in 1893 and then travelled around France, Italy and later Spain. Dodd returned to England in 1895 and settled in Manchester, becoming friends with Charles Holden, before moving to Blackheath in London in 1904. During World War I, in 1916, he was appointed an official war artist by Charles Masterman, the head of the War Propaganda Bureau, WPB. Serving on the Western Front, he produced more than 30 portraits of senior military figures. However, he also earned a considerable peacetime reputation for the quality of his watercolours and portrait commissions. He was appointed a trustee of the Tate Gallery in 1929, a position he held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
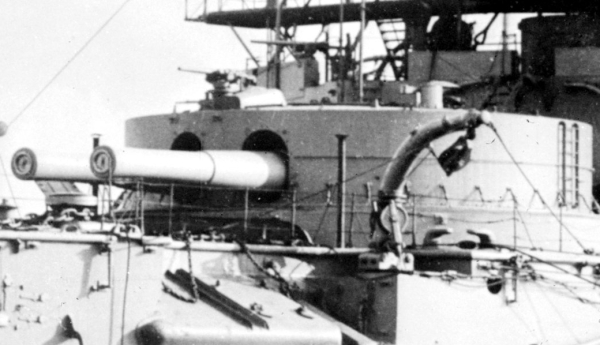
HMS Hood (1891)
HMS ''Hood'' was a modified pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Royal Navy in the early 1890s. She differed from the other ships of the class in that she had cylindrical gun turrets instead of barbettes and a lower freeboard. She served most of her active career in the Mediterranean Sea, where her low freeboard was less of a disadvantage. The ship was placed in reserve in 1907 and later became the receiving ship at Queenstown, Ireland. ''Hood'' was used in the development of anti-torpedo bulges in 1913 and was scuttled in late 1914 to act as a blockship across the southern entrance of Portland Harbour after the start of World War I. Design ''Hood'', the last of the eight ''Royal Sovereign''-class battleships to be built, differed significantly from the other ships of her class in that she had a forward freeboard of only compared to of the other ships. The ''Royal Sovereign''s had reverted to a higher freeboard after several classes of low-freeboard vessel had been cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea, with The Wash to the north-west. The county town is the city of Norwich. With an area of and a population of 859,400, Norfolk is a largely rural county with a population density of 401 per square mile (155 per km2). Of the county's population, 40% live in four major built up areas: Norwich (213,000), Great Yarmouth (63,000), King's Lynn (46,000) and Thetford (25,000). The Broads is a network of rivers and lakes in the east of the county, extending south into Suffolk. The area is protected by the Broads Authority and has similar status to a national park. History The area that was to become Norfolk was settled in pre-Roman times, (there were Palaeolithic settlers as early as 950,000 years ago) with camps along the highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Lynn
King's Lynn, known until 1537 as Bishop's Lynn and colloquially as Lynn, is a port and market town in the borough of King's Lynn and West Norfolk in the county of Norfolk, England. It is located north of London, north-east of Peterborough, north-north-east of Cambridge and west of Norwich. History Toponymy The etymology of King's Lynn is uncertain. The name ''Lynn'' may signify a body of water near the town – the Welsh word means a lake; but the name is plausibly of Anglo-Saxon origin, from ''lean'' meaning a tenure in fee or farm. As the 1085 Domesday Book mentions saltings at Lena (Lynn), an area of partitioned pools may have existed there at the time. Other places with Lynn in the name include Dublin, Ireland. An Dubh Linn....the Black Pool. The presence of salt, which was relatively rare and expensive in the early medieval period, may have added to the interest of Herbert de Losinga and other prominent Normans in the modest parish. The town was named ''Len '' (Bis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fife
Fife (, ; gd, Fìobha, ; sco, Fife) is a council area, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. It is situated between the Firth of Tay and the Firth of Forth, with inland boundaries with Perth and Kinross (i.e. the historic counties of Perthshire and Kinross-shire) and Clackmannanshire. By custom it is widely held to have been one of the major Pictish kingdoms, known as ''Fib'', and is still commonly known as the Kingdom of Fife within Scotland. A person from Fife is known as a ''Fifer''. In older documents the county was very occasionally known by the anglicisation Fifeshire. Fife is Scotland's third largest local authority area by population. It has a resident population of just under 367,000, over a third of whom live in the three principal towns, Dunfermline, Kirkcaldy and Glenrothes. The historic town of St Andrews is located on the northeast coast of Fife. It is well known for the University of St Andrews, the most ancient univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, or fleet admiral. Etymology The word in Middle English comes from Anglo-French , "commander", from Medieval Latin , . These evolved from the Arabic () – (), “king, prince, chief, leader, nobleman, lord, a governor, commander, or person who rules over a number of people,” and (), the Arabic article answering to “the.” In Arabic, admiral is also represented as (), where () means the sea. The 1818 edition of Samuel Johnson's '' A Dictionary of the English Language'', edited and revised by the Rev. Henry John Todd, states that the term “has been traced to the Arab. emir or amir, lord or commander, and the Gr. , the sea, q. d. ''prince of the sea''. The word is written both with and without the d, in other languages, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward VII Of The United Kingdom
Edward VII (Albert Edward; 9 November 1841 – 6 May 1910) was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and Emperor of India, from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910. The second child and eldest son of Queen Victoria and Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, and nicknamed "Bertie", Edward was related to royalty throughout Europe. He was Prince of Wales and heir apparent to the British throne for almost 60 years. During the long reign of his mother, he was largely excluded from political influence and came to personify the fashionable, leisured elite. He travelled throughout Britain performing ceremonial public duties and represented Britain on visits abroad. His tours of North America in 1860 and of the Indian subcontinent in 1875 proved popular successes, but despite public approval, his reputation as a playboy prince soured his relationship with his mother. As king, Edward played a role in the modernisation of the British Home Fleet and the reorganis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Fleet
The British Mediterranean Fleet, also known as the Mediterranean Station, was a formation of the Royal Navy. The Fleet was one of the most prestigious commands in the navy for the majority of its history, defending the vital sea link between the United Kingdom and the majority of the British Empire in the Eastern Hemisphere. The first Commander-in-Chief for the Mediterranean Fleet was the appointment of General at Sea Robert Blake in September 1654 (styled as Commander of the Mediterranean Fleet). The Fleet was in existence until 1967. Pre-Second World War The Royal Navy gained a foothold in the Mediterranean Sea when Gibraltar was captured by the British in 1704 during the War of Spanish Succession, and formally allocated to Britain in the 1713 Treaty of Utrecht. Though the British had maintained a naval presence in the Mediterranean before, the capture of Gibraltar allowed the British to establish their first naval base there. The British also used Port Mahon, on the isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compton Domvile (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Compton Edward Domvile, (10 October 1842 – 19 November 1924) was a distinguished Royal Navy officer in the Edwardian and Victorian eras. Early life Compton Domvile was born on 10 October 1842 to Henry Barry Domvile (1813–1843) and Frances Domvile (née Winnington-Ingram) (d 1884). He was educated at the Royal Academy, Gosport. Career Early career Compton Domvile joined the Royal Navy in 1856. He served in the Royal Yacht and was promoted to lieutenant on 28 October 1862. He commanded the steam-gunboat HMS ''Algerine'' from 16 April 1866 and was promoted to commander on 2 September 1868 for service against piracy. HMS ''Dryad'' On 3 August 1874 he became captain of the screw sloop HMS ''Dryad'' from commissioning at Devonport. ''Dryad'' served on the North America and West Indies Station until December 1877. Domvile was promoted to captain on 27 March 1876, whilst serving in ''Dryad''. Commander John Edward Stokes replaced him as ''Dryad''s captain some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Bulwark (1899)
HMS ''Bulwark'' was one of five pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Royal Navy at the end of the 19th century. The ''London''s were a sub-class of the pre-dreadnoughts. Completed in 1902 she was initially assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet as its flagship. The ship then served with the Channel and Home Fleets from 1907 to 1910, usually as a flagship. From 1910 to 1914, she was in reserve in the Home Fleet. Following the start of the First World War in August 1914, ''Bulwark'', along with the rest of the squadron, was attached to the reformed Channel Fleet to protect the British Expeditionary Force as it moved across the English Channel to France. On 26 November 1914 she was destroyed by a large internal explosion with the loss of 741 men near Sheerness; only a dozen men survived the detonation. It was probably caused by the overheating of cordite charges that had been placed adjacent to a boiler-room bulkhead. Little of the ship survived to be salvaged and her rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Captain
In the Royal Navy, a flag captain was the captain of an admiral's flagship. During the 18th and 19th centuries, this ship might also have a "captain of the fleet", who would be ranked between the admiral and the "flag captain" as the ship's "First Captain", with the "flag captain" as the ship's "Second Captain". Unlike a "captain of the fleet", a flag-captain was generally a fairly junior post-captain Post-captain is an obsolete alternative form of the rank of Captain (Royal Navy), captain in the Royal Navy. The term served to distinguish those who were captains by rank from: * Officers in command of a naval vessel, who were (and still are) ..., as he had the admiral to keep an eye on him, but – like a "captain of the fleet" – a "flag captain" was a post rather than a rank. References F Royal Navy {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

