Antimony Minerals on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Antimony is a


 Antimony is a member of group 15 of the periodic table, one of the elements called
Antimony is a member of group 15 of the periodic table, one of the elements called
 The abundance of antimony in the
The abundance of antimony in the
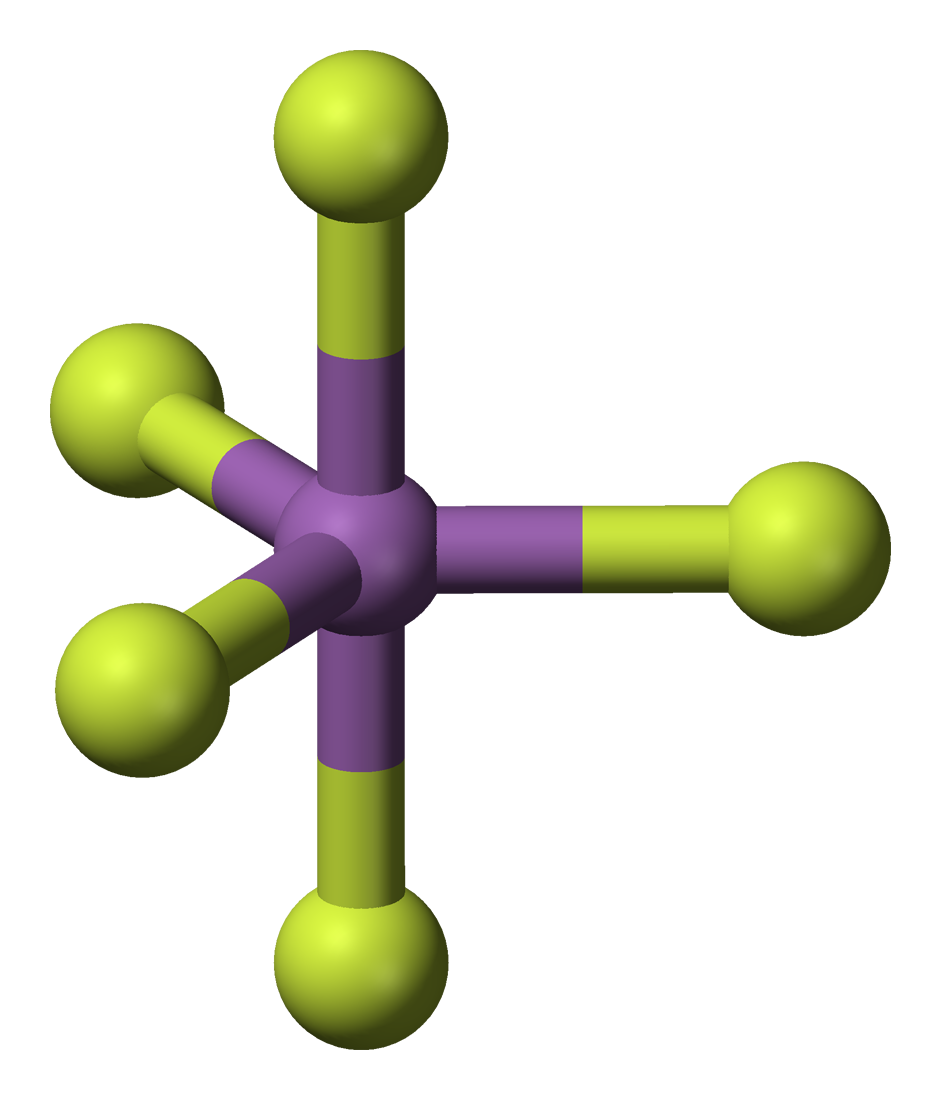 The pentahalides and have
The pentahalides and have

 Antimony was frequently described in alchemical manuscripts, including the ''Summa Perfectionis'' of Pseudo-Geber, written around the 14th century. A description of a procedure for isolating antimony is later given in the 1540 book '' De la pirotechnia'' by Vannoccio Biringuccio, predating the more famous 1556 book by Agricola, '' De re metallica''. In this context Agricola has been often incorrectly credited with the discovery of metallic antimony. The book ''Currus Triumphalis Antimonii'' (The Triumphal Chariot of Antimony), describing the preparation of metallic antimony, was published in Germany in 1604. It was purported to be written by a
Antimony was frequently described in alchemical manuscripts, including the ''Summa Perfectionis'' of Pseudo-Geber, written around the 14th century. A description of a procedure for isolating antimony is later given in the 1540 book '' De la pirotechnia'' by Vannoccio Biringuccio, predating the more famous 1556 book by Agricola, '' De re metallica''. In this context Agricola has been often incorrectly credited with the discovery of metallic antimony. The book ''Currus Triumphalis Antimonii'' (The Triumphal Chariot of Antimony), describing the preparation of metallic antimony, was published in Germany in 1604. It was purported to be written by a
O34:D46-G17-F21:D4
The Greek word, στίμμι (stimmi) is used by


Public Health Statement for Antimony
International Antimony Association vzw (i2a
Chemistry in its element podcast
(MP3) from the
Antimony
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Antimony
Antimony Mineral data and specimen images
{{Authority control Chemical elements Metalloids Native element minerals Nuclear materials Pnictogens Trigonal minerals Minerals in space group 166 Materials that expand upon freezing Chemical elements with rhombohedral structure
chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
with the symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
Sb (from la, stibium
Antimony is a chemical element with the symbol Sb (from la, stibium) and atomic number 51. A lustrous gray metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient time ...
) and atomic number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every ...
51. A lustrous gray metalloid
A metalloid is a type of chemical element which has a preponderance of material property, properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals. There is no standard definition of a metalloid and no complete agreement on ...
, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite (Sb2S3). Antimony compounds have been known since ancient times and were powdered for use as medicine and cosmetics, often known by the Arabic name kohl
Kohl may refer to:
*Kohl (cosmetics), an ancient eye cosmetic
*Kohl (surname), including a list of people with the surname
*Kohl's
Kohl's (stylized in all caps) is an American department store retail chain, operated by Kohl's Corporation. ...
. The earliest known description of the metal in the West was written in 1540 by Vannoccio Biringuccio.
China is the largest producer of antimony and its compounds, with most production coming from the Xikuangshan Mine
Xikuangshan mine () in Lengshuijiang, Hunan, China, contains the world's largest deposit of antimony. It is unique in that there is a large deposit of stibnite (Sb2S3) in a layer of Devonian limestone. There are three mineral beds which are between ...
in Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to ...
. The industrial methods for refining antimony from stibnite are roasting
Roasting is a cooking method that uses dry heat where hot air covers the food, cooking it evenly on all sides with temperatures of at least from an open flame, oven, or other heat source. Roasting can enhance the flavor through caramelization ...
followed by reduction with carbon, or direct reduction of stibnite with iron.
The largest applications for metallic antimony are in alloys with lead and tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, which have improved properties for solders, bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and co ...
s, and plain bearings. It improves the rigidity of lead-alloy plates in lead–acid batteries. Antimony trioxide
Antimony(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb2O3. It is the most important commercial compound of antimony. It is found in nature as the minerals valentinite and senarmontite. Like most polymeric oxides, Sb2O3 dissolves in a ...
is a prominent additive for halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is ...
-containing flame retardants. Antimony is used as a dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. When ...
in semiconductor device
A semiconductor device is an electronic component that relies on the electronic properties of a semiconductor material (primarily silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, as well as organic semiconductors) for its function. Its conductivity li ...
s.
Characteristics
Properties

 Antimony is a member of group 15 of the periodic table, one of the elements called
Antimony is a member of group 15 of the periodic table, one of the elements called pnictogen
A pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group 15 is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group 15 consists of the ele ...
s, and has an electronegativity of 2.05. In accordance with periodic trends, it is more electronegative than tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
or bismuth, and less electronegative than tellurium
Tellurium is a chemical element with the symbol Te and atomic number 52. It is a brittle, mildly toxic, rare, silver-white metalloid. Tellurium is chemically related to selenium and sulfur, all three of which are chalcogens. It is occasionally fou ...
or arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
. Antimony is stable in air at room temperature, but reacts with oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
if heated to produce antimony trioxide
Antimony(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb2O3. It is the most important commercial compound of antimony. It is found in nature as the minerals valentinite and senarmontite. Like most polymeric oxides, Sb2O3 dissolves in a ...
, Sb2O3.
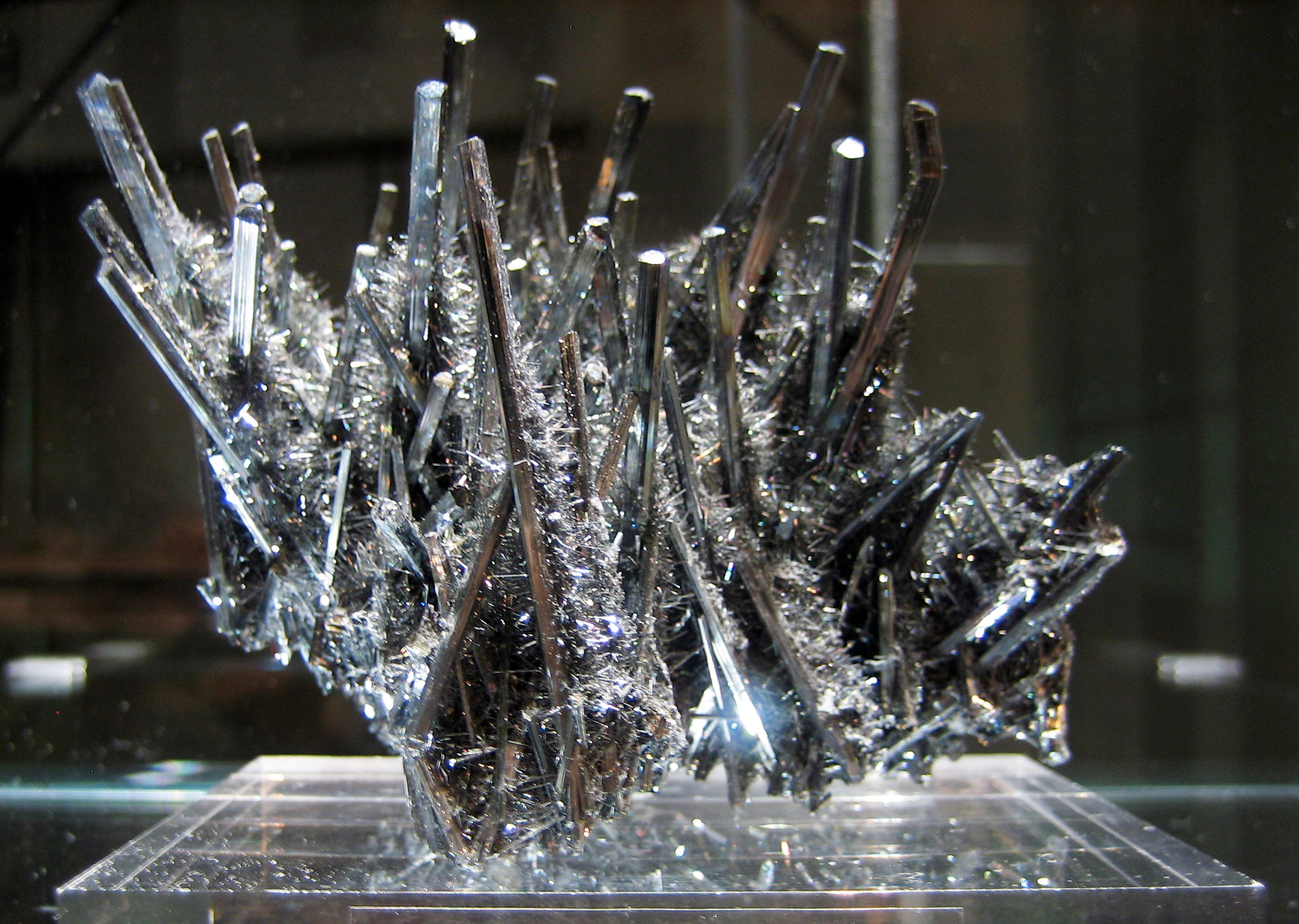
Antimony is a silvery, lustrous gray metalloid with a Mohs scale
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by th ...
hardness of 3, which is too soft to mark hard objects. Coins of antimony were issued in China's Guizhou
Guizhou (; formerly Kweichow) is a landlocked province in the southwest region of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Guiyang, in the center of the province. Guizhou borders the autonomous region of Guangxi to t ...
province in 1931; durability was poor, and minting was soon discontinued. Antimony is resistant to attack by acids.
