|
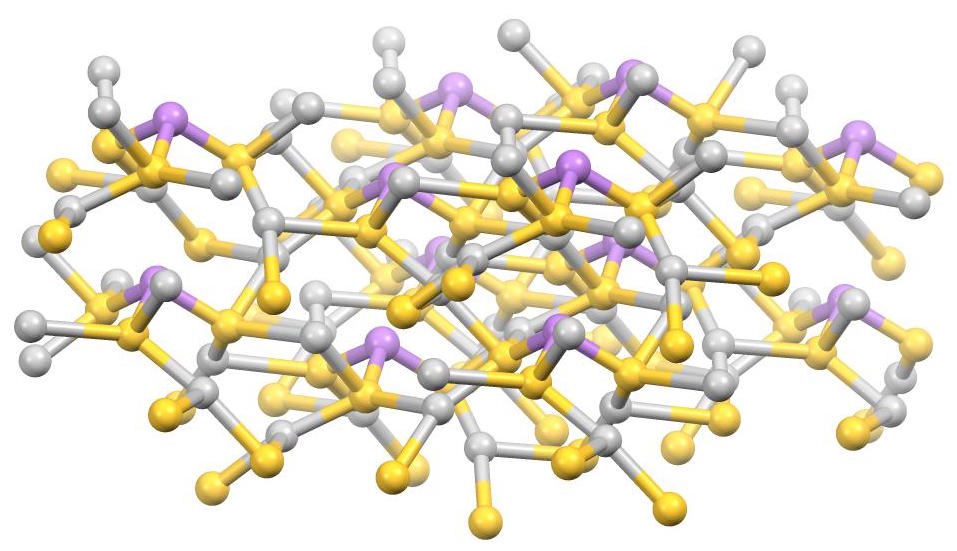
Freieslebenite
Freieslebenite is a sulfosalt mineral composed of antimony, lead, and silver. Sulfosalt minerals are complex sulfide minerals with the formula: AmBnSp. The formula of freieslebenite is AgPbSbS3. Freieslebenite was discovered in approximately 1773 in the Himmelsfurst mines of Freiberg, Saxony, Germany. The mineral was initially called Schilf-Glaserz; however, in 1845 it was given the current name Freieslebenite after the Mining Commissioner of Saxony, Johann Carl Freiesleben (1774–1846).(Palache ''et al.'', 1944) Structure Freieslebenite is a superstructure of a PbS-type substructure. The crystal structure is monoclinic with a space group P21/a, with a = 7.518(1), b = 12.809(4), c = 5.940(1) Å, β = 92.25(1)° and Z = 4(Ito, 1973). Sb has a trigonal-pyramidal coordination of S atoms, this structure isolates the SbS3 pyramids from themselves. The Sb–S distances are 2.431, 2.453 and 2.480(4) Å. Six S atoms are coordinated with Pb in a distorted octahedral arrangement. The Pb–S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfosalt Minerals
Sulfosalt minerals are sulfide minerals with the general formula , where *A represents a metal such as copper, lead, silver, iron, and rarely mercury (element), mercury, zinc, vanadium *B usually represents semi-metal such as arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and rarely germanium, or metals like tin and rarely vanadium *X is sulfur or rarely selenium and/or tellurium. The Strunz classification includes the sulfosalts in a ''sulfides and sulfosalts'' superclass. A group which have similar appearing formulas are the Sulfarsenide mineral, sulfarsenides (for example cobaltite (Co,Fe)AsS). In sulfarsenides the arsenic substitutes for sulfide anions whereas in the sulfosalts the arsenic substitutes for a metal cation.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut (1985). ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York . About 200 sulfosalt minerals are known. Examples include: File:Proustite (long prismatic crystal) - Chanarcillo, Copiapo Province, Atacama Region, Chile.jpg, As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfosalt
Sulfosalt minerals are sulfide minerals with the general formula , where *A represents a metal such as copper, lead, silver, iron, and rarely mercury, zinc, vanadium *B usually represents semi-metal such as arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and rarely germanium, or metals like tin and rarely vanadium *X is sulfur or rarely selenium and/or tellurium. The Strunz classification includes the sulfosalts in a ''sulfides and sulfosalts'' superclass. A group which have similar appearing formulas are the sulfarsenides (for example cobaltite (Co,Fe)AsS). In sulfarsenides the arsenic substitutes for sulfide anions whereas in the sulfosalts the arsenic substitutes for a metal cation.Klein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut (1985). ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., John Wiley and Sons, New York . About 200 sulfosalt minerals are known. Examples include: File:Proustite (long prismatic crystal) - Chanarcillo, Copiapo Province, Atacama Region, Chile.jpg, As illustrated by this specimen of proustite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minerals Named After People
This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition follows name. A *Abelsonite: C31H32N4Ni – American physicist Philip Hauge Abelson (1913–2004)alfred *Abswurmbachite: Cu2+Mn3+6O8SiO4 – German mineralogist Irmgard Abs-Wurmbach * Adamite: Zn2AsO4OH – French mineralogist Gilbert Joseph Adam (1795–1881) *Agrellite: NaCa2Si4O10F – English optical mineralogist Stuart Olof Agrell (1913–1996) * Agricolaite: K4(UO2)(CO3)3 – German scholar Georgius Agricola (1494–1555) * Aheylite: Fe2+Al6 (PO4)2sub>2·4H2O – American geologist Allen V. Heyl (1918–2008) * Albrechtschraufite: Ca4Mg(UO2)2(CO3)6F2·17H2O – Albrecht Schrauf (1837–1897), professor of mineralogy, University of Vienna * Alexandrite (variety of chrysoberyl): – Tsar Alexander II of Russia (1818–1881) *Alforsite: Ba5Cl(PO4)3 – American geologist John T. Alfors (1930–2005) *Allabogdanite: (Fe,Ni)2P – Alla Bogdanova, Geological Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Minerals
This is a list of minerals for which there are articles on Wikipedia. Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish the various ''species''. Within a mineral species there may be variation in physical properties or minor amounts of impurities that are recognized by mineralogists or wider society as a mineral ''variety''. Mineral variety names are listed after the valid minerals for each letter. For a more complete listing of all mineral names, see List of minerals recognized by the International Mineralogical Association. A :Varieties that are not valid species: *Adamantine spar (variety of corundum) *Agate (variety of chalcedony and quartz) *Alabaster (variety of gypsum) *Alexandrite (variety of chrysoberyl) *Allingite (synonym of amber) *Alum *Amazonite (variety of microcline) *Amethyst (purple variety of quartz) *Ametrine (variety of quartz) *Ammolite (organic; also a gems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Carl Freiesleben