Four allotropes
Allotropy or allotropism () is the property of some chemical elements to exist in two or more different forms, in the same physical state, known as allotropes of the elements. Allotropes are different structural modifications of an element: the ...
of antimony are known: a stable metallic form, and three metastable forms (explosive, black, and yellow). Elemental antimony is a brittle, silver-white, shiny metalloid. When slowly cooled, molten antimony crystallizes into a trigonal cell, isomorphic
In mathematics, an isomorphism is a structure-preserving mapping between two structures of the same type that can be reversed by an inverse mapping. Two mathematical structures are isomorphic if an isomorphism exists between them. The word is ...
with the gray allotrope of arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
. A rare explosive form of antimony
Explosive antimony is an allotrope of the chemical element antimony that is so sensitive to shock that it explodes when scratched or subjected to sudden heating. The allotrope was first described in 1855.
Chemists form the allotrope through elec ...
can be formed from the electrolysis of antimony trichloride
Antimony trichloride is the chemical compound with the formula SbCl3. It is a soft colorless solid with a pungent odor and was known to alchemists as butter of antimony.
Preparation
Antimony trichloride is prepared by reaction of chlorine with an ...
. When scratched with a sharp implement, an exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e ...
reaction occurs and white fumes are given off as metallic antimony forms; when rubbed with a pestle in a mortar, a strong detonation occurs. Black antimony is formed upon rapid cooling of antimony vapor. It has the same crystal structure as red phosphorus
Elemental phosphorus can exist in several allotropes, the most common of which are white and red solids. Solid violet and black allotropes are also known. Gaseous phosphorus exists as diphosphorus and atomic phosphorus.
White phosphorus
White ...
and black arsenic; it oxidizes in air and may ignite spontaneously. At 100 °C, it gradually transforms into the stable form. The yellow allotrope of antimony is the most unstable; it has been generated only by oxidation of stibine
Stibine (IUPAC name: stibane) is a chemical compound with the formula SbH3. A pnictogen hydride, this colourless, highly toxic gas is the principal covalent hydride of antimony, and a heavy analogue of ammonia. The molecule is pyramidal with H–S ...
(SbH3) at −90 °C. Above this temperature and in ambient light, this metastable allotrope transforms into the more stable black allotrope.
Elemental antimony adopts a layered structure ( space group Rm No. 166) whose layers consist of fused, ruffled, six-membered rings. The nearest and next-nearest neighbors form an irregular octahedral complex, with the three atoms in each double layer slightly closer than the three atoms in the next. This relatively close packing leads to a high density of 6.697 g/cm3, but the weak bonding between the layers leads to the low hardness and brittleness of antimony.
Isotopes
Antimony has two stableisotope
Isotopes are two or more types of atoms that have the same atomic number (number of protons in their nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemical element), and that differ in nucleon numbers (mass numbers) ...
s: 121Sb with a natural abundance of 57.36% and 123Sb with a natural abundance of 42.64%. It also has 35 radioisotopes, of which the longest-lived is 125Sb with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
of 2.75 years. In addition, 29 metastable states have been characterized. The most stable of these is 120m1Sb with a half-life
Half-life (symbol ) is the time required for a quantity (of substance) to reduce to half of its initial value. The term is commonly used in nuclear physics to describe how quickly unstable atoms undergo radioactive decay or how long stable ato ...
of 5.76 days. Isotopes that are lighter than the stable 123Sb tend to decay by β+ decay, and those that are heavier tend to decay by β− decay, with some exceptions.
Occurrence
 The abundance of antimony in the
The abundance of antimony in the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's crust is estimated to be 0.2 to 0.5 parts per million, comparable to thallium
Thallium is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tl and atomic number 81. It is a gray post-transition metal that is not found free in nature. When isolated, thallium resembles tin, but discolors when exposed to air. Chemists W ...
at 0.5 parts per million and silver at 0.07 ppm. Even though this element is not abundant, it is found in more than 100 mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
species. Antimony is sometimes found natively (e.g. on Antimony Peak), but more frequently it is found in the sulfide stibnite (Sb2S3) which is the predominant ore mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
.
Compounds
Antimony compounds are often classified according to their oxidation state: Sb(III) and Sb(V). The +5oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
is more stable.
Oxides and hydroxides
Antimony trioxide
Antimony(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb2O3. It is the most important commercial compound of antimony. It is found in nature as the minerals valentinite and senarmontite. Like most polymeric oxides, Sb2O3 dissolves in a ...
is formed when antimony is burnt in air. In the gas phase, the molecule of the compound is , but it polymerizes upon condensing. Antimony pentoxide () can be formed only by oxidation with concentrated nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
. Antimony also forms a mixed-valence oxide, antimony tetroxide
Antimony tetroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula Sb2O4. This material, which exists as the mineral cervantite, is white but reversibly yellows upon heating. The material, with empirical formula SbO2, is called antimony tetroxide to s ...
(), which features both Sb(III) and Sb(V). Unlike oxides of phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
and arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
, these oxides are amphoteric, do not form well-defined oxoacids, and react with acids to form antimony salts.
Antimonous acid is unknown, but the conjugate base sodium antimonite () forms upon fusing sodium oxide
Sodium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2 O. It is used in ceramics and glasses. It is a white solid but the compound is rarely encountered. Instead "sodium oxide" is used to describe components of various materials such as glass ...
and . Transition metal antimonites are also known. Antimonic acid exists only as the hydrate , forming salts as the antimonate anion . When a solution containing this anion is dehydrated, the precipitate contains mixed oxides.
Many antimony ores are sulfides, including stibnite (), pyrargyrite (), zinkenite, jamesonite
Jamesonite is a sulfosalt mineral, a lead, iron, antimony sulfide with formula Pb4FeSb6S14. With the addition of manganese it forms a series with benavidesite.http://rruff.geo.arizona.edu/doclib/hom/jamesonite.pdf Handbook of Mineralogy It is a ...
, and boulangerite
Boulangerite is an uncommon monoclinic orthorhombic sulfosalt mineral, lead antimony sulfide, formula Pb5Sb4S11. It was named in 1837 in honor of French mining engineer Charles Boulanger (1810–1849),http://www.mindat.org/min-738.html Mindat and ...
. Antimony pentasulfide is non-stoichiometric
In chemistry, non-stoichiometric compounds are chemical compounds, almost always solid inorganic compounds, having elemental composition whose proportions cannot be represented by a ratio of small natural numbers (i.e. an empirical formula); mos ...
and features antimony in the +3 oxidation state
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. C ...
and S–S bonds. Several thioantimonides are known, such as and .
Halides
Antimony forms two series ofhalide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fluor ...
s: and . The trihalides , , , and are all molecular compounds having trigonal pyramidal molecular geometry
In chemistry, a trigonal pyramid is a molecular geometry with one atom at the apex and three atoms at the corners of a trigonal base, resembling a tetrahedron (not to be confused with the tetrahedral geometry). When all three atoms at the corners ...
.
The trifluoride is prepared by the reaction of with HF:
: + 6 HF → 2 + 3
It is Lewis acid
A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any sp ...
ic and readily accepts fluoride ions to form the complex anions and . Molten is a weak electrical conductor. The trichloride is prepared by dissolving in hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
:
: + 6 HCl → 2 + 3
 The pentahalides and have
The pentahalides and have trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry
In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identi ...
in the gas phase, but in the liquid phase, is polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
ic, whereas is monomeric. is a powerful Lewis acid used to make the superacid
In chemistry, a superacid (according to the classical definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (), which has a Hammett acidity function (''H''0) of −12. According to the modern definition, a superacid ...
fluoroantimonic acid
Fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, containing various cations and anions (the simplest being and ). This substance is a superacid that can be over a billion times stronger than 100% pure sulfuri ...
("H2SbF7").
Oxyhalides
In chemistry, molecular oxohalides (oxyhalides) are a group of chemical compounds in which both oxygen and halogen atoms are attached to another chemical element A in a single molecule. They have the general formula , where X = fluorine (F), ch ...
are more common for antimony than for arsenic and phosphorus. Antimony trioxide
Antimony(III) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Sb2O3. It is the most important commercial compound of antimony. It is found in nature as the minerals valentinite and senarmontite. Like most polymeric oxides, Sb2O3 dissolves in a ...
dissolves in concentrated acid to form oxoantimonyl compounds such as SbOCl and .
Antimonides, hydrides, and organoantimony compounds
Compounds in this class generally are described as derivatives of Sb3−. Antimony forms antimonides with metals, such as indium antimonide (InSb) and silver antimonide (). The alkali metal and zinc antimonides, such as Na3Sb and Zn3Sb2, are more reactive. Treating these antimonides with acid produces the highly unstable gasstibine
Stibine (IUPAC name: stibane) is a chemical compound with the formula SbH3. A pnictogen hydride, this colourless, highly toxic gas is the principal covalent hydride of antimony, and a heavy analogue of ammonia. The molecule is pyramidal with H–S ...
, :
: + 3 →
Stibine can also be produced by treating salts with hydride reagents such as sodium borohydride. Stibine decomposes spontaneously at room temperature. Because stibine has a positive heat of formation
In chemistry and thermodynamics, the standard enthalpy of formation or standard heat of formation of a compound is the change of enthalpy during the formation of 1 mole of the substance from its constituent elements in their reference state, with ...
, it is thermodynamically unstable and thus antimony does not react with hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
directly.Greenwood, N. N.; & Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd Edn.), Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. .
Organoantimony compounds Organoantimony chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing a carbon to antimony (Sb) chemical bond. Relevant oxidation states are Sb(V) and Sb(III). The toxicity of antimony limits practical application in organic chemistry.
Organoantimony ...
are typically prepared by alkylation of antimony halides with Grignard reagent
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide ...
s. A large variety of compounds are known with both Sb(III) and Sb(V) centers, including mixed chloro-organic derivatives, anions, and cations. Examples include Sb(C6H5)3 (triphenylstibine
Triphenylstibine is the chemical compound with the formula Sb(C6H5)3. Abbreviated SbPh3, this colourless solid is often considered the prototypical organoantimony compound. It is used as a ligand in coordination chemistry and as a reagent in orga ...
), Sb2(C6H5)4 (with an Sb-Sb bond), and cyclic b(C6H5)sub>n. Pentacoordinated organoantimony compounds are common, examples being Sb(C6H5)5 and several related halides.
History
Antimony(III) sulfide
Antimony trisulfide (Sb2S3) is found in nature as the crystalline mineral stibnite and the amorphous red mineral (actually a mineraloid) metastibnite. It is manufactured for use in safety matches, military ammunition, explosives and fireworks. It ...
, Sb2S3, was recognized in predynastic Egypt
Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt span the period from the earliest human settlement to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period around 3100 BC, starting with the first Pharaoh, Narmer for some Egyptologists, Hor-Aha for others, with th ...
as an eye cosmetic (kohl
Kohl may refer to:
*Kohl (cosmetics), an ancient eye cosmetic
*Kohl (surname), including a list of people with the surname
*Kohl's
Kohl's (stylized in all caps) is an American department store retail chain, operated by Kohl's Corporation. ...
) as early as about 3100 BC
The 31st century BC was a century that lasted from the year 3100 BC to 3001 BC.
Events
*c. 3100 BC: Polo ( mni, Sagol Kangjei) was first played in Manipur state.
*c. 3100 BC?: The Anu Ziggurat and White Temple are built in Uruk.
*c. 3100 BC?: P ...
, when the cosmetic palette was invented.
An artifact, said to be part of a vase, made of antimony dating to about 3000 BC was found at Telloh
Girsu ( Sumerian ; cuneiform ) was a city of ancient Sumer, situated some northwest of Lagash, at the site of modern Tell Telloh, Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq.
History
Girsu was possibly inhabited in the Ubaid period (5300-4800 BC), but sign ...
, Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
(part of present-day Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
), and a copper object plated with antimony dating between 2500 BC and 2200 BC has been found in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
. Austen, at a lecture by Herbert Gladstone
Herbert John Gladstone, 1st Viscount Gladstone, (7 January 1854 – 6 March 1930) was a British Liberal politician. The youngest son of William Ewart Gladstone, he was Home Secretary from 1905 to 1910 and Governor-General of the Union of South ...
in 1892, commented that "we only know of antimony at the present day as a highly brittle and crystalline metal, which could hardly be fashioned into a useful vase, and therefore this remarkable 'find' (artifact mentioned above) must represent the lost art of rendering antimony malleable."
The British archaeologist Roger Moorey
Peter Roger Stuart Moorey, (30 May 1937 – 23 December 2004) was a British archaeologist, historian, and academic, specialising in Mesopotamia and the Ancient Near East. He was Keeper of Antiquities at the Ashmolean Museum of the University of ...
was unconvinced the artifact was indeed a vase, mentioning that Selimkhanov, after his analysis of the Tello object (published in 1975), "attempted to relate the metal to Transcaucasian natural antimony" (i.e. native metal) and that "the antimony objects from Transcaucasia are all small personal ornaments." This weakens the evidence for a lost art "of rendering antimony malleable."
The Roman scholar Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
described several ways of preparing antimony sulfide for medical purposes in his treatise ''Natural History'', around 77 AD. Pliny the Elder also made a distinction between "male" and "female" forms of antimony; the male form is probably the sulfide, while the female form, which is superior, heavier, and less friable, has been suspected to be native metallic antimony.
The Greek naturalist Pedanius Dioscorides mentioned that antimony sulfide could be roasted by heating by a current of air. It is thought that this produced metallic antimony.
Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
monk, writing under the name Basilius Valentinus
Basil Valentine is the Anglicised version of the name Basilius Valentinus, ostensibly a 15th-century alchemist, possibly Canon of the Benedictine Priory of Saint Peter in Erfurt, Germany but more likely a pseudonym used by one or several 16th-ce ...
in the 15th century; if it were authentic, which it is not, it would predate Biringuccio.
The metal antimony was known to German chemist Andreas Libavius in 1615 who obtained it by adding iron to a molten mixture of antimony sulfide, salt and potassium tartrate. This procedure produced antimony with a crystalline or starred surface.
With the advent of challenges to phlogiston theory
The phlogiston theory is a superseded scientific theory that postulated the existence of a fire-like element called phlogiston () contained within combustible bodies and released during combustion. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''burni ...
, it was recognized that antimony is an element forming sulfides, oxides, and other compounds, as do other metals.
The first discovery of naturally occurring pure antimony in the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
was described by the Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
scientist and local mine district engineer Anton von Swab
Anton may refer to: People
*Anton (given name), including a list of people with the given name
*Anton (surname)
Places
*Anton Municipality, Bulgaria
**Anton, Sofia Province, a village
*Antón District, Panama
**Antón, a town and capital of th ...
in 1783; the type-sample was collected from the Sala Silver Mine
Sala Silver Mine ( sv, Sala silvergruva) is a mine in Sala Municipality, Sweden, Sala Municipality, in Västmanland County in Sweden. The mine was in continuous production from the 15th century until 1908. Additional mining occurred in 1950–1951 ...
in the Bergslagen mining district of Sala, Västmanland
Västmanland ( or ), is a historical Swedish province, or ''landskap'', in middle Sweden. It borders Södermanland, Närke, Värmland, Dalarna and Uppland.
Västmanland means "(The) Land of the Western Men", where the "western men" (''västerm ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
.
Etymology
The medieval Latin form, from which the modern languages and lateByzantine Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman co ...
take their names for antimony, is ''antimonium''. The origin of this is uncertain; all suggestions have some difficulty either of form or interpretation. The popular etymology
A false etymology (fake etymology, popular etymology, etymythology, pseudo-etymology, or par(a)etymology) is a popular but false belief about the origin or derivation of a specific word. It is sometimes called a folk etymology, but this is also a ...
, from ἀντίμοναχός ''anti-monachos'' or French ''antimoine'', still has adherents; this would mean "monk-killer", and is explained by many early alchemist
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscience, protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in Chinese alchemy, C ...
s being monks, and antimony being poisonous. However, the low toxicity of antimony (see below) makes this unlikely.
Another popular etymology is the hypothetical Greek word ἀντίμόνος ''antimonos'', "against aloneness", explained as "not found as metal", or "not found unalloyed"."Antimony" in ''Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology'', 5th ed. 2004. Lippmann conjectured a hypothetical Greek word ανθήμόνιον ''anthemonion'', which would mean "floret", and cites several examples of related Greek words (but not that one) which describe chemical or biological efflorescence
In chemistry, efflorescence (which means "to flower out" in French) is the migration of a salt to the surface of a porous material, where it forms a coating. The essential process involves the dissolving of an internally held salt in water, or ...
.
The early uses of ''antimonium'' include the translations, in 1050–1100, by Constantine the African
Constantine the African ( la, Constantinus Africanus; died before 1098/1099, Monte Cassino) was a physician who lived in the 11th century. The first part of his life was spent in Ifriqiya and the rest in Italy. He first arrived in Italy in the c ...
of Arabic medical treatises. Several authorities believe ''antimonium'' is a scribal corruption of some Arabic form; Meyerhof derives it from ''ithmid''; other possibilities include ''athimar'', the Arabic name of the metalloid, and a hypothetical ''as-stimmi'', derived from or parallel to the Greek.
The standard chemical symbol for antimony (Sb) is credited to Jöns Jakob Berzelius
Jöns is a Swedish given name and a surname.
Notable people with the given name include:
* Jöns Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848), Swedish chemist
* Jöns Budde (1435–1495), Franciscan friar from the Brigittine monastery in NaantaliVallis Gratiae ...
, who derived the abbreviation from ''stibium''.
The ancient words for antimony mostly have, as their chief meaning, kohl
Kohl may refer to:
*Kohl (cosmetics), an ancient eye cosmetic
*Kohl (surname), including a list of people with the surname
*Kohl's
Kohl's (stylized in all caps) is an American department store retail chain, operated by Kohl's Corporation. ...
, the sulfide of antimony.
The Egyptians called antimony ''mśdmt''; quotes Meyerhof, the translator of the book he is reviewing. in hieroglyphs, the vowels are uncertain, but the Coptic form of the word is ⲥⲧⲏⲙ (stēm).
Egyptian ''stm'': Attic
An attic (sometimes referred to as a '' loft'') is a space found directly below the pitched roof of a house or other building; an attic may also be called a ''sky parlor'' or a garret. Because attics fill the space between the ceiling of the ...
tragic poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or writte ...
s of the 5th century BC, and is possibly a loan word from Arabic or from Egyptian ''stm''. Later Greeks also used στἰβι ''stibi'', as did Celsus and Pliny, writing in Latin, in the first century AD. Pliny also gives the names ''stimi'', ''larbaris'', alabaster, and the "very common" ''platyophthalmos'', "wide-eye" (from the effect of the cosmetic). Later Latin authors adapted the word to Latin as ''stibium''.
The Arabic word for the substance, as opposed to the cosmetic, can appear as إثمد ''ithmid, athmoud, othmod'', or ''uthmod''. Littré suggests the first form, which is the earliest, derives from ''stimmida'', an accusative for ''stimmi''.
Production
Process
The extraction of antimony from ores depends on the quality and composition of the ore. Most antimony is mined as the sulfide; lower-grade ores are concentrated by froth flotation, while higher-grade ores are heated to 500–600 °C, the temperature at which stibnite melts and separates from the gangue minerals. Antimony can be isolated from the crude antimony sulfide by reduction with scrap iron: : + 3 Fe → 2 Sb + 3 FeS The sulfide is converted to an oxide; the product is then roasted, sometimes for the purpose of vaporizing the volatile antimony(III) oxide, which is recovered. This material is often used directly for the main applications, impurities being arsenic and sulfide. Antimony is isolated from the oxide by a carbothermal reduction: :2 + 3 C → 4 Sb + 3 The lower-grade ores are reduced inblast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
s while the higher-grade ores are reduced in reverberatory furnaces.
Top producers and production volumes
TheBritish Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey (BGS) is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research.
The BGS h ...
(BGS) reported that in 2005 China was the top producer of antimony with approximately 84% of the world share, followed at a distance by South Africa, Bolivia and Tajikistan. Xikuangshan Mine
Xikuangshan mine () in Lengshuijiang, Hunan, China, contains the world's largest deposit of antimony. It is unique in that there is a large deposit of stibnite (Sb2S3) in a layer of Devonian limestone. There are three mineral beds which are between ...
in Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi to ...
province has the largest deposits in China with an estimated deposit of 2.1 million metric tons.
In 2016, according to the US Geological Survey, China accounted for 76.9% of total antimony production, followed in second place by Russia with 6.9% and Tajikistan with 6.2%.
Chinese production of antimony is expected to decline in the future as mines and smelters are closed down by the government as part of pollution control. Especially due to an environmental protection law having gone into effect in January 2015 and revised "Emission Standards of Pollutants for Stanum, Antimony, and Mercury" having gone into effect, hurdles for economic production are higher. According to the National Bureau of Statistics in China, by September 2015 50% of antimony production capacity in the Hunan province (the province with biggest antimony reserves in China) had not been used.
Reported production of antimony in China has fallen and is unlikely to increase in the coming years, according to the Roskill report. No significant antimony deposits in China have been developed for about ten years, and the remaining economic reserves are being rapidly depleted.
The world's largest antimony producers, according to Roskill, are listed below:
Reserves
Supply risk
For antimony-importing regions such as Europe and the U.S., antimony is considered to be a critical mineral for industrial manufacturing that is at risk of supply chain disruption. With global production coming mainly from China (74%), Tajikistan (8%), and Russia (4%), these sources are critical to supply. *European Union: Antimony is considered a critical raw material for defense, automotive, construction and textiles. The E.U. sources are 100% imported, coming mainly from Turkey (62%), Bolivia (20%) and Guatemala (7%). *United Kingdom: TheBritish Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey (BGS) is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research.
The BGS h ...
's 2015 risk list ranks antimony second highest (after rare earth elements
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silve ...
) on the relative supply risk index.
*United States: Antimony is a mineral commodity considered critical to the economic and national security. In 2021, no antimony was mined in the U.S.
Applications
About 60% of antimony is consumed in flame retardants, and 20% is used in alloys for batteries, plain bearings, and solders.Flame retardants
Antimony is mainly used as the trioxide for flame-proofing compounds, always in combination with halogenated flame retardants except in halogen-containing polymers. The flame retarding effect of antimony trioxide is produced by the formation of halogenated antimony compounds, which react with hydrogen atoms, and probably also with oxygen atoms and OH radicals, thus inhibiting fire. Markets for these flame-retardants include children's clothing, toys, aircraft, and automobile seat covers. They are also added to polyester resins infiberglass
Fiberglass (American English) or fibreglass (Commonwealth English) is a common type of fiber-reinforced plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth ...
composites for such items as light aircraft engine covers. The resin will burn in the presence of an externally generated flame, but will extinguish when the external flame is removed.Grund, Sabina C.; Hanusch, Kunibert; Breunig, Hans J.; Wolf, Hans Uwe (2006) "Antimony and Antimony Compounds" in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
Alloys
Antimony forms a highly usefulalloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductility, ...
with lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, increasing its hardness and mechanical strength. For most applications involving lead, varying amounts of antimony are used as alloying metal. In lead–acid batteries, this addition improves plate strength and charging characteristics. For sailboats, lead keels are used to provide righting moment, ranging from 600 lbs to over 200 tons for the largest sailing superyachts; to improve hardness and tensile strength of the lead keel, antimony is mixed with lead between 2% and 5% by volume. Antimony is used in antifriction alloys (such as Babbitt metal
Babbitt metal or bearing metal is any of several alloys used for the bearing surface in a plain bearing.
The original Babbitt alloy was invented in 1839 by Isaac Babbitt in Taunton, Massachusetts, United States. He disclosed one of his alloy recip ...
), in bullet
A bullet is a kinetic projectile, a component of firearm ammunition that is shot from a gun barrel. Bullets are made of a variety of materials, such as copper, lead, steel, polymer, rubber and even wax. Bullets are made in various shapes and co ...
s and lead shot, electrical cable
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used to carry electric current.
One or more electrical cables and their corresponding connectors may be formed into a ''cable assembly'', which ...
sheathing, type metal (for example, for linotype printing machines), solder (some "lead-free
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive 2002/95/EC (RoHS 1), short for Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, was adopted in February 2003 by the European Unio ...
" solders contain 5% Sb), in pewter, and in hardening alloys with low tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
content in the manufacturing of organ pipes.
Other applications
Three other applications consume nearly all the rest of the world's supply. One application is as a stabilizer and catalyst for the production ofpolyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
. Another is as a fining agent to remove microscopic bubbles in glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
, mostly for TV screens antimony ions interact with oxygen, suppressing the tendency of the latter to form bubbles. The third application is pigments.
In the 1990s antimony was increasingly being used in semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glas ...
s as a dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. When ...
in n-type silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
wafers for diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode ...
s, infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
detectors, and Hall-effect
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discove ...
devices. In the 1950s, the emitters and collectors of n-p-n alloy junction transistors were doped with tiny beads of a lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
-antimony alloy. Indium antimonide is used as a material for mid- infrared detectors.
Biology and medicine have few uses for antimony. Treatments containing antimony, known as antimonial
Antimonials, in pre-modern medicine, were remedies principally containing antimony, used chiefly for emetic purposes. They might also have qualified for cathartic, diaphoretic, or simply alternative uses. Such treatments were considered unparall ...
s, are used as emetics. Antimony compounds are used as antiprotozoan drugs. Potassium antimonyl tartrate
Antimony potassium tartrate, also known as potassium antimonyl tartrate, potassium antimontarterate, or tartar emetic, has the formula K2Sb2(C4H2O6)2. The compound has long been known as a powerful emetic, and was used in the treatment of schistoso ...
, or tartar emetic, was once used as an anti- schistosomal drug from 1919 on. It was subsequently replaced by praziquantel. Antimony and its compounds are used in several veterinary preparations, such as anthiomaline and lithium antimony thiomalate, as a skin conditioner in ruminants. Antimony has a nourishing or conditioning effect on keratinized tissues in animals.
Antimony-based drugs, such as meglumine antimoniate
Meglumine antimoniate is a medicine used to treat leishmaniasis. This includes visceral, mucocutaneous, and cutaneous leishmaniasis. It is given by intramuscular injection, injection into a muscle or into the area infected.
Side effects include ...
, are also considered the drugs of choice for treatment of leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most freq ...
in domestic animals. Besides having low therapeutic indices, the drugs have minimal penetration of the bone marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic ce ...
, where some of the ''Leishmania'' amastigote
An amastigote is a protist
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryot ...
s reside, and curing the disease – especially the visceral form – is very difficult. Elemental antimony as an antimony pill
An antimony pill is a pill made from metallic antimony. It was a popular remedy in the nineteenth century, and it was used to purge and revitalise the bowels. In use, it is swallowed and allowed to pass through the body, after which it is customari ...
was once used as a medicine. It could be reused by others after ingestion and elimination.
Antimony(III) sulfide
Antimony trisulfide (Sb2S3) is found in nature as the crystalline mineral stibnite and the amorphous red mineral (actually a mineraloid) metastibnite. It is manufactured for use in safety matches, military ammunition, explosives and fireworks. It ...
is used in the heads of some safety matches. Antimony sulfides help to stabilize the friction coefficient in automotive brake pad materials. Antimony is used in bullets, bullet tracers, paint, glass art, and as an opacifier
An opacifier is a substance added to a material in order to make the ensuing system opaque. An example of a chemical opacifier is titanium dioxide (TiO2), which is used as an opacifier in paints, in paper, and in plastics. It has very high refracti ...
in enamel. Antimony-124
Antimony (51Sb) occurs in two stable isotopes, 121Sb and 123Sb. There are 35 artificial radioactive isotopes, the longest-lived of which are 125Sb, with a half-life of 2.75856 years; 124Sb, with a half-life of 60.2 days; and 126Sb, with a half-lif ...
is used together with beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form mi ...
in neutron sources; the gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically ...
s emitted by antimony-124 initiate the photodisintegration of beryllium. The emitted neutrons have an average energy of 24 keV. Natural antimony is used in startup neutron source
Startup neutron source is a neutron source used for stable and reliable initiation of nuclear chain reaction in nuclear reactors, when they are loaded with fresh nuclear fuel, whose neutron flux from spontaneous fission is insufficient for a reliab ...
s.
Historically, the powder derived from crushed antimony (''kohl
Kohl may refer to:
*Kohl (cosmetics), an ancient eye cosmetic
*Kohl (surname), including a list of people with the surname
*Kohl's
Kohl's (stylized in all caps) is an American department store retail chain, operated by Kohl's Corporation. ...
'') has been applied to the eyes with a metal rod and with one's spittle, thought by the ancients to aid in curing eye infections. The practice is still seen in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and in other Muslim countries.
Precautions
The effects of antimony and its compounds on human and environmental health differ widely. Elemental antimony metal does not affect human and environmental health. Inhalation of antimony trioxide (and similar poorly soluble Sb(III) dust particles such as antimony dust) is considered harmful and suspected of causing cancer. However, these effects are only observed with female rats and after long-term exposure to high dust concentrations. The effects are hypothesized to be attributed to inhalation of poorly soluble Sb particles leading to impaired lung clearance, lung overload, inflammation and ultimately tumour formation, not to exposure to antimony ions (OECD, 2008). Antimony chlorides are corrosive to skin. The effects of antimony are not comparable to those of arsenic; this might be caused by the significant differences of uptake, metabolism, and excretion between arsenic and antimony. For oral absorption, ICRP (1994) has recommended values of 10% for tartar emetic and 1% for all other antimony compounds. Dermal absorption for metals is estimated to be at most 1% (HERAG, 2007). Inhalation absorption of antimony trioxide and other poorly soluble Sb(III) substances (such as antimony dust) is estimated at 6.8% (OECD, 2008), whereas a value <1% is derived for Sb(V) substances. Antimony(V) is not quantitatively reduced to antimony(III) in the cell, and both species exist simultaneously. Antimony is mainly excreted from the human body via urine. Antimony and its compounds do not cause acute human health effects, with the exception of antimony potassium tartrate ("tartar emetic"), aprodrug
A prodrug is a medication or compound that, after intake, is metabolized (i.e., converted within the body) into a pharmacologically active drug. Instead of administering a drug directly, a corresponding prodrug can be used to improve how the drug ...
that is intentionally used to treat leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a wide array of clinical manifestations caused by parasites of the trypanosome genus ''Leishmania''. It is generally spread through the bite of phlebotomine sandflies, ''Phlebotomus'' and ''Lutzomyia'', and occurs most freq ...
patients.
Prolonged skin contact with antimony dust may cause dermatitis. However, it was agreed at the European Union level that the skin rashes observed are not substance-specific, but most probably due to a physical blocking of sweat ducts (ECHA/PR/09/09, Helsinki, 6 July 2009). Antimony dust may also be explosive when dispersed in the air; when in a bulk solid it is not combustible.
Antimony is incompatible with strong acids, halogenated acids, and oxidizers; when exposed to newly formed hydrogen it may form stibine
Stibine (IUPAC name: stibane) is a chemical compound with the formula SbH3. A pnictogen hydride, this colourless, highly toxic gas is the principal covalent hydride of antimony, and a heavy analogue of ammonia. The molecule is pyramidal with H–S ...
(SbH3).
The 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA) is set at 0.5 mg/m3 by the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists and by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration'' (OSHA ) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. Congress established the agenc ...
(OSHA) as a legal permissible exposure limit
The permissible exposure limit (PEL or OSHA PEL) is a legal limit in the United States for exposure of an employee to a chemical substance or physical agent such as high level noise. Permissible exposure limits are established by the Occupational S ...
(PEL) in the workplace. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) has set a recommended exposure limit (REL) of 0.5 mg/m3 as an 8-hour TWA.
Antimony compounds are used as catalysts for polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and foods ...
(PET) production. Some studies report minor antimony leaching from PET bottles into liquids, but levels are below drinking water guidelines. Antimony concentrations in fruit juice concentrates were somewhat higher (up to 44.7 µg/L of antimony), but juices do not fall under the drinking water regulations. The drinking water guidelines are:
* World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
: 20 µg/L
* Japan: 15 µg/L
* United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it be ...
, Health Canada and the Ontario Ministry of Environment: 6 µg/L
* EU and German Federal Ministry of Environment: 5 µg/L
The tolerable daily intake Tolerable daily intake (TDI) refers to the daily amount of a chemical that has been assessed safe for human being on long-term basis (usually whole lifetime). Originally acceptable daily intake (ADI) was introduced in 1961 to define the daily intake ...
(TDI) proposed by WHO is 6 µg antimony per kilogram of body weight. The immediately dangerous to life or health
The term immediately dangerous to life or health (IDLH) is defined by the US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as exposure to airborne contaminants that is "likely to cause death or immediate or delayed permanent advers ...
(IDLH) value for antimony is 50 mg/m3.
Toxicity
Certain compounds of antimony appear to be toxic, particularly antimony trioxide and antimony potassium tartrate. Effects may be similar to arsenic poisoning. Occupational exposure may cause respiratory irritation,pneumoconiosis
Pneumoconiosis is the general term for a class of interstitial lung disease where inhalation of dust ( for example, ash dust, lead particles, pollen grains etc) has caused interstitial fibrosis. The three most common types are asbestosis, silicos ...
, antimony spots on the skin, gastrointestinal symptoms, and cardiac arrhythmias. In addition, antimony trioxide is potentially carcinogenic to humans.
Adverse health effects have been observed in humans and animals following inhalation, oral, or dermal exposure to antimony and antimony compounds. Antimony toxicity typically occurs either due to occupational exposure, during therapy or from accidental ingestion. It is unclear if antimony can enter the body through the skin. The presence of low levels of antimony in saliva may also be associated with dental decay
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
.
See also
* Phase change memoryNotes
References
Bibliography
* *Edmund Oscar von Lippmann
Edmund Oscar von Lippmann (9 January 1857 in Vienna – 24 September 1940 in Halle) was a German chemist and natural science historian. For his writings he was awarded a couple honoris causa doctorates from German universities, as well as the ...
(1919) Entstehung und Ausbreitung der Alchemie, teil 1. Berlin: Julius Springer (in German).
Public Health Statement for Antimony
External links
International Antimony Association vzw (i2a
Chemistry in its element podcast
(MP3) from the
Royal Society of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society (professional association) in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Ro ...
's Chemistry World
''Chemistry World'' is a monthly chemistry news magazine published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. The magazine addresses current events in world of chemistry including research, international business news and government policy as it affects ...
Antimony
at '' The Periodic Table of Videos'' (University of Nottingham)
CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Antimony
Antimony Mineral data and specimen images
{{Authority control Chemical elements Metalloids Native element minerals Nuclear materials Pnictogens Trigonal minerals Minerals in space group 166 Materials that expand upon freezing Chemical elements with rhombohedral structure