Johann Karl Freiesleben (14 June 1774 – 20 March 1846) was a German mineralogist and mining commissioner in Saxony. He was a childhood friend and correspondent of Alexander von Humboldt and was a promoter of stratigraphy and geognosy as taught by Abraham Gottlob Werner. The mineral Freieslebenite is named in his honour. Freiesleben was born in Freiberg, Saxony, in a mining family. He went to study at the mining academy in 1790 where he became a favourite student of Abraham Gottlob Werner. He also became a friend of Alexander von Humboldt at the academy. Along with Christian Leopold von Buch, he travelled through Saxony and Thuringia and reported on it in a mining journal in 1792. He travelled with Humboldt to Bohemia and the Swiss Alps. In 1795 he discussed with Humboldt, they compared the rocks of Thuringia with those in the Swiss alps and concluded that they corresponded stratigraphically and called it Jura limestone which is no longer considered correct. He studied jurisprudenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentite
In mineralogy, argentite (from the Latin ''argentum'', silver) is cubic silver sulfide (Ag2S), which can only exist at temperatures above 173 °C, 177 °C or 179 °C. When it cools to ordinary temperatures it turns into its monoclinic polymorph, acanthite. The International Mineralogical Association has decided to reject argentite as a proper mineral. The name "argentite" sometimes also refers to pseudomorphs of argentite: specimens of acanthite which still display some of the outward signs of the cubic crystal form, even though their actual crystal structure is monoclinic due to the lower temperature. This form of acanthite is occasionally found as uneven cubes and octahedra, but more often as dendritic or earthy masses, with a blackish lead-grey color and metallic luster. Argentite belongs to the galena group. Cleavage, which is so prominent a feature in galena, here presents only in traces. The mineral is perfectly sectile and has a shining streak; hardness 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antimony Minerals
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from la, stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name kohl. The earliest known description of the metal in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio. China is the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine in Hunan. The industrial methods for refining antimony from stibnite are roasting followed by reduction with carbon, or direct reduction of stibnite with iron. The largest applications for metallic antimony are in alloys with lead and tin, which have improved properties for solders, bullets, and plain bearings. It improves the rigidity of lead-alloy plates in lead–acid batteries. Antimony trioxide is a prominent additive for halog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Minerals
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of the seven metals of antiquity, silver has had an enduring role in most human cultures. Other than in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Minerals
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited to organolead compounds. Like the lighter members of the group, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramayoite
Aramayoite ( IMA symbol: Ary) is a mineral with the chemical formula . Its type locality is Sud Chichas, Potosí, Bolivia. on mindat.org
Mindat.org is a non-commercial online database, claiming to be the largest mineral database and mineralogy, mineralogical reference website on the Internet. It is used by professional mineralogists, geologists, and amateur mineral collecting, mi ...

References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polybasite
Polybasite is a sulfosalt mineral of silver, copper, antimony and arsenic. Its chemical formula is . It forms black monoclinic crystals (thin, tabular, with six corners) which can show dark red internal reflections. It has a Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3. It is found worldwide and is an ore of silver. The name comes from the number of base metals in the mineral. Images File:Polybasite-tmu16a.jpg, Unusual polybasite specimen from Mayo Mining District, Yukon Territory Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ..., Canada. References Silver minerals Copper(I) minerals Antimony minerals Arsenic minerals Sulfosalt minerals Monoclinic minerals Minerals in space group 15 {{Sulfide-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freibergite
Freibergite is a complex sulfosalt mineral of silver, copper, iron, antimony and arsenic with formula . It has cubic crystals and is formed in hydrothermal deposits. It forms one solid solution series with tetrahedrite and another with argentotennantite. Freibergite is an opaque, metallic steel grey to black and leaves a reddish-black streak. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 to 4.0 and a specific gravity of 4.85 - 5. It is typically massive to granular in habit with no cleavage and an irregular fracture. The mineral was first described in 1853 from an occurrence in the silver mines of the type locality at Freiberg, Saxony Freiberg is a university and former mining town in Saxony, Germany. It is a so-called ''Große Kreisstadt'' (large county town) and the administrative centre of Mittelsachsen district. Its historic town centre has been placed under heritage c .... References Mineral handbook [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |